How To Find The X and Y Intercepts of a Line
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a clear guide on how to find the x and y intercepts from both a graph and an equation. It demonstrates the process with several examples, including equations in slope-intercept form and standard form. The video explains how to graph a linear equation using the x and y intercepts, step by step. Viewers will also learn how to handle fractional coefficients and graph linear equations by finding intercepts, making it easier to understand and visualize linear relationships. Additionally, the video promotes an algebra course for further learning.
Takeaways
- 😀 Identify the x-intercept as the point where the graph touches the x-axis, with a y-value of 0.
- 😀 The y-intercept is the point where the graph touches the y-axis, with an x-value of 0.
- 😀 To find the x-intercept from an equation, set y = 0 and solve for x.
- 😀 The y-intercept can be directly read from the equation when it is in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), where b is the y-intercept.
- 😀 In slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), the slope (m) is the coefficient of x, and the y-intercept (b) is the constant term.
- 😀 To graph a linear equation, plot the x and y intercepts and draw a straight line through them.
- 😀 From the graph, find the x-intercept by identifying the point where the graph crosses the x-axis and the y-intercept where it crosses the y-axis.
- 😀 For standard form equations (Ax + By = C), to find the x-intercept, set y = 0 and solve for x. To find the y-intercept, set x = 0 and solve for y.
- 😀 Example 1: For y = 2x + 1, the x-intercept is (-1/2, 0), and the y-intercept is (0, 1).
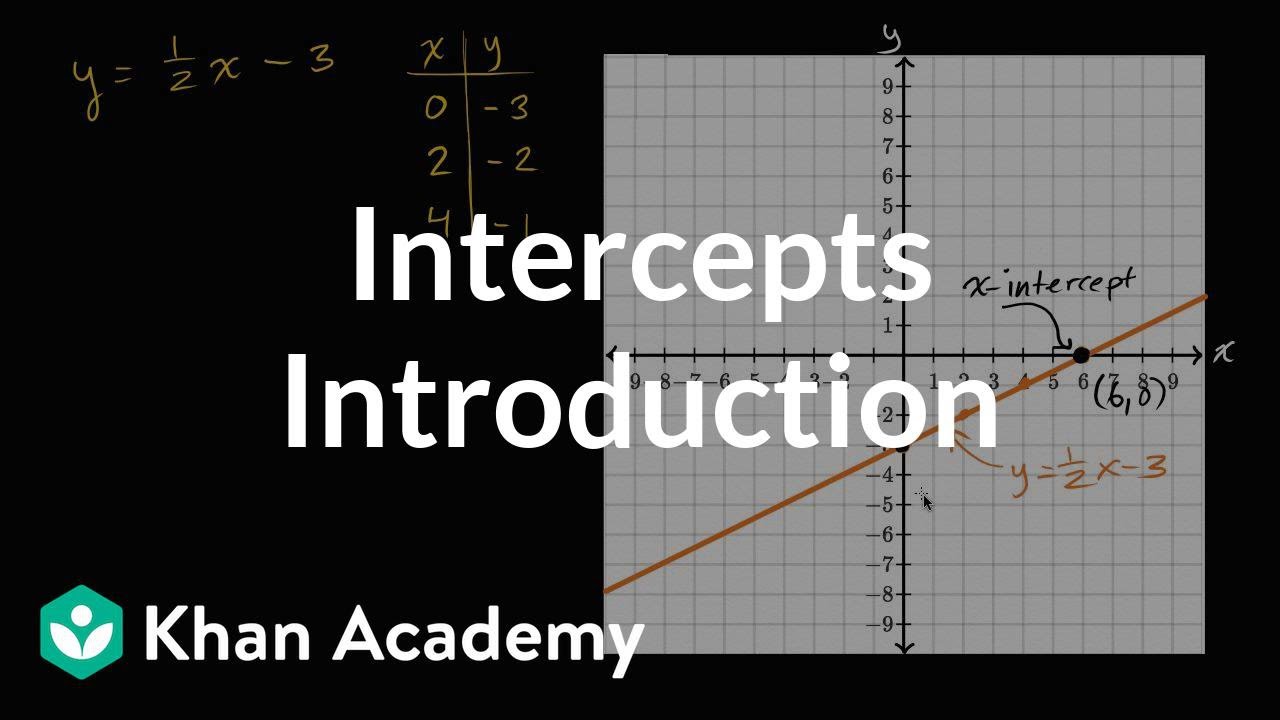
- 😀 Example 2: For 1/2x - 3, the x-intercept is (6, 0), and the y-intercept is (0, -3).
- 😀 For standard form equations like 2x + 3y = 6, set y = 0 to find the x-intercept and x = 0 to find the y-intercept, then plot the points to graph the line.
Q & A
What are the x and y intercepts of a graph?
-The x-intercept is the point where the graph touches the x-axis, and the y-intercept is the point where the graph touches the y-axis. The x-coordinate of the x-intercept is the value where y equals zero, and the y-coordinate of the y-intercept is where x equals zero.
How do you find the x and y intercepts from a graph?
-To find the x-intercept, locate where the graph touches the x-axis and read the x-coordinate. For the y-intercept, locate where the graph touches the y-axis and read the y-coordinate. These points can also be written as ordered pairs (x, 0) for the x-intercept and (0, y) for the y-intercept.
How do you calculate the x-intercept from a linear equation in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b)?
-To calculate the x-intercept from a linear equation in slope-intercept form, replace y with 0 and solve for x. For example, in the equation y = 2x + 1, setting y = 0 gives 0 = 2x + 1, and solving for x gives x = -1/2.
What is the process for finding the y-intercept from a linear equation in slope-intercept form?
-The y-intercept is simply the value of b in the equation y = mx + b. You do not need to solve for it because the y-intercept is the value of y when x is zero. For example, in the equation y = 2x + 1, the y-intercept is 1, so the point is (0, 1).
How do you find the intercepts for an equation in standard form (Ax + By = C)?
-For an equation in standard form, to find the x-intercept, set y equal to 0 and solve for x. To find the y-intercept, set x equal to 0 and solve for y.
How do you graph a linear equation using intercepts?
-To graph a linear equation using intercepts, first plot the x-intercept (where y = 0) and the y-intercept (where x = 0). Then, draw a straight line through these two points to complete the graph.
In the equation y = 2x + 1, what are the x and y intercepts?
-In the equation y = 2x + 1, the y-intercept is at (0, 1), and the x-intercept is at (-1/2, 0). To find the x-intercept, set y = 0 and solve for x, which gives x = -1/2.
How do you graph the equation 1/2x - 3 using its intercepts?
-For the equation 1/2x - 3, the y-intercept is at (0, -3). To find the x-intercept, set y = 0, solve for x, and you get x = 6, so the x-intercept is at (6, 0). Plot both intercepts and draw a line connecting them.
What is the difference between graphing equations in slope-intercept form and standard form?
-The main difference is that in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), the slope (m) and y-intercept (b) are immediately visible, making it easy to graph. In standard form (Ax + By = C), you must find the intercepts by setting x or y equal to zero and solving for the other variable.
How can you use algebraic methods to find the intercepts of an equation in standard form?
-To find the x-intercept, replace y with 0 and solve for x. To find the y-intercept, replace x with 0 and solve for y. These methods allow you to determine the intercepts without graphing the equation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

FINDING THE EQUATION OF A LINE GIVEN THE X AND Y - INTERCEPTS || GRADE 8 MATHEMATICS Q1
Introduction to intercepts | Algebra I | Khan Academy

Cara mudah menggambarkan grafik fungsi kuadrat
Cara membuat grafik fungsi kuadrat

AP Precalculus – 4.2 Parametric Functions Modeling Planar Motion
How To Graph Polynomial Functions Using End Behavior, Multiplicity & Zeros
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)