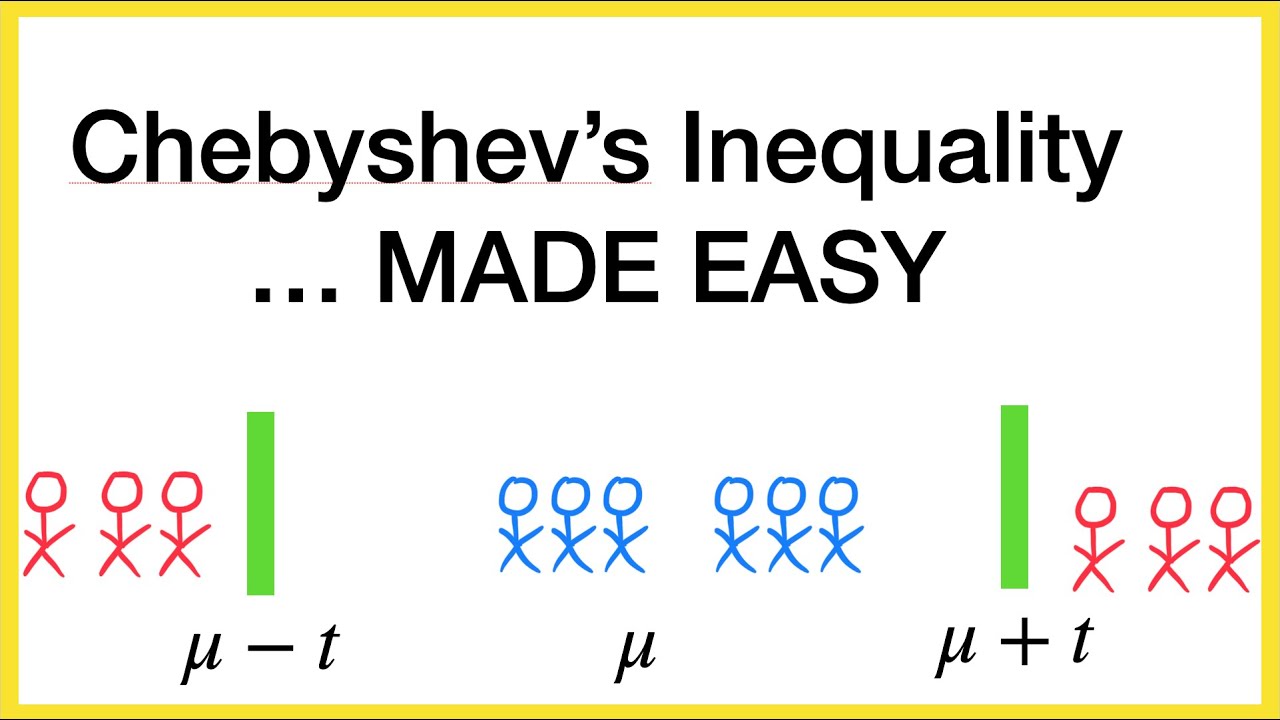Probability Theory L51a Section 5.8 Part 1 Chebyshev's Inequality and Convergence in Probability
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture on probability theory, Mark Ledbetter discusses Chebyshev's inequality and convergence in probability. He reviews the Central Limit Theorem and emphasizes the significance of having a sufficient sample size. The lecture defines convergence in probability, explaining how a sequence of random variables can approach a limit, and introduces Chebyshev's inequality, which provides a crucial formula for understanding the distribution of random variables. The proof of this inequality is broken down step-by-step, culminating in its application to estimating population proportions. Ledbetter encourages students to engage with the material and seek help as needed.
Takeaways
- 😀 Chebyshev's inequality helps establish convergence in probability, providing important bounds for probability distributions.
- 😀 A sample size of n ≥ 30 is a general rule of thumb for approximating a normal distribution using the Central Limit Theorem.
- 😀 The sample mean (x̄) is a reliable estimator of the population mean (μ) under appropriate conditions.
- 😀 The estimated proportion (p̂) is calculated as the number of observations in a category (y) divided by the total sample size (n).
- 😀 A sequence of random variables converges in probability if the probability of deviating from a fixed value approaches zero as the sample size increases.
- 😀 Chebyshev's inequality states that for any ε > 0, the probability of a random variable deviating from its mean by more than ε is bounded by the variance divided by ε squared.
- 😀 The proof of Chebyshev's inequality involves integrating the squared distance from the mean and applying the properties of probabilities.
- 😀 The expected value (E[X]) is denoted as μ, while the variance (Var(X)) is represented as σ².
- 😀 Visual representations of distributions and their properties enhance understanding of key statistical concepts.
- 😀 Students are encouraged to submit their lecture notes by the deadline and seek help via email or office hours for better assistance.
Please replace the link and try again.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)