Topic # 8.1 - Basic Concepts of Stress Transformation
Summary
TLDRThis lecture focuses on stress transformation in structural analysis, detailing how the stress state of a material element changes when rotated about a point. Key concepts include the calculation of normal and shear stresses in rotated coordinates, emphasizing the fundamental equations that govern these transformations. The lecturer highlights the significance of understanding these transformations for accurate structural assessment and offers insights into practical applications through example problems. By grasping these principles, engineers can better predict material behavior under various loading conditions, which is crucial for effective design and safety.
Takeaways
- 😀 The rotation of structural elements affects the orientation of stress components while some normals remain unchanged.
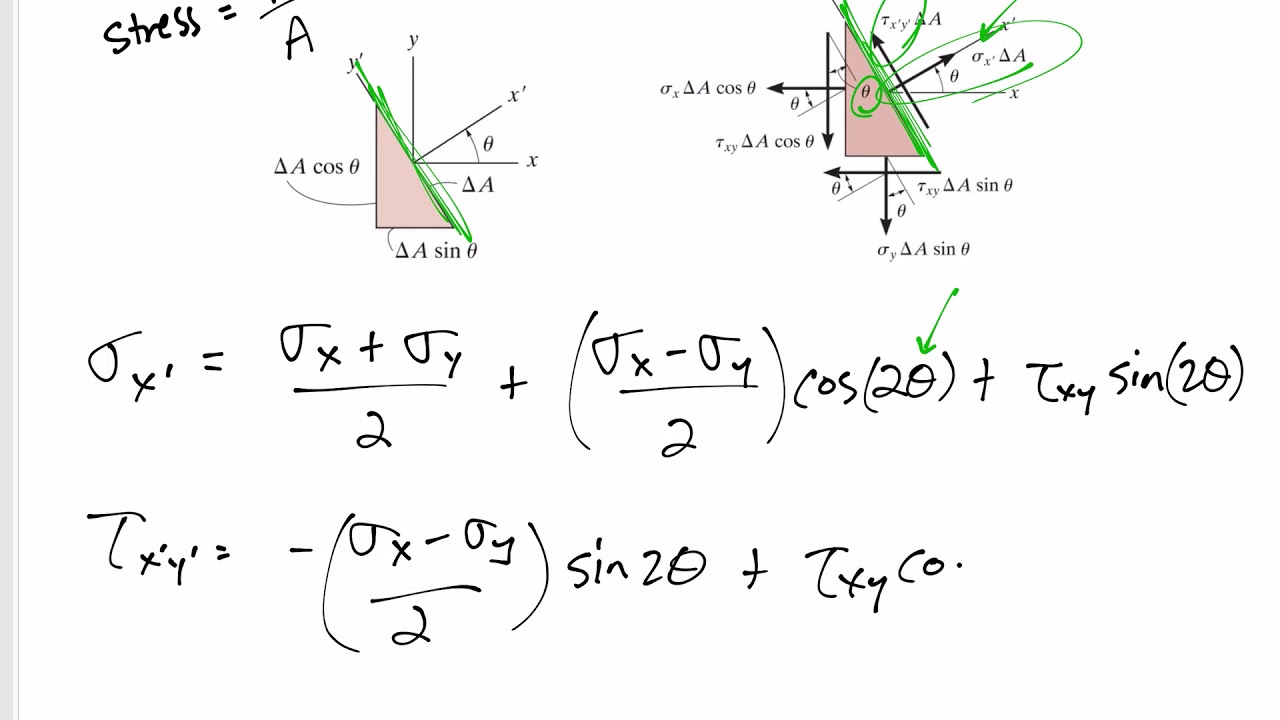
- 😀 There are three primary stress components to consider in a 2D element: σ_x, σ_y, and τ_xy.
- 😀 The expressions for stresses in a rotated coordinate system depend on the angle of rotation (θ) and are derived based on the original stresses.
- 😀 The rotation is defined as positive in the anticlockwise direction, which is an important convention in stress analysis.
- 😀 The sum of the normal stresses in the rotated element is conserved and equals the sum of the normal stresses in the original element.
- 😀 Understanding the relationship between the original and rotated stresses is essential for accurate structural analysis.
- 😀 The lecture emphasizes the importance of visualizing the element and its stresses during rotation for better comprehension.
- 😀 Example problems will help solidify the theoretical concepts by applying them to practical scenarios.
- 😀 The rotation of elements and stress analysis is crucial for fields like civil and mechanical engineering.
- 😀 Mastery of these concepts can lead to improved design and analysis of structural components under various loading conditions.
Q & A
What are the primary stresses considered in a 2D element?
-The primary stresses in a 2D element are σₓ (normal stress in the x-direction), σᵧ (normal stress in the y-direction), and τₓᵧ (shear stress on the xy-plane).
How does the rotation of an element affect its stress components?
-When an element is rotated, the stress components change according to specific equations, but the sum of normal stresses remains the same as in the original orientation.
What does the angle θ represent in the context of stress rotation?
-The angle θ represents the angle of rotation from the horizontal, measured positively in the anticlockwise direction.
Why is it important to understand the behavior of normals during rotation?
-Understanding the behavior of normals during rotation is crucial because some normals remain unchanged, affecting how we calculate and interpret stress in structures.
What is the significance of the equations provided for rotated elements?
-The equations for rotated elements allow us to compute the new stress components at the same point in the structure after rotation, providing essential information for analysis.
Can the sum of the normal stresses for a rotated element differ from the original element?
-No, the sum of the normal stresses for a rotated element equals the sum of the normal stresses for the original element, regardless of the rotation angle.
What example problem is introduced in the lecture?
-The lecture introduces an example problem where a specific element is rotated at a particular angle, and the task is to find the set of stresses for the rotated element.
How are the stress equations derived for a rotated element?
-The stress equations for a rotated element are derived based on the original stress state and the angle of rotation, using principles from mechanics of materials.
What role do shear stresses play in 2D stress analysis?
-Shear stresses, such as τₓᵧ, are crucial in 2D stress analysis as they represent the forces acting parallel to the cross-section of the element, affecting its overall strength and stability.
What can be inferred about the material behavior from the discussion of stress components?
-The discussion indicates that understanding stress components and their transformations is vital for predicting material behavior under different loading conditions and ensuring structural integrity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Mechanics of Materials - 2D Plane stress transformation equations

Transformasi Tegangan (Part 1) - Mekanika Material / Kekuatan Material

Mechanics of Solids Interview Questions
Understanding Stress Transformation and Mohr's Circle

52/2025 - AE1 - Mecânica e Resistência dos Materiais
Finite Element Analysis and Design of A Heavy Lift Padeye
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)