🔴 How to select Participants: Quantitative Research
Summary
TLDRIn this video on sampling in quantitative research, the presenter outlines four key sampling methods: Simple Random Sampling, where participants are randomly selected for equal representation; Systematic Sampling, which involves choosing every nth individual from a list; Stratified Sampling, designed to capture various demographic groups within a population; and Clustered Sampling, suitable for large populations by selecting random clusters (e.g., universities). Each method is illustrated with examples, particularly focused on YouTube users, providing viewers with a comprehensive understanding of effective sampling strategies for their research.
Takeaways
- 😀 Quantitative research focuses on understanding cause-and-effect relationships and measuring variables in a fixed reality.
- 😀 Sampling is crucial in quantitative research as it helps generalize findings to a larger population.
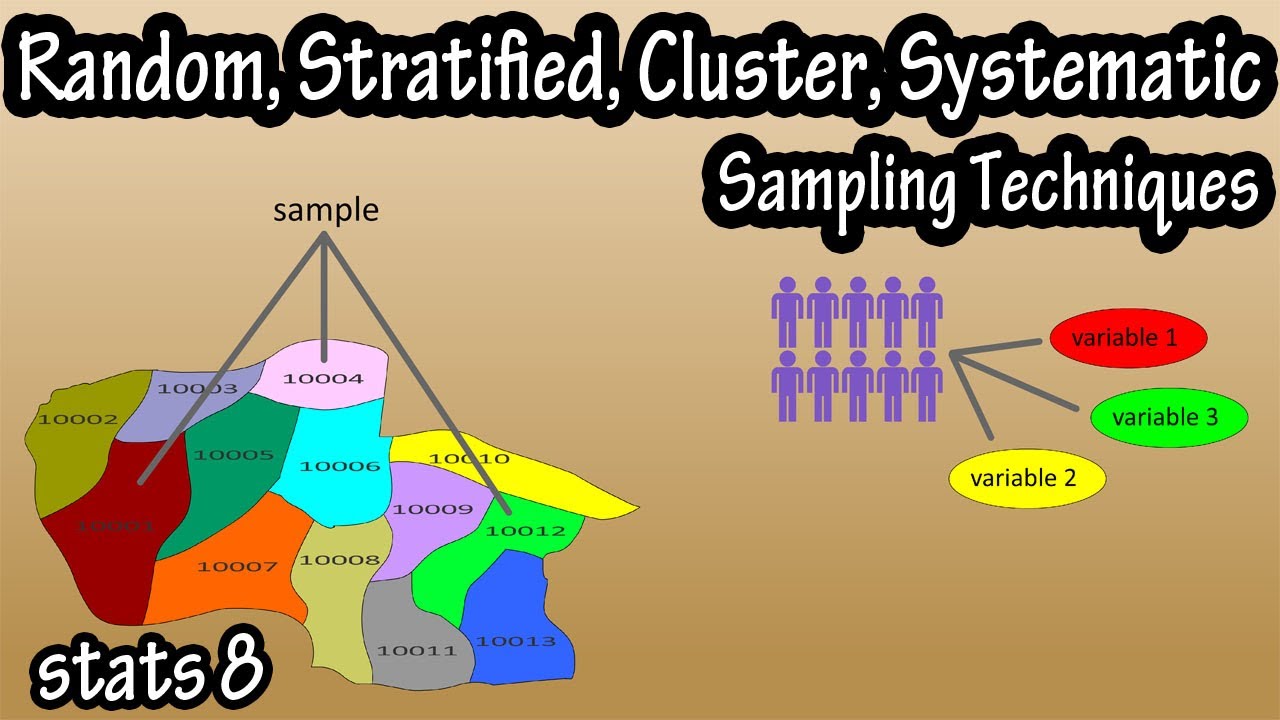
- 😀 Simple random sampling ensures every individual in the population has an equal chance of selection.
- 😀 To implement simple random sampling, researchers must define their population and create a comprehensive list of potential participants.
- 😀 Systematic sampling involves selecting participants at regular intervals from a numbered list, ensuring representativeness.
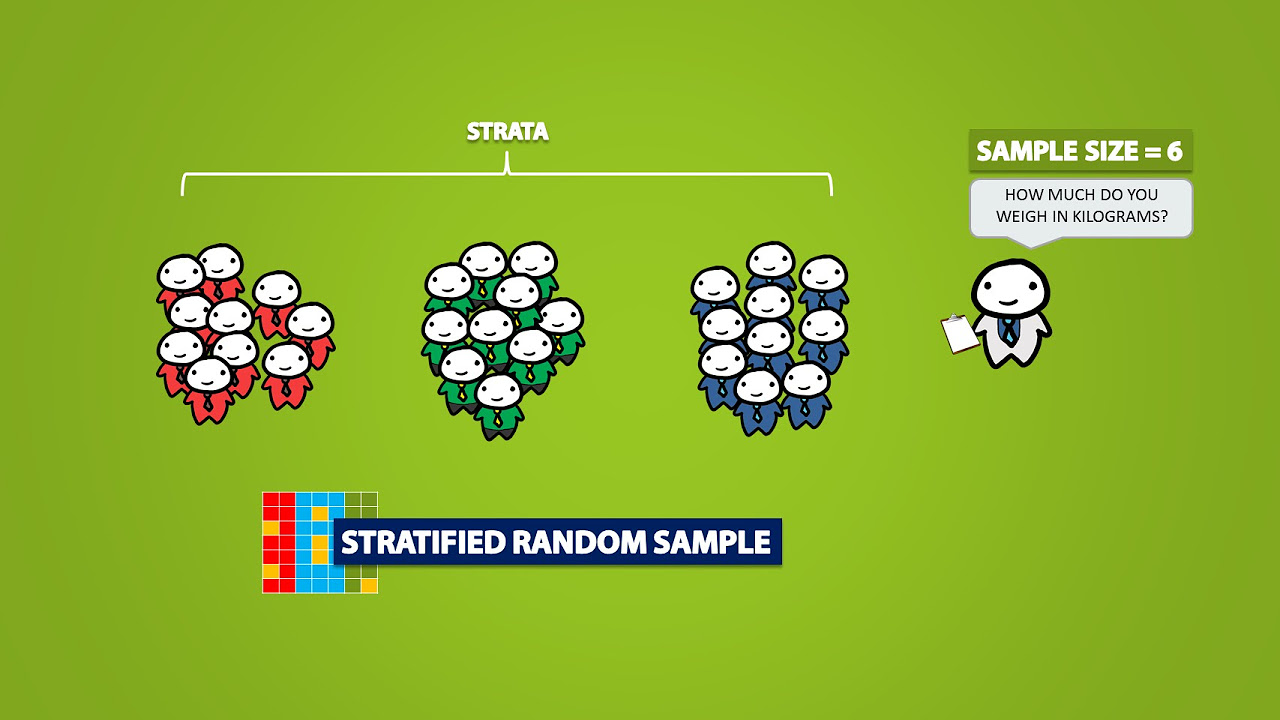
- 😀 Stratified sampling captures various demographic groups by dividing the population into strata based on specific characteristics.
- 😀 Each stratum in stratified sampling must be represented to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the population.
- 😀 Cluster sampling is effective for large populations, where entire clusters (e.g., universities) are randomly selected for inclusion.
- 😀 Using a mix of sampling methods can enhance the reliability and validity of quantitative research findings.
- 😀 Understanding different sampling techniques helps researchers choose the most suitable method for their specific study needs.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of quantitative research?
-The primary goal of quantitative research is to understand causal relationships and measure variables in a way that allows for generalization of findings.
What is simple random sampling?
-Simple random sampling is a method where participants are randomly selected from a population, giving everyone an equal chance of being included.
How can a researcher ensure a sample is representative of the general population?
-A researcher can ensure a sample is representative by using methods like simple random sampling, which randomizes participant selection, or stratified sampling, which accounts for demographic diversity.
What steps are involved in simple random sampling?
-First, define the population of interest, create a list of potential participants, assign random numbers to them, and then randomly select participants until the desired sample size is reached.
What is systematic sampling?
-Systematic sampling is a method of selecting participants at regular intervals from a numbered list of the population, such as choosing every 10th person.
What is the purpose of stratified sampling?
-Stratified sampling is used to ensure that different demographic groups within a population are represented in the sample, by categorizing participants into strata based on characteristics like age or gender.
Can you give an example of how stratified sampling works?
-If a researcher wants to study YouTube users by age group, they would categorize users into age strata and then sample from each stratum to ensure diverse representation.
What is clustered sampling, and when is it most useful?
-Clustered sampling involves dividing the population into clusters and randomly selecting entire clusters for study. It is most useful when dealing with large and dispersed populations.
How does clustered sampling differ from simple random sampling?
-Clustered sampling selects entire groups (clusters) at once, whereas simple random sampling selects individuals randomly from the entire population.
Why is understanding sampling methods important for researchers?
-Understanding sampling methods is crucial because the choice of sampling technique affects the reliability, validity, and generalizability of research findings.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)