#22 Free Lean Six Sigma Green Belt | Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Summary
TLDRThe video explores Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) as a transformative approach to equipment management, emphasizing operator empowerment and cultural shifts within organizations. By encouraging operators to take ownership of their machines, TPM fosters proactive maintenance practices that enhance overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). The module outlines the importance of training, relevant KPIs, and collaborative efforts between operators and maintenance staff. It highlights the necessity of addressing all stages of the equipment lifespan and sets the stage for the next topic: SMED, a powerful tool for reducing setup and changeover times.
Takeaways
- 😀 TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) aims to maximize machine output by minimizing downtime, speed losses, and defects.
- 🔧 Operators play a crucial role in TPM by taking ownership of their machines and performing routine maintenance.
- 🚀 A proactive maintenance approach, as demonstrated by Company B, leads to zero unplanned downtime and reduced costs.
- 📊 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should focus on leading indicators like operator training rather than just the number of repairs.
- 🔄 Continuous improvement and a culture of shared responsibility are essential components of a successful TPM strategy.
- 🛠️ Operators' intimate knowledge of their machines enables them to identify issues early, enhancing maintenance effectiveness.
- 🏆 The goal of TPM is not just equipment maintenance but also instilling pride in operators for their machines.
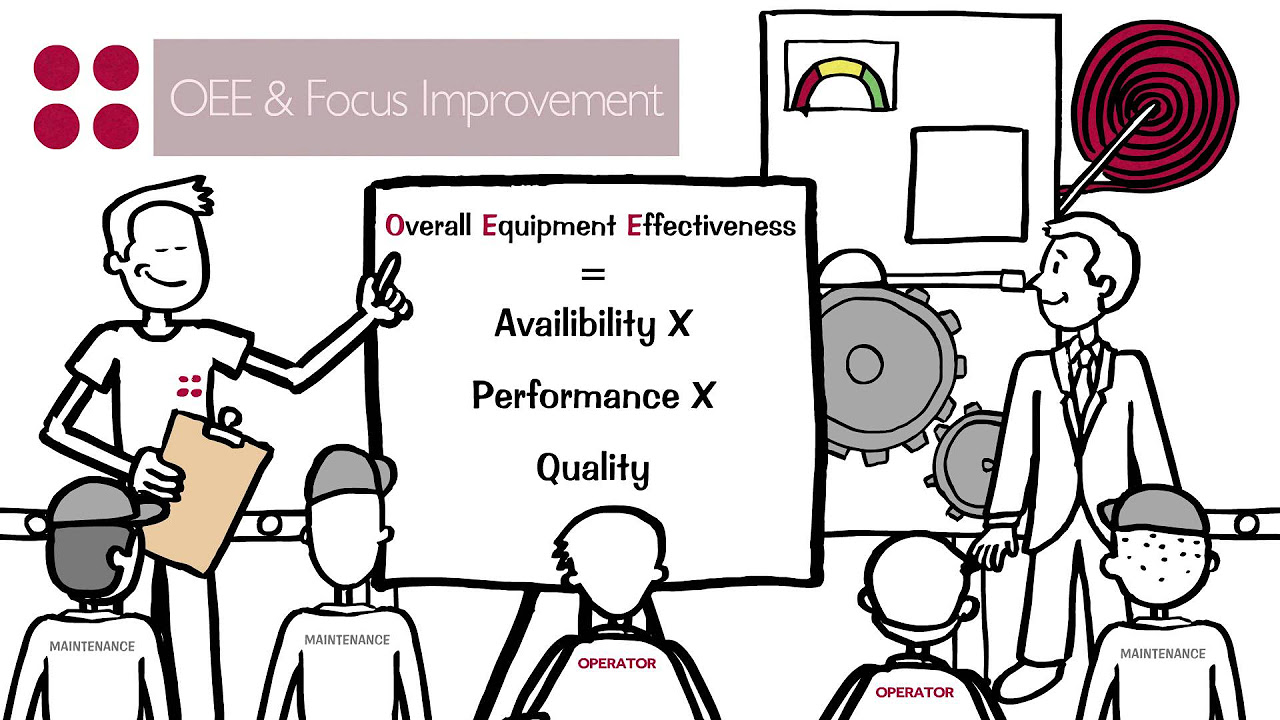
- 🌱 Kaizen events are valuable for addressing inefficiencies and improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
- ⚙️ Autonomous maintenance empowers operators, freeing maintenance staff to focus on complex issues and innovations.
- 📈 TPM represents a shift in mindset from reactive to proactive maintenance, emphasizing the importance of employee involvement.
Q & A
What is Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)?
-TPM is a maintenance approach aimed at maximizing equipment effectiveness by involving all employees in the maintenance process, reducing downtime, speed losses, and defects.
How does TPM differ from traditional maintenance approaches?
-Unlike traditional maintenance, which often reacts to breakdowns, TPM focuses on proactive maintenance by empowering operators to take responsibility for their equipment.
What are some key objectives of implementing TPM?
-Key objectives include maximizing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), improving reliability, reducing maintenance costs, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
How do operators contribute to TPM?
-Operators are trained to perform routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and basic inspections, which allows maintenance staff to focus on complex issues.
What is the significance of Kaizen events in the TPM process?
-Kaizen events are structured workshops that help identify inefficiencies and implement solutions to improve OEE through continuous improvement metrics.
Why is a cultural shift important in the context of TPM?
-A cultural shift promotes ownership and responsibility among operators, encouraging collaboration between production and maintenance teams for better equipment management.
What types of key performance indicators (KPIs) are emphasized in TPM?
-TPM emphasizes leading KPIs such as the number of improvements made and the percentage of operators trained in autonomous maintenance, rather than just the number of repairs completed.
How does TPM instill pride among operators?
-By allowing operators to take ownership of their machines and engage in maintenance tasks, TPM fosters a sense of pride and responsibility in their work.
What role do operators play in recognizing machine issues?
-Operators are often the first to notice changes in machine performance, such as vibrations or sounds, enabling early detection and proactive maintenance.
What is the next module about after discussing TPM?
-The next module will cover SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die), which focuses on reducing setup and changeover times in production.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Four Principles TPM

What is Total Productive Maintenance | 8 Pillars of TPM | 6 Big Losses | Type of Maintenance

How 7 Companies Mastered TPM (Total Productive Maintenance)

What is TPM -Total Productive Maintenance ? | 8 TPM pillars Total Productive Maintenance

Four Principles – Lean Manufacturing & TPM

Interview Questions for Maintenance Engineers
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)