Materi Organisasi Komputer Pertemuan 10-Memori Eksternal
Summary
TLDRThis lecture on computer organization focuses on external memory, discussing its importance and various types, including magnetic and optical disks. The presenter explains the distinct characteristics of external memory compared to internal memory, elaborating on the structure and organization of magnetic disks, such as tracks and sectors. The mechanics of data reading and writing are highlighted, showcasing the role of magnetoresistive sensors and the physical movement of heads. The session concludes with a reflection on the relevance of understanding external memory for efficient data management in computing systems.
Takeaways
- 😀 External memory is essential for data storage, differing from internal memory in accessibility and capacity.
- 💾 Various types of external memory include magnetic disks, optical disks (like CDs and DVDs), and newer mobile storage options.
- 🧲 Magnetic disks operate on principles of magnetism, using magnetic fields to read and write data.
- 🔄 The reading and writing processes in magnetic disks involve rotating mechanisms that maintain constant angular velocity.
- 📏 Data on magnetic disks is organized into tracks and sectors, which facilitates efficient data retrieval.
- 🖥️ Modern magnetic disks often use glass substrates for improved durability and surface uniformity.
- 🧠 The principle of inductive and magnetoresistive sensing is crucial for the operation of magnetic disk drives.
- 📝 Floppy disks are a type of removable magnetic storage, characterized by low capacity and slow access speeds.
- 🚀 The speed and efficiency of data transfer are influenced by the design and mechanics of the read/write head in storage devices.
- 🔐 Data protection mechanisms are essential to prevent data loss during the read/write processes.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the lecture?
-The main topic of the lecture is external memory, specifically focusing on different types of external storage such as magnetic disks and optical media.
How does external memory differ from internal memory?
-External memory requires external devices for access, unlike internal memory, which is built into the computer system.
What are some examples of external memory mentioned in the transcript?
-Examples of external memory include magnetic disks, optical disks like CDs and DVDs, and various types of removable storage.
What materials are commonly used in magnetic disks?
-Magnetic disks are typically made with iron oxide and may also be coated with glass to improve surface uniformity and resistance to small damage.
Can you explain the principle of how magnetic disks operate?
-Magnetic disks operate using principles of electromagnetism, where electrical signals create magnetic fields that read and write data on the disk.
What are tracks and sectors in the context of magnetic disks?
-Tracks are concentric circles on a magnetic disk, while sectors are divisions within those tracks used to organize and store data.
What is the role of the read/write head in magnetic disks?
-The read/write head is responsible for reading data from and writing data to the magnetic disk. It moves over the surface of the disk to access the stored data.
What types of removable disks are mentioned, and how do they differ?
-The transcript mentions removable disks that can be easily detached from the device, allowing for flexible data storage solutions, differing from fixed disks which are permanently installed.
What factors affect the speed of data access in external memory devices?
-Factors affecting data access speed include the rotational speed of the disk, the read/write head movement, and the overall design of the storage device.
What is the significance of the term 'data transfer rate' in external storage?
-Data transfer rate refers to the speed at which data can be read from or written to the external storage, usually measured in megabytes per second.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
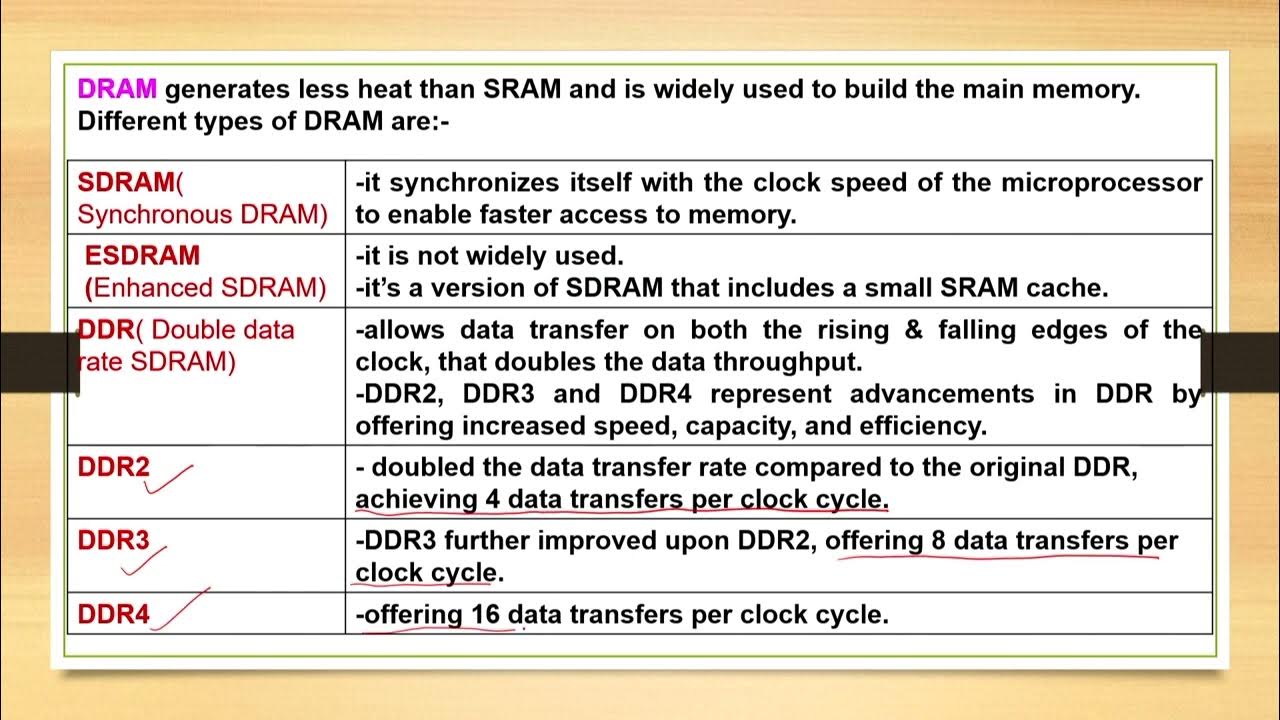
Lecture 06: Computers Memory

PERTEMUAN 3 MEMORI KOMPUTER

L-3.1: Memory Hierarchy in Computer Architecture | Access time, Speed, Size, Cost | All Imp Points
10. OCR A Level (H046-H446) SLR3 - 1.1 Magnetic, flash and optical storage

Magnetic Systems | Introduction to Computing | CS101_Topic015
Memory & Storage: Crash Course Computer Science #19
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)