2.5 Heating/Cooling Curves (Potential and Kinetic Energy Changes)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains heating and cooling curves, illustrating the relationship between temperature and kinetic energy. It emphasizes that temperature reflects average kinetic energy, as shown in graphs plotting heat added to a substance. The video details phase changes, such as melting and boiling, marked by flat lines where temperature remains constant while potential energy increases. It contrasts heating curves with cooling processes, highlighting that during phase transitions, potential energy decreases while average kinetic energy varies. The content connects molecular behavior with energy transformations, providing a comprehensive understanding of thermal dynamics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy of particles in a substance.
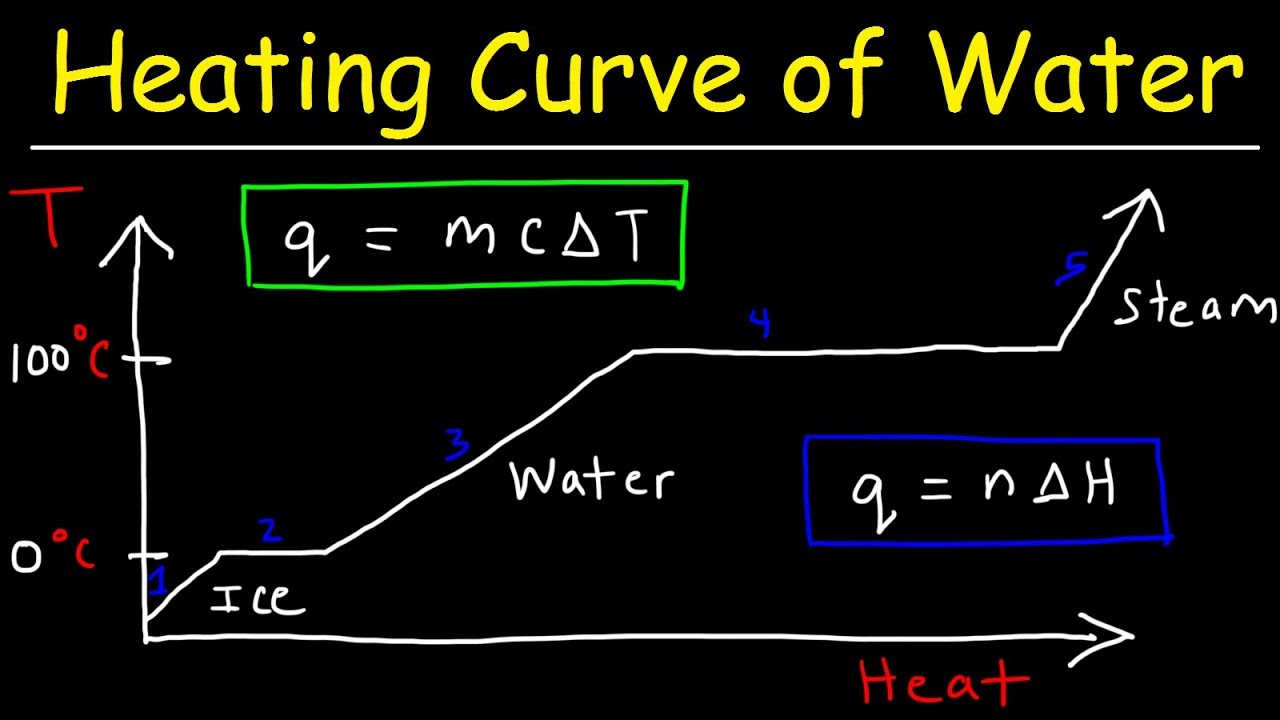
- 🌡️ Heating curves graph the relationship between temperature and heat added over time.
- 🔄 During the solid phase, temperature increases as heat is added, indicating rising kinetic energy.
- 🧊 At the melting point, a flat line appears on the graph, signifying a phase change from solid to liquid with constant temperature.
- 💧 In the liquid phase, further heating raises temperature and kinetic energy while potential energy remains constant.
- 🔥 A flat line at the boiling point represents the transition from liquid to gas, where temperature remains unchanged but potential energy increases.
- ❄️ Cooling curves show the opposite process, where heat removal decreases temperature and kinetic energy.
- 🔄 During phase changes in cooling curves, potential energy decreases while temperature remains constant.
- ⚖️ Only one type of energy (kinetic or potential) changes at a time during phase transitions.
- 💡 Understanding these curves helps illustrate molecular behavior and energy transitions during heating and cooling processes.
Q & A
What do heating and cooling curves represent?
-Heating and cooling curves illustrate the relationship between temperature and heat added to or removed from a substance, showing how its phase changes with temperature.
How is temperature related to kinetic energy?
-Temperature is a measure of average kinetic energy; as temperature increases, the average kinetic energy of the substance's molecules also increases.
What happens to the temperature of a solid as it is heated?
-As a solid is heated, its temperature rises until it reaches its melting point, where the temperature remains constant as the solid begins to melt.
What does the flat line on a heating curve signify?
-The flat line on a heating curve indicates that the temperature is constant during a phase change, meaning that the energy added is used to change the phase rather than increase temperature.
At what temperature does water melt and freeze?
-Water melts and freezes at 0 degrees Celsius, depending on whether heat is being added (melting) or removed (freezing).
What energy change occurs during melting?
-During melting, potential energy increases as heat is added to break the bonds holding the solid together, while kinetic energy remains constant.
What occurs at a substance's boiling point?
-At the boiling point, the temperature remains constant while potential energy increases as the liquid transitions to a gas.
How does a cooling curve differ from a heating curve?
-A cooling curve shows the process of a substance losing heat, leading to decreases in temperature and potential energy during phase changes, while a heating curve shows the substance gaining heat.
What happens to the average kinetic energy of a substance during cooling?
-During cooling, the average kinetic energy decreases as the temperature drops, especially during phase changes like condensation and freezing.
Why is it important to understand the relationships between temperature, kinetic energy, and potential energy?
-Understanding these relationships is crucial in thermodynamics and physical chemistry, as it explains how energy transfers and transforms during heating and cooling processes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cooling curve vs Heating curve Grade 10 Chemistry

Heating Curve Grade 10: Kinetic Molecular Theory
Heating Curve and Cooling Curve of Water - Enthalpy of Fusion & Vaporization

IGCSE Physics [Syllabus 2.1] Kinetic molecular model of matter

lesson 7 4 calculating heat of phase changes

Física - Aula 112 - Curvas de aquecimento - Calorimetria
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)