Video SE 5_2 Siklus Hidup Pengembangan ERP
Summary
TLDRThis video lecture on enterprise systems focuses on the ERP implementation lifecycle. It outlines key differences between ERP software, such as IARBI, and other software types, emphasizing the complexity and high costs associated with ERP systems. The lecture covers three main implementation plans: comprehensive, middle-of-the-road, and vanilla, detailing the need for business process re-engineering. It also discusses various methodologies for implementing ERP systems, including traditional and agile approaches. Ultimately, the success of ERP implementation hinges on careful planning, management commitment, and effective communication throughout the process.
Takeaways
- 😀 ERP implementation requires significant financial investment, often in the millions, compared to other software solutions that may start from hundreds to thousands of dollars.
- 😀 The complexity of ERP systems typically leads to longer implementation times, ranging from one to several years, while other software can be implemented more quickly.
- 😀 There are three main implementation strategies for ERP: Comprehensive, Middle-of-the-Road, and Vanilla, each with varying costs and levels of required business process re-engineering.
- 😀 Comprehensive implementations cover all ERP functionalities and necessitate high-level business process re-engineering, making them the most expensive.
- 😀 The Middle-of-the-Road strategy involves some changes to core ERP modules and requires considerable business process adjustments.
- 😀 Vanilla implementation is the least costly and time-efficient approach, using core functionalities of the ERP without significant modifications.
- 😀 Change management is crucial for ERP success, necessitating strategies for effective communication, training, and stakeholder involvement throughout the project.
- 😀 The traditional ERP implementation lifecycle consists of several phases, including Scope, Analysis, Design, Implementation, and Operation, with formal approvals needed at each milestone.
- 😀 A comparison between ERP implementation and the System Development Lifecycle (SDLC) reveals that ERP focuses more on packaged solutions, while SDLC targets new system development.
- 😀 Top management commitment and strong program management are critical for ERP success, along with minimizing customizations and ensuring effective communication among all stakeholders.
Q & A
What are the main differences between ERP systems and other software?
-ERP systems, such as IARBI, require significantly higher implementation costs, often in the millions, and take much longer to implement, typically spanning one to several years. They are closely aligned with a company's core mission, whereas other software focuses on improving productivity.
What are the three main implementation plans for ERP systems?
-The three main implementation plans are: 1) Comprehensive Plan, which involves full functionality and extensive business process reengineering; 2) Middle of the Road Plan, which requires moderate changes to core modules; and 3) Vanilla Approach, which utilizes key functionalities with minimal modifications.
Why is change management significant in ERP implementation?
-Change management is critical in ERP implementation because it involves significant alterations to business processes and requires extensive training and communication to ensure all stakeholders are aligned and prepared for the new system.
What are the key stages of ERP implementation?
-The key stages of ERP implementation include: 1) Scope and Commitment, 2) Analysis and Design, 3) Installation and Testing, 4) Go-Live, and 5) Operation.
What does the Scope and Commitment stage involve?
-The Scope and Commitment stage involves conducting feasibility studies, defining the project's scope, assessing resource needs, and securing commitment from top management.
What is the role of gap analysis during the Analysis and Design stage?
-Gap analysis assesses the differences between current business processes and the functionalities offered by the ERP system, helping to determine necessary adjustments to either the software or business processes.
What is the purpose of the Go-Live stage in ERP implementation?
-The Go-Live stage marks the official launch of the ERP system, which includes finalizing system configurations, user training, and ongoing support to address any immediate issues.
How does the Vanilla Approach to ERP implementation differ from customization?
-The Vanilla Approach involves using the ERP system's standard functionalities without making modifications, whereas customization entails altering the software to fit specific business needs, which can increase complexity and cost.
What are some challenges organizations face when modifying ERP systems?
-Challenges include the increased cost and complexity of modifications, the potential for significant time delays during upgrades, and the difficulty of ensuring that modifications remain compatible with future system updates.
Why is top management commitment crucial for ERP implementation success?
-Top management commitment is vital because it provides the necessary support and resources for the project, facilitates decision-making, and ensures alignment of the implementation goals with the organization's strategic objectives.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
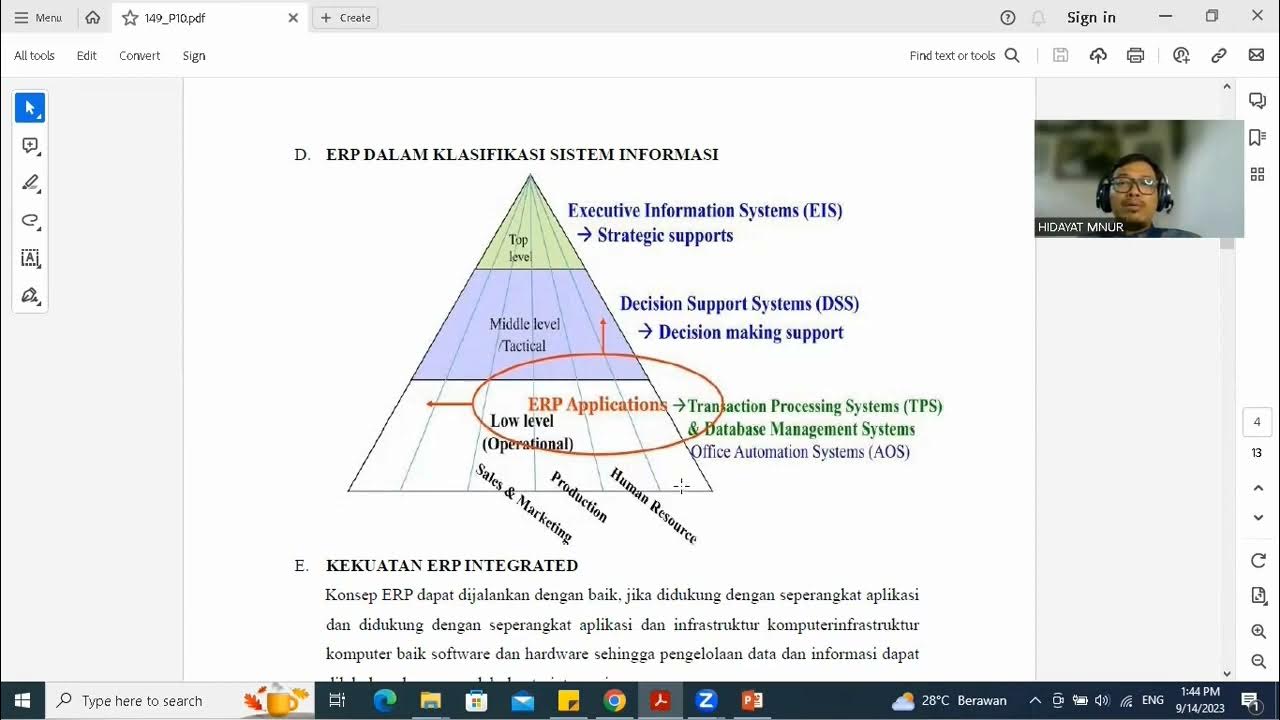
Video Pembelajaran E Business Pertemuan 10

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) in 15 minutes
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?

Oracle Fusion Cloud Enterprise Resource Planning
SAP SD | Configuration & definition of Enterprise structure | Enterprise Structure | Part 1

What is ERP Software? Here is everything you need to know.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)