Synchronous Machines - Introduction (Part1)
Summary
TLDRThis lecture introduces synchronous machines, crucial AC electrical machines with two main parts: a stationary stator and a rotating rotor separated by a small air gap. The stator has three-phase AC windings, while the rotor's field winding generates the main magnetic field with DC excitation. Synchronous machines can operate as generators or motors, converting between mechanical and electrical energy. They also play a significant role in power factor and reactive power control within electrical systems, impacting the balance of active and reactive power.
Takeaways
- 😀 Synchronous machines are a crucial type of AC electrical machine, consisting of a stationary stator and a rotating rotor separated by a small air gap.
- 🔧 The stator is made of laminated magnetic material to reduce eddy current loss and is wound with three-phase AC windings, while the rotor includes a magnetic core and field winding that produces the main operating magnetic field when excited by DC current.
- 🔌 The DC excitation system for the rotor field winding can be external with brushes and slip rings or an internal system with a small machine and rotating rectifier, eliminating the need for brushes and slip rings.
- 🌐 Synchronous machines can utilize either field windings with DC current or permanent magnets to produce the machine's main magnetic field, with the latter being known as permanent magnet synchronous machines.
- 🔄 There are two main rotor constructions: Salient pole rotors, typically used in low-speed applications like hydro generators, and cylindrical pole rotors, used in high-speed applications such as turbo generators.
- 📊 The type of rotor impacts the air gap characteristics, self-inductance, and torque characteristics of the machine, with Salient pole rotors having non-uniform air gaps and cylindrical pole rotors having uniform air gaps.
- ⚙️ The electrical angle in synchronous machines is related to the mechanical angle by a factor of the number of poles, meaning the angle between poles in electrical terms is half the number of poles times the mechanical angle.
- 🔌 Synchronous machines are doubly excited, with AC and DC windings, and can operate as either generators (alternators) or motors, converting between mechanical and electrical energy.
- ⚡ The speed of a synchronous machine, known as synchronous speed, is directly related to the electrical frequency and the number of poles, and is a fixed speed in steady-state operation.
- 🔗 Synchronous machines play a significant role in power generation and are interconnected through transmission lines in power stations, with over 80% of the world's electrical power generated by synchronous generators.
- 🛠️ In addition to energy conversion, synchronous machines can control the active and reactive power of the electrical system, primarily through the control of the excitation field current of the rotor field winding.
Q & A
What are the two main parts of a synchronous machine?
-The two main parts of a synchronous machine are the stationary part called the stator or armature, and the rotating part called the rotor.
Why are the stator cores made of laminated magnetic materials?
-The stator cores are made of laminated magnetic materials to reduce eddy current loss and therefore reduce the heat inside the machine.
What are the stator windings or coils usually called, and what type of windings do they typically have?
-The stator windings or coils are usually called armature windings, and they typically have three-phase AC windings.
What is the function of the rotor winding, and why is it also called the field winding?
-The rotor winding is used to produce the main operating magnetic field when excited by DC current, which is why it is also called the field winding.
How is the DC current supplied to the rotor winding in a synchronous machine?
-The DC current is supplied to the rotor winding through two carbon brushes B1 and B2 that slip on two rotating slip rings S1 and S2 mounted on the rotor shaft.
What is the DC excitation system, and what are its two common types?
-The DC excitation system is used to excite the rotor field winding with DC current. The two common types are the external type, usually a rectifier, and the internal type, which is a small machine generating three-phase AC voltage connected to a rotating rectifier.
What is the difference between a wound rotor synchronous machine and a permanent magnet synchronous machine?
-A wound rotor synchronous machine has a rotor with field windings that require DC excitation, while a permanent magnet synchronous machine has a rotor with permanent magnets that produce the main magnetic field without the need for brushes and slip rings.
What are the two types of rotor construction in synchronous machines, and how do they differ in application?
-The two types are the Salient pole rotor and the cylindrical pole rotor. Salient pole rotors are usually used in low-speed applications like hydro generators, while cylindrical pole rotors are used in high-speed applications such as turbo generators.
Why is the direction of the DC current important in the rotor field winding?
-The direction of the DC current determines the direction of the rotor's magnetic field and therefore the rotor poles, which is crucial for the machine's operation.
What is the relationship between the synchronous speed of a synchronous machine and its electrical frequency?
-The synchronous speed (NS) of a synchronous machine is directly related to its electrical frequency (F) by the formula NS = (120 * F) / P, where P is the number of poles.
How does the type of rotor impact the characteristics of a synchronous machine?
-The type of rotor impacts the air gap characteristics, self-inductance, and torque characteristics of the machine. For example, a Salient pole rotor machine has non-uniform air gap and variable self-inductance with rotor position, while a cylindrical pole rotor machine has a uniform air gap and constant self-inductance.
What is the significance of the d-axis and q-axis in synchronous machines?
-The d-axis and q-axis are important in understanding the electrical characteristics of synchronous machines. The d-axis is along the poles axis, and the q-axis is along the inter-pole axis. They are perpendicular to each other, and the machine's operation, especially in terms of torque production, is analyzed with respect to these axes.
What is the role of synchronous machines in power generation and power factor control?
-Synchronous machines play a crucial role in power generation by converting mechanical energy to electrical energy in generators and vice versa in motors. They can also be used for power factor control or reactive power control in electrical systems by adjusting the excitation field current of the rotor field winding.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Electrical Machines - II
Construction and Working of a Single phase Induction Motor | Skill-Lync

Electrical Machine 1 | Introduction | B.Tech 2nd Year | Abdul Kalam Technical University | AKTutor
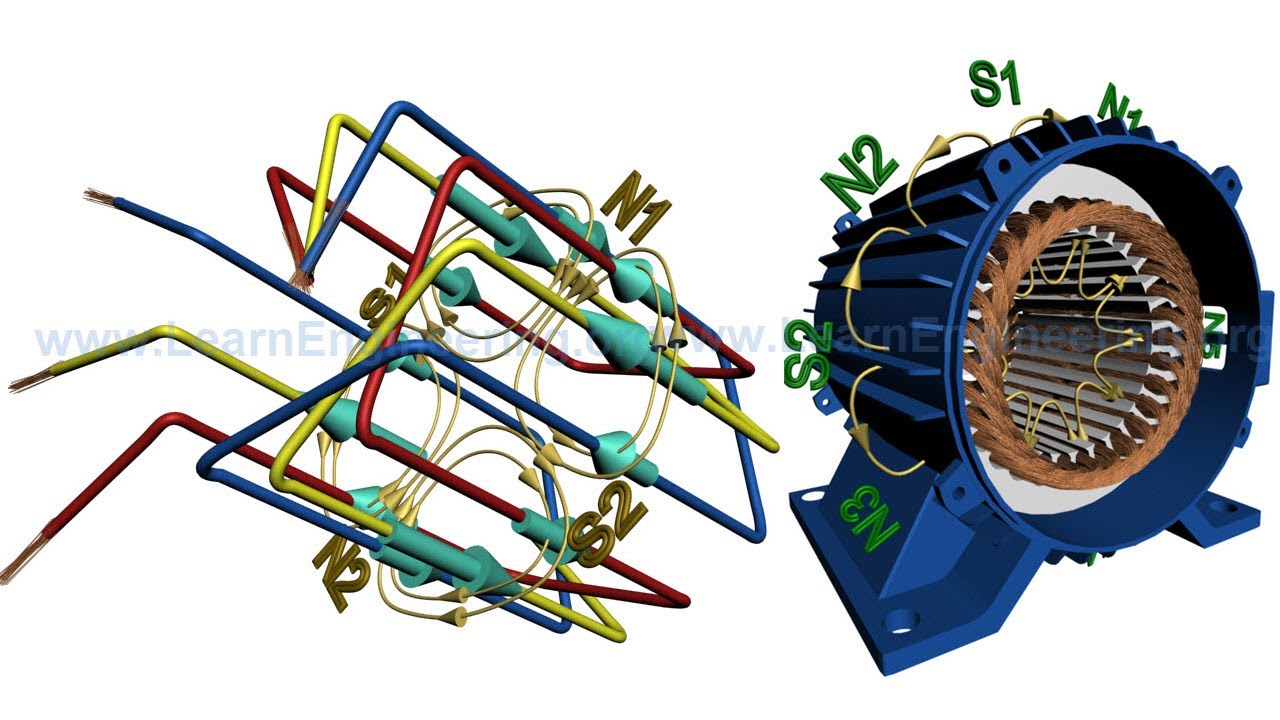
Rotating Magnetic Field & Synchronous Speed

Cara Kerja Generator Pembangkit Listrik

How Three-Phase Induction Motors Work in Telugu | Understanding Three-Phase Induction Motors.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)