MATERI III. AMPLIFIKASI DNA IN-VITRO
Summary
TLDRIn this practical biotechnology session, students explored in vitro DNA amplification using the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Key components of PCR include DNA template, primers, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), and PCR buffer with magnesium chloride. The process involves denaturation, annealing, and extension to create specific DNA fragments. A hands-on demonstration showed how to prepare a PCR mixture, run the machine, and visualize results through gel electrophoresis. The session emphasized understanding PCR principles, aiming to empower students to conduct independent amplifications in future labs.
Takeaways
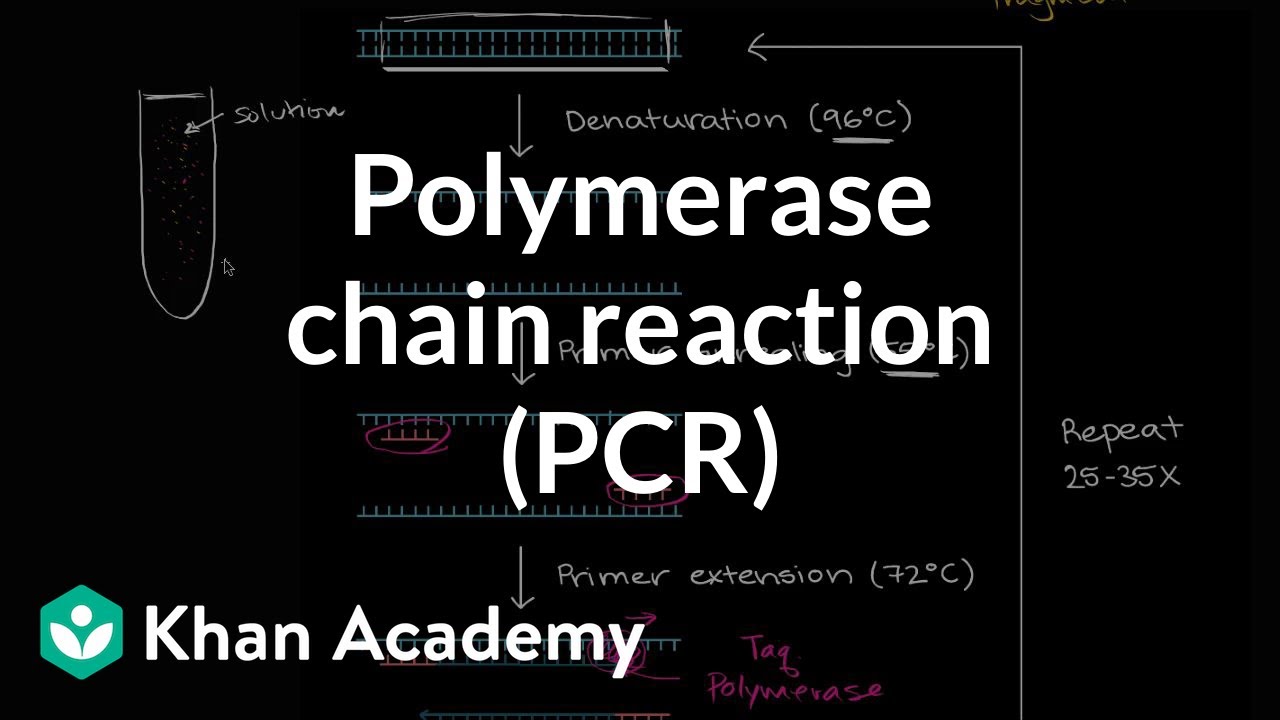
- 😀 PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a technique used for the amplification of specific DNA molecules in vitro.
- 😀 The process involves four main components: DNA template, primers, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), and a buffer solution with magnesium chloride.
- 😀 The DNA template serves as the blueprint for creating new DNA molecules.
- 😀 Primers are short oligonucleotides that bind to the target DNA fragments and initiate the synthesis of new DNA strands.
- 😀 dNTPs are the building blocks needed for DNA extension and are added to the growing DNA strand.
- 😀 The buffer solution maintains pH stability during the PCR process, while magnesium chloride enhances the activity of the DNA polymerase enzyme.
- 😀 The PCR process includes three main steps: denaturation, annealing, and extension.
- 😀 Denaturation occurs at approximately 94°C, where double-stranded DNA separates into single strands.
- 😀 During annealing, primers bind to their complementary sequences on the single-stranded DNA.
- 😀 Extension is facilitated by Taq polymerase, which synthesizes new DNA strands by adding dNTPs to the primers.
Q & A
What is PCR and what does it stand for?
-PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction, and it is a technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences in vitro.
What are the four main components required for PCR?
-The four main components are the DNA template, primers, deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), and PCR buffer with magnesium chloride.
What is the role of the DNA template in PCR?
-The DNA template serves as a blueprint for synthesizing new DNA strands during the amplification process.
How do primers function in the PCR process?
-Primers are short sequences of nucleotides that bind to the template DNA and provide a starting point for DNA synthesis.
Why is magnesium chloride important in PCR?
-Magnesium chloride is crucial for enhancing the activity of DNA polymerase and improving the interaction between primers and the DNA template.
What are the three main steps involved in the PCR cycle?
-The three main steps are denaturation (separating the DNA strands), annealing (binding of primers to the template), and extension (synthesizing new DNA strands).
What temperature is used for the denaturation step in PCR?
-The denaturation step typically occurs at 94°C, which causes the double-stranded DNA to separate into single strands.
What is the purpose of the extension step in PCR?
-During the extension step, Taq polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands by adding complementary nucleotides to the primers.
How can the results of PCR be visualized after amplification?
-Results can be visualized using electrophoresis, where DNA samples are loaded onto a gel and separated based on size.
What should participants be able to do after learning about PCR?
-Participants should be able to independently perform PCR techniques and understand the underlying principles of the process.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)