Pharmacology: Drugs for Asthma and COPD, Animation
Summary
TLDRAsthma and COPD are chronic inflammatory airway diseases with distinct characteristics. Asthma's airway obstruction is reversible and episodic, driven by mast cells and eosinophils, while COPD's obstruction is persistent, primarily involving macrophages and neutrophils. Despite differences, treatments for both overlap, including inhaled bronchodilators and corticosteroids. Bronchodilators are classified as β2-agonists, which relax airway muscles by stimulating the sympathetic system, and muscarinic antagonists, which suppress parasympathetic activity. For moderate to severe COPD, combining long-acting bronchodilators is preferred. Other treatments like PDE-4 inhibitors and asthma-specific medications, such as anti-IgE antibodies and leukotriene modifiers, target inflammation and bronchoconstriction.
Takeaways
- 🫁 Both asthma and COPD are chronic airway obstructive diseases caused by inflammation, but asthma is episodic and reversible, while COPD is persistent and progressive.
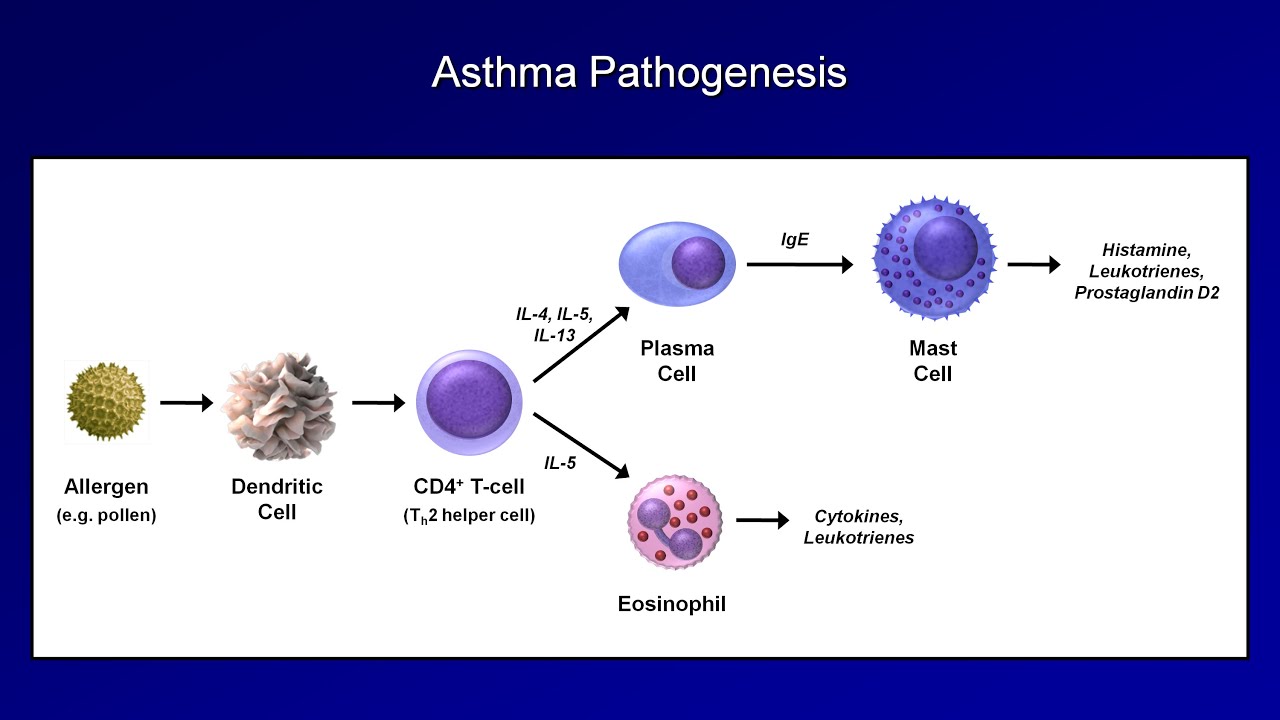
- 🧬 Inflammation in COPD is driven by macrophages and neutrophils, while asthma involves activated mast cells and eosinophils, with asthma being a type 1 hypersensitivity disease.
- 💉 Asthma triggers cause IgE-sensitized mast cells to release inflammatory chemicals, such as leukotrienes, which cause bronchoconstriction and attract eosinophils.
- 💊 Medications used to treat both asthma and COPD include inhaled bronchodilators to widen airways and inhaled corticosteroids to control inflammation.
- ⏳ Short-acting bronchodilators are used for acute bronchospasms, while long-acting bronchodilators are for long-term disease control.
- 📌 Inhaled corticosteroids are the first-line treatment for long-term asthma management, whereas long-acting bronchodilators are the first-line treatment for moderate COPD.
- ⚖️ Patients with severe COPD often use a combination of bronchodilators and corticosteroids for better control.
- 🔄 β2-agonists stimulate the sympathetic system to relax airway smooth muscles, while muscarinic antagonists block the parasympathetic system to prevent airway constriction.
- 🚨 Combination therapy with long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA) and long-acting beta-agonists (LABA) is preferred in COPD due to their amplified effects.
- 🌟 Asthma-specific drugs include mast cell stabilizers, anti-IgE antibodies, and leukotriene modifiers, which target inflammation and provide bronchodilation.
Q & A
What are the main differences between asthma and COPD in terms of airway obstruction?
-Asthma airway obstruction is episodic and reversible, while COPD obstruction is persistent and progressive.
What cells are primarily responsible for inflammation in asthma and COPD?
-In asthma, inflammation is driven by activated mast cells and eosinophils. In COPD, it is driven by macrophages and neutrophils.
How does asthma relate to type 1 hypersensitivity reactions?
-Asthma is a type 1 hypersensitivity disease where IgE-sensitized mast cells release inflammatory chemicals, such as leukotrienes, upon re-exposure to certain triggers.
What role do leukotrienes play in an asthmatic attack?
-Leukotrienes cause bronchoconstriction and attract eosinophils to the lungs, amplifying inflammation during an asthmatic attack.
Which drugs are commonly used to treat both asthma and COPD?
-Inhaled bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids are used to treat both asthma and COPD. Bronchodilators widen airways, while corticosteroids control inflammation.
What is the difference between short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators?
-Short-acting bronchodilators are used for emergency treatment of acute bronchospasms, while long-acting bronchodilators are used for long-term disease management.
What is the first-line therapy for long-term asthma management?
-Inhaled corticosteroids are the first-line therapy for long-term asthma management.
How do β2-agonists help in asthma and COPD treatment?
-β2-agonists activate β2-adrenergic receptors, leading to the production of cAMP, which relaxes airway smooth muscles. They are highly selective for receptors in the lungs.
Why are long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA) and long-acting beta-agonists (LABA) often combined in COPD treatment?
-These two drug classes amplify each other’s effects, making the combination more effective in treating moderate to severe COPD than using either drug alone.
What is the function of phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4) inhibitors in COPD treatment?
-PDE-4 inhibitors prevent the degradation of cAMP, which leads to smooth muscle relaxation and anti-inflammatory effects, making them useful as second-line treatment.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Pharmacology - DRUGS FOR ASTHMA AND COPD (MADE EASY)
Asthma and COPD - Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology

Curso de Farmacologia: Aula 38 - Farmacologia da asma e DPOC (1a parte)

How to Properly Use a Nebulizer

Interview with Dr. Andra Fee, Pulmonologist at Meadville Medical Center

Asthma - signs and symptoms, pathophysiology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)