Aristotle's Theory of Causation
Summary
TLDRThis engaging discussion explores Aristotle's theory of causation, contrasting his empirical approach with Plato's rationalism. The dialogue delves into the four causes: material, formal, efficient, and final, illustrating how they explain change and purpose in the universe. Central to Aristotle's philosophy is the concept of the prime mover, an eternal entity that draws all motion without intervening in the world. The conversation raises critical questions about the subjectivity of empirical knowledge, the role of chance in nature, and the implications of Aristotle's prime mover on the understanding of divinity, encouraging viewers to reflect on these philosophical ideas.
Takeaways
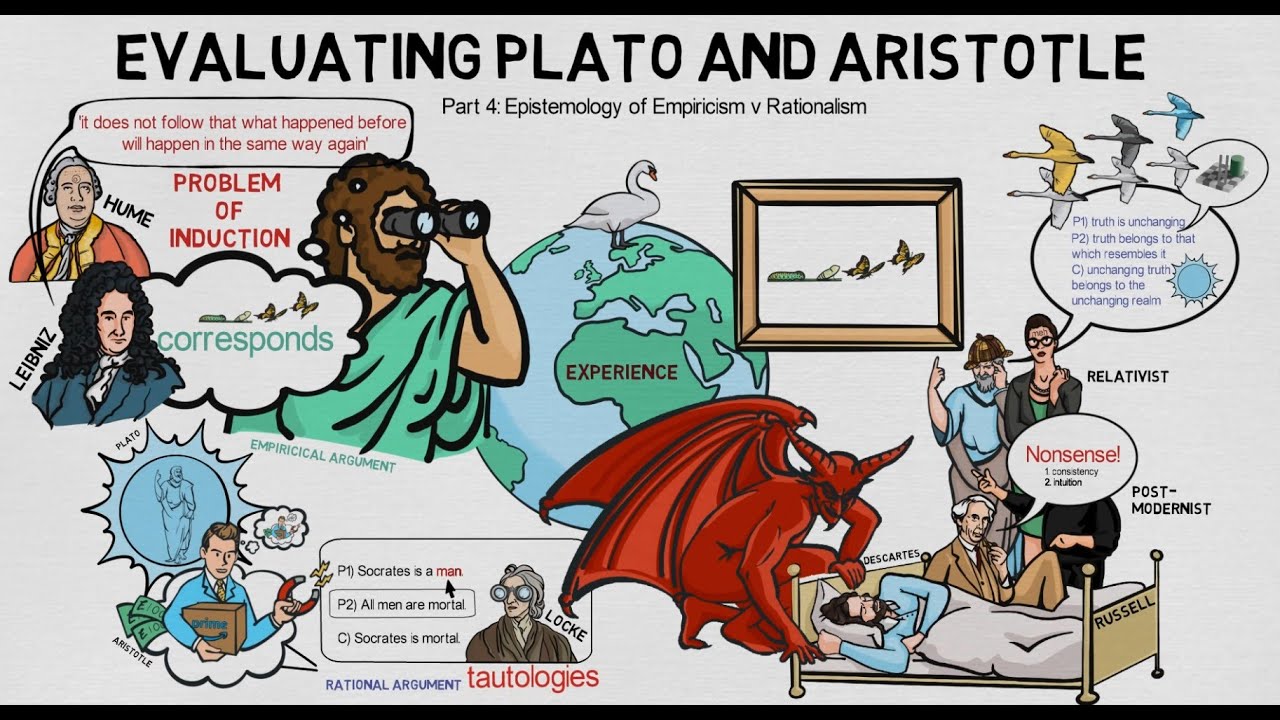
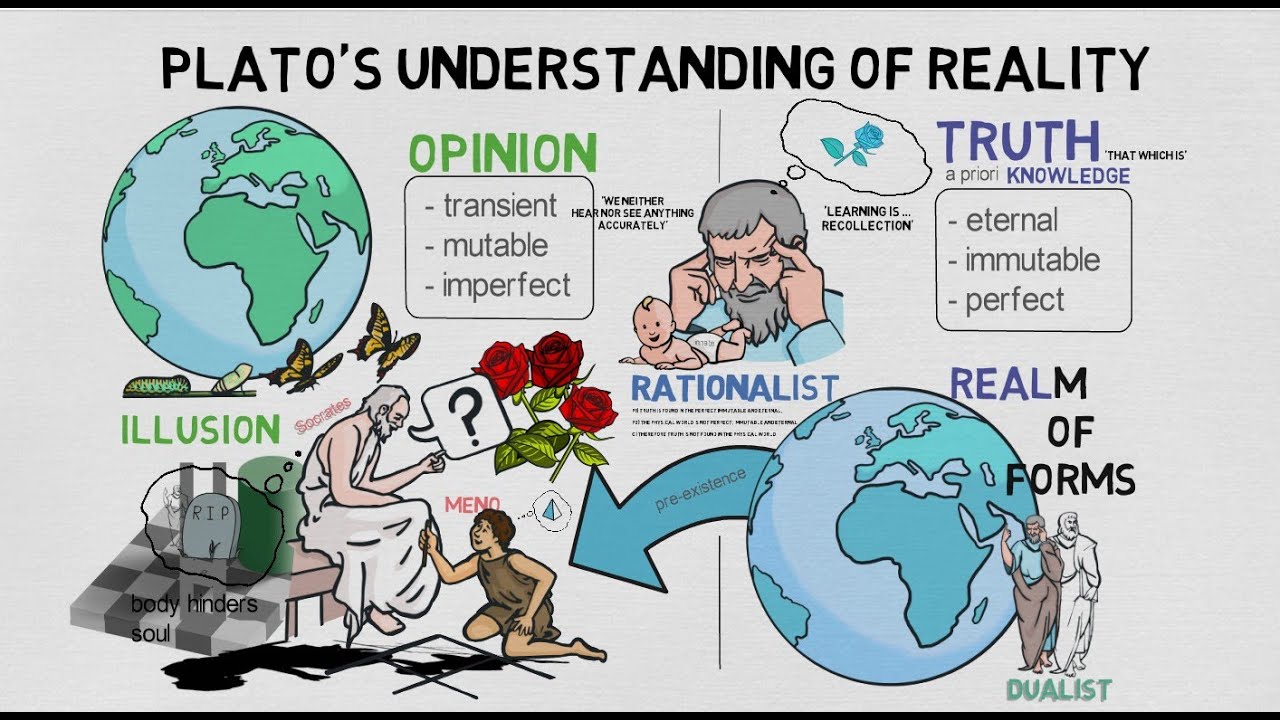
- 😀 Aristotle was an empiricist who believed in gaining knowledge through observation of the empirical world, contrasting with Plato's rationalism.
- 😀 Aristotle identified a state of constant change in all organisms, arguing that everything is moving toward a purpose or 'telos.'
- 😀 The four causes introduced by Aristotle are: material cause, formal cause, efficient cause, and final cause, which explain how and why things exist.
- 😀 The material cause refers to the substance something is made from, while the formal cause is its shape or form necessary to achieve its purpose.
- 😀 The efficient cause is the external agent that brings about change, and the final cause is the ultimate purpose a thing serves.
- 😀 Aristotle's theory of causation applies to all entities, including humans, where each aspect of existence can be traced back to the four causes.
- 😀 Aristotle rejected the notion of a 'before' the universe, asserting that the universe is eternal and has always existed.
- 😀 The concept of the Prime Mover is central to Aristotle's philosophy, representing an unchanging being that attracts all motion without intervening.
- 😀 Aristotle's Prime Mover differs from the Judeo-Christian God, as it does not engage in human affairs or possess knowledge of the universe's details.
- 😀 Critiques of Aristotle's theory highlight the subjectivity of empirical knowledge, the role of chance in existence, and the nature of the Prime Mover as potentially inadequate.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The video discusses Aristotle's theory of causation and his philosophical ideas, contrasting them with those of his teacher, Plato.
How did Aristotle's approach to knowledge differ from Plato's?
-Aristotle was an empiricist who believed knowledge comes from observing the empirical world, while Plato was a rationalist who believed truth could be discovered through reason without needing external experience.
What are the four causes proposed by Aristotle?
-The four causes are the material cause (the substance), the formal cause (the shape), the efficient cause (the agent that brings it into being), and the final cause (the purpose or end goal of an object).
Can you explain the concept of potentiality and actuality in Aristotle's philosophy?
-Potentiality refers to the inherent capacity of an object to reach its purpose, while actuality is the realization of that purpose. For example, a seed has the potential to become a plant, and when it grows, it achieves its actuality.
What role does the prime mover play in Aristotle's cosmology?
-The prime mover is an eternal, unchanging being that attracts all motion and change in the universe, leading everything from potentiality to actuality, but does not directly intervene in the world.
How does Aristotle's concept of the prime mover differ from the Judeo-Christian understanding of God?
-Aristotle's prime mover is not a conscious, moral being that intervenes in the world; rather, it is an impersonal entity that simply attracts motion without awareness of its existence.
What is a criticism of Aristotle's empirical approach to understanding truth?
-Critics argue that empirical senses vary among individuals, making the pursuit of universal truths through empirical observation subjective and potentially unreliable.
What alternative explanation does the discussion suggest regarding purpose in nature?
-The discussion suggests that the theory of evolution and natural selection may explain the development of life without attributing specific purposes or goals to organisms, indicating that many occurrences may be due to chance.
What issue arises from the concept of the prime mover as presented in the video?
-The video questions how a prime mover, which is described as an ignorant and powerless being, can adequately define the concept of God, suggesting it lacks the characteristics typically attributed to a deity.
How does Aristotle's theory of causation contribute to the understanding of science?
-Aristotle's theory of causation provides a framework for understanding the causes of change and existence in the empirical world, which has significantly influenced the development of scientific inquiry and methodology.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)