The Effects of Population Growth
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the social, political, and economic impacts of population growth in both more economically developed countries (MEDCs) and less economically developed countries (LEDCs). It highlights challenges such as overcrowding, pressure on healthcare and education systems, aging populations, and financial strain on governments. Strategies to manage population change include encouraging skilled migration, offering housing incentives, and implementing policies like tax benefits for larger families or retirement age adjustments. The video also explores the importance of sustainable population management to balance current needs with the future well-being of each country’s citizens.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Population growth creates social, political, and economic challenges for both less economically developed countries (LEDCs) and more economically developed countries (MEDCs).
- 🏠 In LEDCs, population growth puts pressure on land and resources, leading to overcrowded areas and conflicts, especially with migrants.
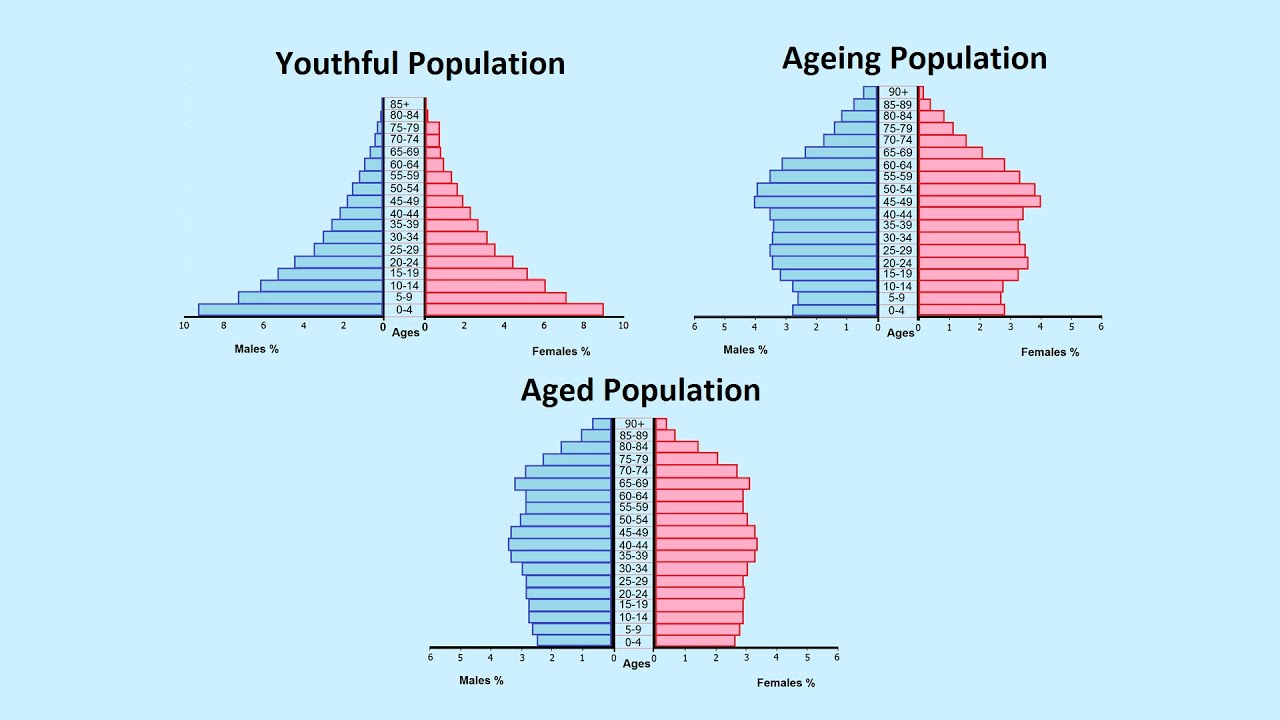
- ⚖️ Aging populations in LEDCs reduce the number of skilled workers, slowing industries and straining medical systems.
- 💰 Economically, LEDCs often lack the financial resources to provide adequate medical services, making it harder to support population growth.
- 🏥 In MEDCs like the UK, aging populations cause concerns about rising taxes needed to cover healthcare costs for elderly citizens.
- 👴 The aging baby boomer generation in MEDCs poses financial challenges, as governments may struggle to support their growing healthcare needs.
- 🏗️ Political issues in LEDCs include government corruption and strained finances, which hinder investment in essential services and industries.
- 📈 MEDCs are adopting strategies like promoting immigration of skilled workers to sparsely populated areas and offering housing subsidies to help cope with population challenges.
- 👨👩👦 In countries like France, tax incentives encourage larger families to increase birth rates and sustain population growth.
- 🔄 Sustainability is key, with measures like raising retirement ages and controlling immigration to ensure economic and social stability in both LEDCs and MEDCs.
Q & A
What are some of the social effects of population growth in LEDCs (Less Economically Developed Countries)?
-Social effects of population growth in LEDCs include increased pressure on land as people move to densely populated areas, which can lead to conflicts among migrants, potential civil wars, and additional strain on medical systems and schools due to overpopulation.
How does an aging population affect LEDCs and MEDCs (More Economically Developed Countries) differently?
-In LEDCs, an aging population results in a lack of skilled workers and economic slowdown. In MEDCs, it leads to higher taxes to support growing healthcare costs and puts pressure on social services due to the need to care for an increasing number of elderly people.
What economic challenges do LEDCs face due to population growth?
-LEDCs face economic challenges such as strained government finances, limited funds for medical services, and the inability to invest in developing industries, often exacerbated by corruption.
How do governments in MEDCs address the economic impact of an aging population?
-Governments in MEDCs address the economic impact of an aging population by implementing higher taxes to cover medical and social care costs and by creating policies to attract skilled workers from other countries to fill labor shortages.
What are some strategies that MEDCs use to manage population changes?
-Strategies include subsidizing housing in sparsely populated areas, offering tax incentives for large families (e.g., France), and urbanizing new areas to encourage migration from densely populated cities (e.g., the Netherlands and the UK).
What policies have been used in LEDCs to control population growth?
-LEDCs have implemented policies such as China's one-child policy to curb population growth and incentivizing people to move from densely populated areas to lesser-populated islands, as seen in Indonesia.
How does Brazil address its housing issues related to population growth?
-Brazil is focused on relocating housing developments away from densely built-up shanty towns and neighborhoods to better manage population density and improve living conditions.
What is meant by the term 'sustainable population management'?
-'Sustainable population management' refers to controlling the population in a way that supports economic and social stability while ensuring future needs are met and people’s rights are protected. This may involve adjusting retirement ages or enforcing immigration laws that match labor needs.
How do some countries use immigration laws as a tool for managing population?
-Countries use immigration laws to control the flow of people by setting specific criteria, such as only allowing permits for needed skills or limiting access to education and services to natives. Some countries, like Dubai, use more liberal immigration policies to increase their labor force and economic capital.
What role do government subsidies play in population management in LEDCs and MEDCs?
-Government subsidies, such as those for housing or contraceptives, help manage population growth by making it easier for people to afford living expenses and by controlling birth rates without infringing on individual rights.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Green Fields, Clean Planet: Exploring Sustainable Agricultural Systems for ESS topic 5.2

Women in Agriculture & The Informal Economy [AP Human Geography Unit 5 Topic 12]
How to Read a Population Pyramid

Gr 11: Geography development

Understanding Development Issues: Economic Social & Environmental Aspects | Geography Grade 9 Term 2

Negara Maju dan Berkembang
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)