RECEPTORES ADRENÉRGICOS Y COLINÉRGICOS
Summary
Please replace the link and try again.
Takeaways
- 😀 Adrenergic receptors play a critical role in the sympathetic nervous system and regulate various physiological responses such as heart rate, blood pressure, and smooth muscle contraction.
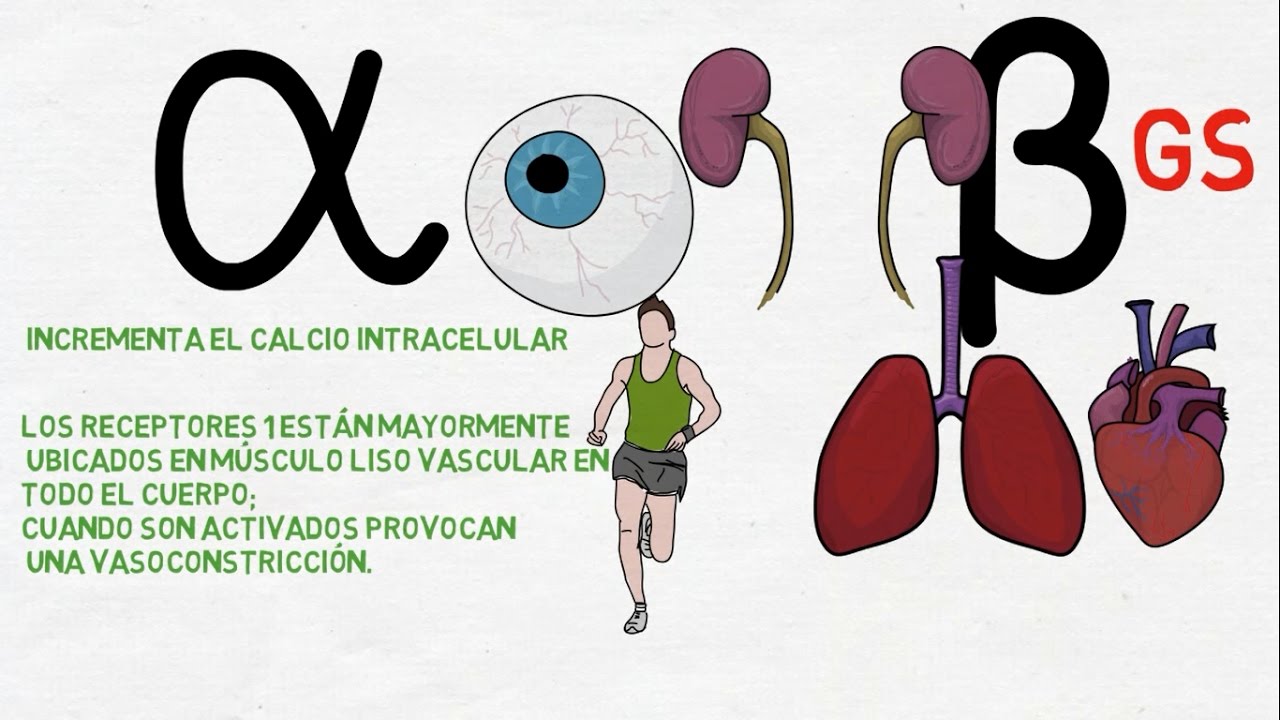
- 😀 There are two main types of adrenergic receptors: alpha (α) and beta (β), with subtypes α1, α2, β1, β2, and β3 that have distinct effects on different organs and tissues.
- 😀 α1 receptors, located in smooth muscles, mainly cause vasoconstriction, leading to increased blood pressure.
- 😀 α2 receptors are inhibitory and regulate neurotransmitter release, playing a role in feedback mechanisms that modulate neurotransmission.
- 😀 β1 receptors are primarily found in the heart, where they increase heart rate and contractility, contributing to the 'fight or flight' response.
- 😀 β2 receptors are involved in smooth muscle relaxation, particularly in the bronchi, leading to bronchodilation and improved airflow.
- 😀 Cholinergic receptors, which respond to acetylcholine, are divided into nicotinic and muscarinic receptors, influencing a wide range of bodily functions, including muscle contraction and parasympathetic responses.
- 😀 Muscarinic receptors (M1, M2, M3, M4, M5) mediate various parasympathetic actions, such as slowing heart rate (M2) and promoting glandular secretion (M3).
- 😀 The molecular mechanism of adrenergic receptor activation involves G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) that trigger intracellular signaling pathways, influencing various cellular responses.
- 😀 The cardiovascular effects of adrenergic and cholinergic receptor activation include changes in heart rate, blood vessel diameter, and blood pressure regulation, influencing the overall circulation and organ function.
Please replace the link and try again.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

PROTEINA G, 2do MENSAJEROS - Receptores ADRENÉRGICO COLINÉRGICO, NEUROFARMACOLOGÍA |INTRO |P3
Receptores adrenérgicos alfa y beta - Simpaticomiméticos

Neurotransmisión Colinérgica (Parte 1) - Mauro Ortiz

Neurotransmisión Colinérgica (Parte 2) - Mauro Ortiz

Semana 2 - Módulo 4 - Bioquímica

CAP 8 FÁRMACOS BLOQUEADORES DE RECEPTORES COLINERGICOS-KATZUNG-PODCAST

Neurotransmisores | Sistema nervioso | Noradrenalina neurotransmisor | Adrenalina neurotransmisor
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)