Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (7 of 31) Differences Between Series and Parallel Current
Summary
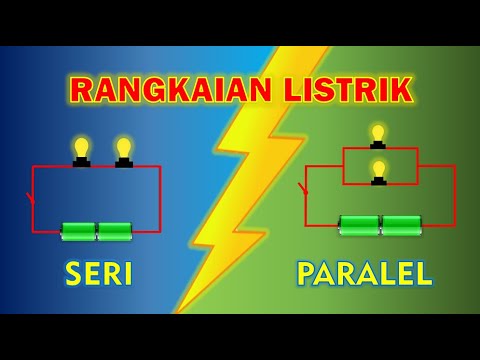
TLDRThis video explains the difference between series and parallel circuits. In a series circuit, elements are connected such that they share a node exclusively, resulting in the same current through all components. In a parallel circuit, multiple elements share the same two nodes, and the voltage across each branch is the same. The video highlights key characteristics of both circuit types, providing a foundational understanding of how they function, which will be useful for future circuit analysis.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Series circuits have components connected one after another, sharing exclusive nodes.
- 🔋 In a series circuit, current through all elements is the same because they share nodes exclusively with no other elements.
- 💡 Parallel circuits have components connected in such a way that they share the same two nodes.
- ⚡ In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each parallel branch is the same.
- 🔧 In a series circuit, resistor R1 and resistor R2 are in series if they share an exclusive node with no other shared components.
- 🔌 Resistors R2 and R3 in a series circuit are also in series if they share a node not connected to other elements.
- 🔋 The current through a series circuit remains constant through each element due to their connection.
- 💡 In a parallel circuit, resistors share two nodes, which makes them parallel, and the voltage remains the same across each branch.
- ⚡ In a series circuit, current remains consistent across all elements, while in a parallel circuit, voltage remains consistent.
- 🔧 Understanding the characteristics of series and parallel circuits is essential for circuit analysis in the future.
Q & A
What is the main difference between a series and a parallel circuit?
-The main difference is that in a series circuit, elements share a node exclusively between two components, while in a parallel circuit, two or more elements share the same two nodes.
How can you identify if two resistors are in series?
-Two resistors are in series if they share a node that is not connected to any other elements in the circuit.
Why is the entire circuit considered a series circuit in the example provided?
-The entire circuit is considered a series circuit because every two elements share a node exclusively with each other and not with any other element.
How can you tell if two resistors are in parallel in a circuit?
-Two resistors are in parallel if they share the same two nodes.
What is the defining characteristic of a series circuit in terms of current?
-In a series circuit, the current is the same through every element of the circuit.
What is the defining characteristic of a parallel circuit in terms of voltage?
-In a parallel circuit, the voltage is the same across each branch.
Why can't the elements in a parallel circuit be considered in series?
-In a parallel circuit, elements share the same nodes with other elements, which breaks the rule for a series connection where nodes should not be shared with more than two elements.
What happens to the current in a series circuit when multiple elements are connected?
-The current remains the same through all elements connected in series.
What happens to the voltage in a parallel circuit when multiple branches are connected?
-The voltage remains the same across all branches connected in parallel.
Why is it important to understand the difference between series and parallel circuits?
-Understanding the difference is important because it helps in analyzing circuits, predicting the behavior of current and voltage in different components, and solving circuit-related problems efficiently.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)