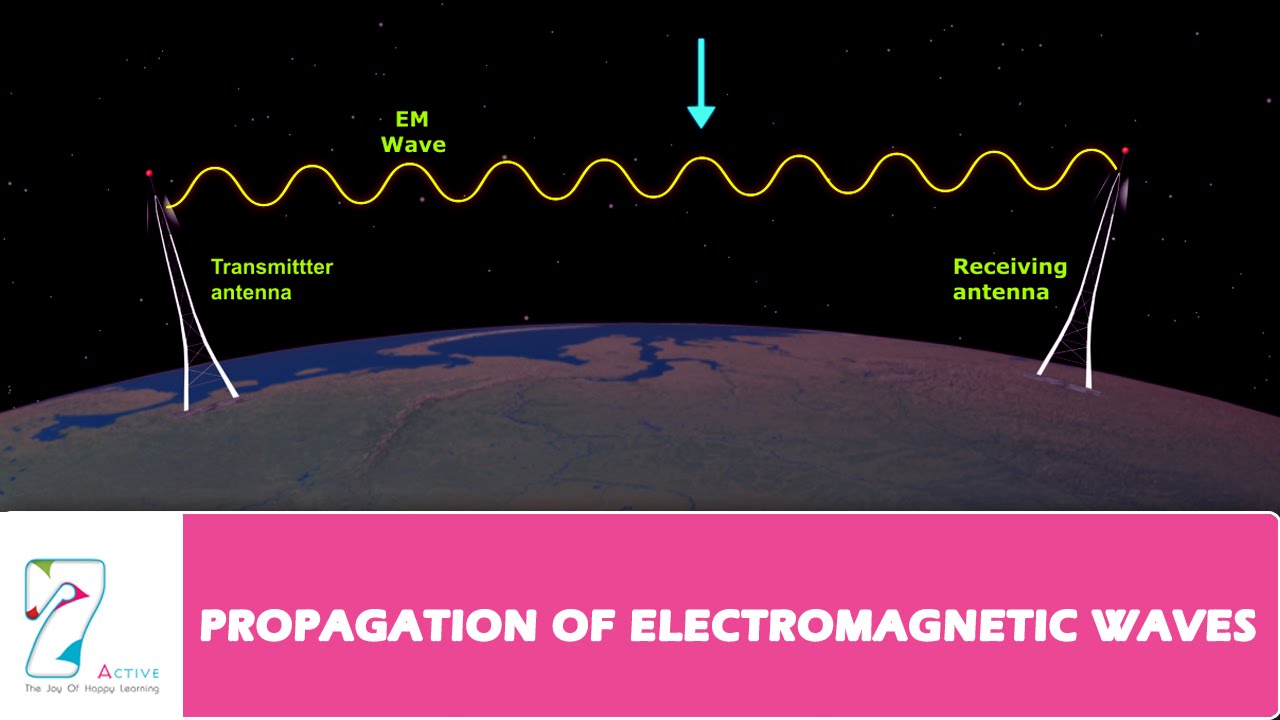
Effects of Electromagnetic Waves | Grade 10 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 2 Module 3
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the effects of electromagnetic waves on living organisms and the environment. It explains the difference between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, highlighting their sources and potential health risks. The video covers ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwave, radio waves, and gamma rays, along with their applications and dangers. It emphasizes the importance of the ALARA principle (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) to minimize radiation exposure using time, distance, and shielding. Lastly, practical safety tips for reducing exposure to electromagnetic frequencies from everyday devices are shared.
Takeaways
- 🌞 Electromagnetic radiation surrounds us from both natural and man-made sources, categorized into ionizing and non-ionizing radiation.
- 🔋 Ionizing radiation removes electrons from atoms and can damage living tissues, while non-ionizing radiation lacks the energy to do so and is generally less harmful.
- 🛡️ The ALARA principle (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) emphasizes minimizing exposure to radiation through time, distance, and shielding.
- 🌅 Ultraviolet radiation from the sun helps in Vitamin D production but overexposure can lead to sunburn, skin cancer, and cataracts.
- 🔥 Infrared radiation, felt as heat, is abundant in the sun's energy, but excessive exposure can cause eye damage and contribute to the greenhouse effect.
- 📡 Microwave radiation excites water molecules in food to generate heat and can cause burns or cataracts with overexposure.
- 📱 Radio frequency waves from devices like cell phones and Wi-Fi can warm up body parts exposed to them, especially with prolonged use.
- 💡 Lasers, made from non-ionizing radiation, can cause severe burns and damage to body parts like the eyes if used improperly.
- ⚛️ Ionizing radiation, like gamma and x-rays, is powerful enough to penetrate materials and can be harmful, but is also used in medical treatments such as cancer therapy.
- 🧲 To reduce exposure to electromagnetic radiation, practical tips include limiting screen time, using speakerphones, and turning off devices at night.
Q & A
What are the two main types of radiation mentioned in the video?
-The two main types of radiation mentioned are ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. Ionizing radiation can remove electrons from atoms and molecules, while non-ionizing radiation does not have enough energy to do so.
Where does ultraviolet radiation come from, and what are its effects on humans?
-Ultraviolet radiation comes from the sun, welding, black lights, and UV lasers. While it is important for the production of vitamin D, overexposure can lead to sunburn, skin cancer, and cataracts over time.
How does infrared radiation affect the environment, and what is the greenhouse effect?
-Infrared radiation is absorbed by the Earth's surface and clouds and then released as heat into the atmosphere. When trapped by water vapor, nitrogen, sulfur, and fluorocarbons, it causes the greenhouse effect, leading to climate change by increasing atmospheric temperature.
What principle should be followed to minimize radiation exposure, and what does it stand for?
-The principle to minimize radiation exposure is called ALARA, which stands for 'As Low As Reasonably Achievable.' It means that even small doses of radiation should be avoided if they do not provide any direct benefit.
What protective measures can reduce radiation exposure based on the ALARA principle?
-The three protective measures based on the ALARA principle are time, distance, and shielding. This means minimizing the time spent near a radiation source, maximizing the distance from it, and using appropriate shielding materials.
How do microwave ovens work, and what potential health effects can arise from overexposure to microwave radiation?
-Microwave ovens work by exciting water molecules in food, causing them to vibrate and generate heat. Overexposure to microwave radiation can cause cataracts and skin burns.
What is the primary health risk of using cell phones according to the video?
-The primary health risk of using cell phones is the warming of exposed body parts, such as the ear and head, due to the absorption of radiofrequency waves, which convert to heat.
Why are gamma rays considered both dangerous and useful?
-Gamma rays are dangerous because they can penetrate most materials, including living tissues, and cause cellular damage, mutations, and cancer. However, they are also useful in treating cancer as they can target and destroy cancerous cells.
What materials can effectively shield against alpha, beta, and gamma radiation?
-Alpha particles can be shielded with a sheet of paper or dead skin cells, beta particles can be blocked by a few inches of plastic or clothing, and gamma rays require dense materials like lead or depleted uranium for effective shielding.
What are some recommendations for reducing electromagnetic radiation exposure at home?
-Recommendations include limiting screen time for children, using speakerphone or wired headsets for calls, keeping wireless routers in less-used rooms or turning them off at night, and using wired connections for the internet and devices whenever possible.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)