ONDULATÓRIA | CONCEITOS INICIAIS | Professor Boaro - Aula 1
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Professor Marcelo Kohara introduces the study of waves, focusing on mechanical and electromagnetic waves. He explains concepts such as resonance, sound waves, light waves, and their propagation in different media. The video covers important topics including the nature of longitudinal and transverse waves, the differences between mechanical and electromagnetic waves, and their behavior in various environments. Additionally, Kohara discusses the Doppler effect, acoustics, and the application of waves in real-life scenarios like radar and sonar. The video concludes with a practical exercise to solidify understanding and links to further resources for in-depth learning.
Takeaways
- 😀 The teacher introduces the subject of wave theory, specifically focusing on the study of waves and oscillations.
- 😀 He demonstrates resonance with a tuning fork and explains how it causes vibrations due to matching frequencies.
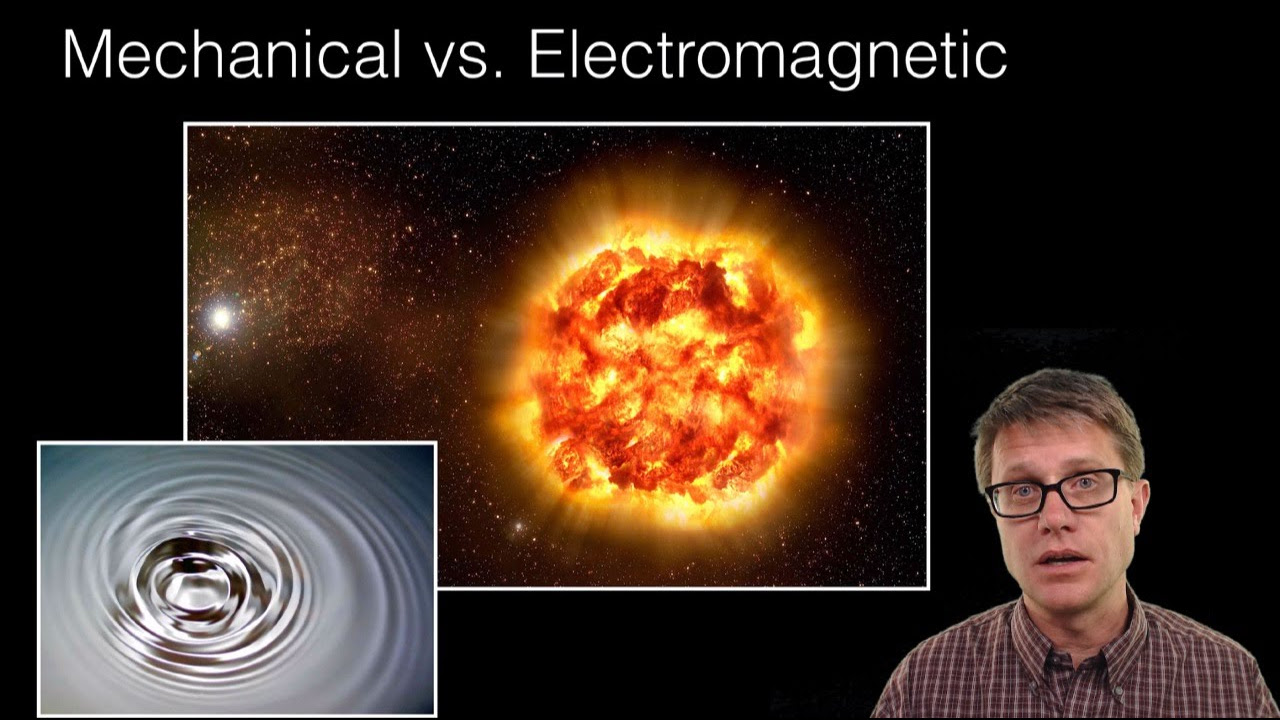
- 😀 The lesson covers mechanical and electromagnetic waves, including their propagation methods and behavior.
- 😀 The teacher introduces the concept of sound waves and explains how they require a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) to propagate.
- 😀 The speed of sound differs in various mediums: around 340 m/s in air, 1500 m/s in water, and 5000 m/s in iron.
- 😀 Light waves, as an example of electromagnetic waves, do not require a medium and can propagate in a vacuum.
- 😀 The teacher introduces the distinction between mechanical waves (like sound) and electromagnetic waves (like light).
- 😀 Sound waves are longitudinal, meaning the oscillation direction is along the wave propagation direction.
- 😀 Light waves are transversal, with oscillations perpendicular to the direction of propagation.
- 😀 The teacher emphasizes the importance of both theoretical understanding and solving many exercises to master the topic.
- 😀 The class will also cover topics like the Doppler effect, the spectrum of electromagnetic waves, and acoustics (study of sound).
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lesson presented in the script?
-The main topic is the study of waves, specifically mechanical and electromagnetic waves, focusing on concepts such as resonance, wave propagation, and the Doppler effect.
How does the teacher explain the concept of resonance?
-The teacher uses a tuning fork to demonstrate resonance, where the sound frequency of the tuning fork matches the natural frequency of another object, causing it to vibrate at the same frequency.
What is the difference between mechanical and electromagnetic waves as described in the script?
-Mechanical waves, such as sound waves, require a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) to propagate, while electromagnetic waves, such as light, can propagate through a vacuum and do not require a medium.
What type of wave is sound, according to the script?
-Sound is described as a mechanical longitudinal wave, meaning it propagates through a medium via the oscillation of particles in the direction of the wave's motion.
What is the speed of sound in different media?
-The speed of sound varies depending on the medium: around 340 meters per second in air, 1,500 meters per second in water, and 5,000 meters per second in iron.
What does the teacher say about the speed of light compared to sound?
-The teacher emphasizes that light travels at a much higher speed than sound, with light in a vacuum traveling at 300 million meters per second, while sound is much slower.
What is the Doppler effect and how is it explained in the script?
-The Doppler effect is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave as observed by someone moving relative to the source of the wave. The teacher gives the example of hearing a car’s engine sound change as it approaches and then moves away.
How does the teacher demonstrate the difference between mechanical and electromagnetic waves?
-The teacher demonstrates mechanical waves using sound and mechanical oscillations, while electromagnetic waves are explained using light, with a focus on their ability to travel through a vacuum and their transverse nature.
What is the significance of the 'tuning fork' demonstration in the script?
-The tuning fork is used to demonstrate how sound waves can be resonated in different objects. The teacher shows how an object vibrates at the same frequency as the tuning fork, illustrating the concept of resonance.
How are the concepts of wave dimensions explained in the lesson?
-The teacher explains waves in terms of their dimensionality: unidimensional (e.g., a vibrating string), bidimensional (e.g., ripples on water), and tridimensional (e.g., sound waves in a room).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)