Radiações eletromagnéticas – Ciências – 9º ano – Ensino Fundamental
Summary
TLDRThis lecture on electromagnetic radiation explores its various types, characteristics, and applications. It covers the concept of waves propagating through space and matter, from low-frequency, non-ionizing radiation like radio waves and microwaves, to high-frequency, ionizing radiation such as UV rays, X-rays, and gamma radiation. The script explains their effects on living beings, highlighting both safe uses (e.g., communication, medical exams) and dangerous ones (e.g., cancer risks, radiation accidents). With real-world examples and safety considerations, the lecture offers a comprehensive understanding of how electromagnetic waves influence our daily lives.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electromagnetic radiation is a fundamental part of daily life, impacting communication, medical treatments, internet, radio, and TV.
- 😀 These radiations are waves that propagate both on Earth and in space, and their discovery has led to many technological advancements.
- 😀 Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (300,000 km/s) and are a result of electrical and magnetic energy release.
- 😀 There are two main categories of electromagnetic radiation: non-ionizing (low frequency, safe) and ionizing (high frequency, harmful).
- 😀 Non-ionizing radiation, like radio waves and microwaves, does not have enough energy to remove electrons from atoms, and thus is generally safe.
- 😀 Ionizing radiation, such as gamma radiation and X-rays, has high frequencies and can remove electrons from atoms, leading to potential damage to living beings.
- 😀 Radio waves are commonly used in communication systems like FM radio, TV, and even underwater communication.
- 😀 Microwaves heat food by agitating water molecules, and caution should be taken when using them as non-water-based materials can catch fire.
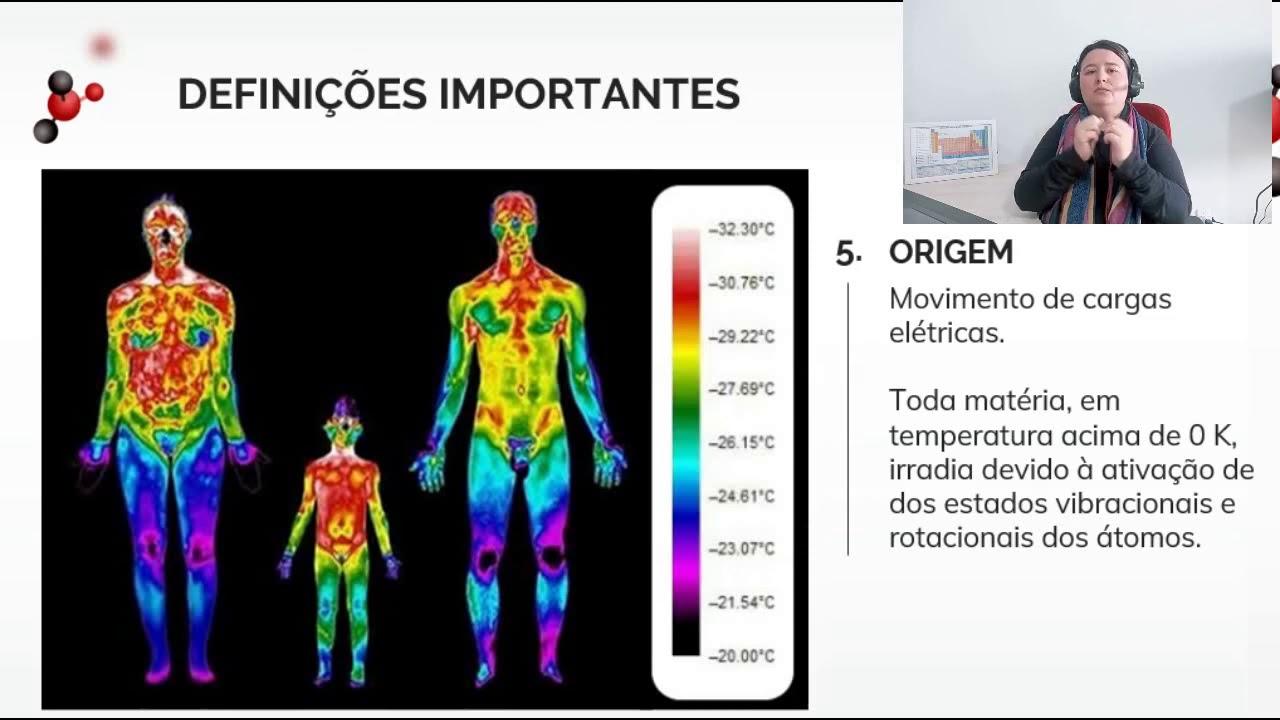
- 😀 Infrared radiation is emitted by all living beings as heat, and it is used in devices like TV remotes and thermal cameras.
- 😀 Visible light is the electromagnetic radiation we can see, with different frequencies corresponding to different colors.
- 😀 Ultraviolet radiation is essential for vitamin D production but can cause harm, including skin burns and aging, due to its ionizing nature.
- 😀 X-rays and gamma radiation are used in medical imaging and diagnostics but require precautions due to their potential to cause cancer and other damage.
Q & A
What is electromagnetic radiation?
-Electromagnetic radiation consists of waves that propagate through space and air, carrying electrical and magnetic energy. These waves travel at the speed of light, approximately 300,000 kilometers per second.
What does the frequency of electromagnetic radiation refer to?
-The frequency of electromagnetic radiation refers to the number of oscillations or cycles the wave completes per second. Higher frequencies correspond to shorter wavelengths, while lower frequencies correspond to longer wavelengths.
What is the difference between non-ionizing and ionizing radiation?
-Non-ionizing radiation has lower frequency and energy, which means it does not have enough energy to remove electrons from atoms. Ionizing radiation, with higher frequency and energy, can remove electrons, causing potential harm to living beings.
What types of electromagnetic waves are considered non-ionizing radiation?
-Non-ionizing radiation includes low-frequency waves like radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, and visible light. These waves generally do not cause damage to cells and tissues.
What are some examples of ionizing radiation?
-Ionizing radiation includes ultraviolet (UV) light, X-rays, and gamma rays. These have higher frequencies and can cause damage to living tissues by removing electrons from atoms.
Why is ultraviolet radiation dangerous?
-Ultraviolet radiation can be harmful because it is ionizing and can cause skin burns, premature aging, and even cancer due to its high energy, which can damage DNA in cells.
How do microwaves work in cooking food?
-Microwaves heat food by agitating water molecules, which causes friction and heat. However, if food lacks water or is left in the microwave for too long, it can dry out or even catch fire.
Why do we use antennas to capture radio waves?
-Antennas are used to capture radio waves because they help overcome barriers like buildings that may prevent radio signals from reaching devices such as radios and TVs.
What is the role of infrared radiation in daily life?
-Infrared radiation is used in devices like remote controls, and it is also emitted by living beings as heat. Additionally, infrared cameras are used to detect temperature variations in objects or environments.
What are the potential health risks associated with X-rays?
-X-rays are ionizing radiation and can be potentially harmful as they have high energy that can damage tissues, cells, and DNA, leading to cancer or other health issues with excessive exposure.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Electromagnetic Spectrum-Grade 10 Waves, Sound and Light- Lesson 7

Lesson 3: Uses and Effects of EM Waves
3.2.2 - O que é radiação eletromagnética?

Electromagnetic Spectrum Explained - Radio, Microwave, Infrared, Visible Light, UV, X-ray, Gamma Ray

GATE XL | Chemistry | Lecture 1 | Gurmantra Academy

Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 2 Module 4 | Visible Light, UV, X-rays and Gamma Rays
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)