Central Processing Unit (CPU)- Parts, Definition & Function
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the role and importance of a computer's central processing unit (CPU) and how technological advancements have increased processing speed. It highlights the key components of a CPU, including the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), control unit (CU), and cache, which work together to execute instructions. The video also explains how transistors within the CPU store binary information, enabling complex calculations. Modern CPUs contain millions or even billions of transistors, all aimed at enhancing performance, especially for demanding tasks like video editing or 3D animation.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the 'brain' of a computer that carries out instructions from programs and performs basic operations.
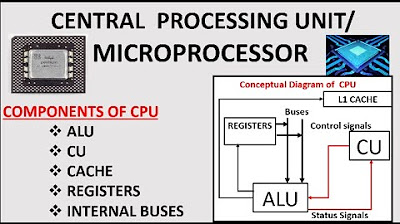
- 🔢 The CPU consists of components like the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) that handles arithmetic and logic, and the Control Unit (CU) that manages the CPU's activities.
- 🔥 A CPU needs a cooling system, usually a heatsink or fan, because it generates a lot of heat during operation.
- ⚡ Transistors in the CPU control the flow of electricity, representing binary values (1s and 0s) for calculations.
- 💾 Modern CPUs are built as microprocessors, integrating millions or even billions of transistors on a small chip.
- 🧮 The ALU performs simple calculations, while the control unit sends signals to activate different parts of the computer to perform tasks.
- 🔁 CPU components, once separate, are now highly integrated into one microprocessor since the 1970s.
- 💻 CPUs have sockets on motherboards that are specific to certain processors, connecting them to the rest of the computer system.
- 🏎️ CPUs are designed for speed, especially for complex tasks like 3D animations or video editing, which demand more processing power.
- ⚙️ The cache in a CPU acts as high-speed memory, storing frequently used instructions for quick retrieval.
Q & A
What is the CPU, and why is it important in a computer?
-The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the hardware responsible for carrying out the instructions of a computer program. It's often referred to as the brain of the computer because it performs all basic arithmetic, logical, and input/output operations that make the system function.
What is the difference between a processor and a microprocessor?
-A processor is a general term for the central processing unit (CPU), while a microprocessor specifically refers to a CPU that has been integrated into a single chip. Since the 1970s, most CPUs have been constructed as microprocessors.
What does the term '64-bit quad-core' mean when referring to a CPU?
-'64-bit' refers to the width of the CPU’s data bus, meaning it can process 64 bits of data at a time. 'Quad-core' means the CPU has four processing cores, allowing it to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, making it more efficient at multitasking and processing complex tasks.
How does the CPU perform calculations and execute commands?
-The CPU performs calculations using an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which handles arithmetic and logical operations. It executes commands by interpreting instructions through the control unit (CU), which activates other parts of the computer and directs the ALU to perform the necessary calculations.
Why is the CPU critical for tasks like 3D animation or video editing?
-Tasks like 3D animation or video editing require the computer to process large amounts of data and perform complex calculations quickly. The CPU's speed and processing power determine how efficiently these tasks can be executed, as they demand more from the processor.
What role does cache memory play in a CPU?
-Cache memory serves as high-speed memory in the CPU. It stores frequently used instructions, allowing the CPU to quickly access them and reduce the time it takes to retrieve data from the main memory.
Why does a CPU need a cooling system, and how is it implemented?
-CPUs generate significant heat during operation, which can damage the hardware if not properly managed. To prevent overheating, a CPU is equipped with a cooling system, such as a heatsink and/or a fan, that helps dissipate heat.
What are transistors, and how do they relate to CPU operations?
-Transistors are microscopic switches inside a CPU that control the flow of electricity. They store binary information (1 or 0) and are the building blocks of digital logic in computers. The CPU uses these transistors to perform calculations by switching the signals on or off.
How many transistors can a modern CPU contain, and why is this important?
-Modern CPUs can contain several hundred million to over a billion transistors within a square inch. The high number of transistors enables the CPU to perform a vast number of calculations simultaneously, which increases processing speed and efficiency.
What technological advancements have driven improvements in CPU performance over time?
-The demand for faster processing speeds, especially for complex tasks like video editing, gaming, and 3D rendering, has driven advancements in CPU technology. This includes increasing the number of cores, enhancing clock speeds, and integrating more transistors onto smaller chips.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)