CPU and Its Components|| Components of MIcroprocessor
Summary
TLDRThis lesson explains the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and its key components, comparing it to the brain of a computer. It covers how the CPU processes information through its Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, registers, cache memory, and internal buses. The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations, while the Control Unit manages the execution of instructions. Additionally, the video discusses the importance of registers for temporary data storage and the role of cache memory in speeding up data access. Finally, the lesson highlights how buses connect the CPU to other system components.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The CPU, also known as the brain of the computer, is the main unit responsible for controlling and performing all computing tasks.
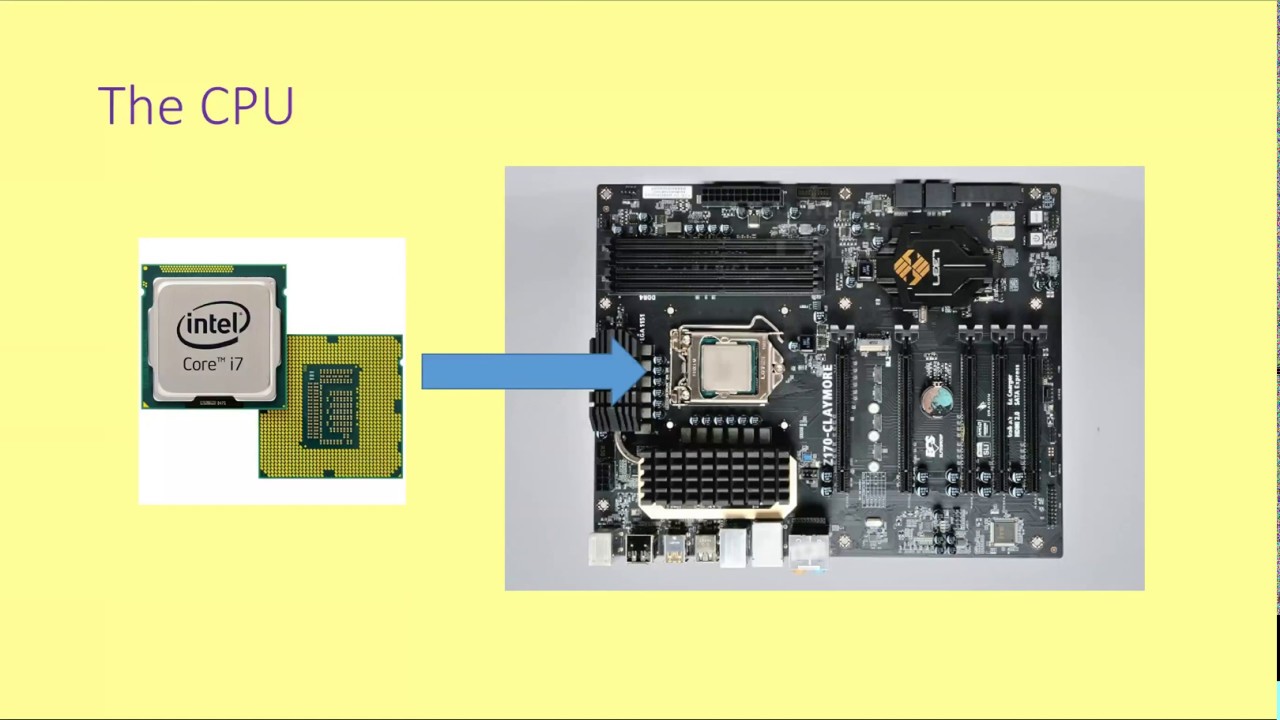
- 💻 Every computer contains a microprocessor, and without it, the computer cannot function.
- ⚡ The CPU processes large amounts of data at high speeds and can work for long hours without errors.
- 📍 The CPU is located on the motherboard and is highlighted by its red square in diagrams.
- ⚙️ The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) inside the CPU performs arithmetic and logical operations such as addition, subtraction, and comparisons.
- 🔢 Registers within the CPU are high-speed temporary storage units that hold data and instructions during processing.
- 🕹️ The Control Unit manages and coordinates all activities of the computer, executing instructions from programs in proper order.
- 📊 Cache memory is a small, fast, and expensive type of memory within the CPU that stores frequently accessed data.
- 🔌 Internal buses inside the CPU carry data and instructions between components, including address, data, and control buses.
- 📡 External buses extend outside the CPU to connect and communicate with other devices and components of the computer.
Q & A
What is the central processing unit (CPU) often compared to in the human body?
-The CPU is often compared to the brain in the human body, as it controls the computer system in a similar way the brain controls the body.
Why is the CPU considered the most important part of a computer?
-The CPU is considered the most important part because it performs all of the computer's computing and decision-making tasks, without which the computer cannot function.
What are the main components of the central processing unit?
-The main components of the CPU are the arithmetic and logic unit (ALU), control unit, registers, cache memory, and internal buses.
What are the functions of the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) in the CPU?
-The ALU performs arithmetic operations (like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) and logical operations (such as AND, OR, NOT) on data based on instructions from the control unit.
How does the ALU perform an addition operation, for example, adding 15 and 45?
-First, the number 15 is stored in the accumulator register, and 45 is stored in the data register. The control unit then sends a command to add the two numbers, and the ALU adds them. The result, 60, is stored back in the accumulator register.
What role does the control unit play in the CPU?
-The control unit controls and coordinates all the activities of the computer system. It communicates with the ALU, input/output devices, and memory to execute instructions in the correct order.
What are some common types of registers in the CPU, and what do they do?
-Common types of CPU registers include the instruction register, accumulator register, data register, program counter register, and memory address register. These registers store data, instructions, or memory addresses temporarily during processing.
What is cache memory, and why is it important in the CPU?
-Cache memory is a high-speed memory inside the CPU that stores frequently accessed data, allowing the CPU to access it faster than from the main memory (RAM). It helps speed up processing but is expensive and smaller in size.
What are internal buses in the CPU, and what are their types?
-Internal buses are groups of parallel wires that carry data within the CPU. The three types of internal buses are the address bus, data bus, and control bus.
How do internal and external buses in the CPU differ?
-Internal buses are used to transfer data within the CPU, while external buses extend outside the CPU to communicate with other components connected to the computer.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

2. Arsitektur Komputer Struktur CPU

CPU - Organisasi dan Arsitektur Komputer
GCSE Computer Architecture 2 - The CPU

IGCSE Computer Science 2023-25 - Topic 3: HARDWARE (1) - COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE - Von Neumann & CPU

PROCESSOR | Cara Kerja Processor Komputer - Di jamin 100% paham

The Central Processing Unit | (components and functions)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)