Meiosis 1 | Crossing over and Phase identification
Summary
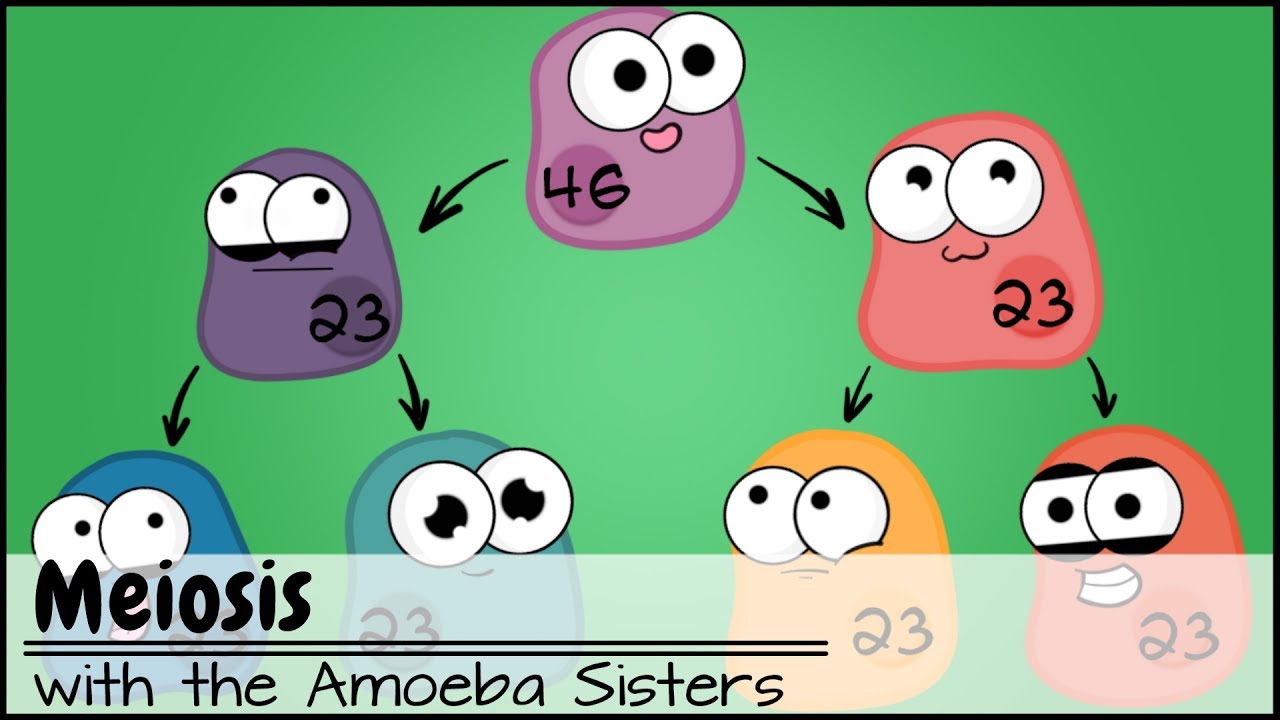
TLDRThis video script delves into meiosis, contrasting it with mitosis. Meiosis, which occurs in two phases, results in four non-identical haploid cells, each with half the genetic material of the original. Key processes include DNA replication in interphase, crossing over for genetic variation in prophase, random arrangement in metaphase, separation of chromosomes in anaphase, and cytokinesis in telophase. The script emphasizes the importance of these stages in creating genetic diversity.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Meiosis is a type of cell division that differs from mitosis by producing non-identical, haploid cells instead of identical, diploid cells.
- 🔄 Both mitosis and meiosis involve cell division, but meiosis occurs in two phases (meiosis I and II), while mitosis is a single event.
- 🧬 Meiosis results in four non-identical cells, each with half the number of chromosomes of the original cell, contributing to genetic diversity.
- 🕒 Interphase is the phase where the cell spends most of its time and is crucial for DNA replication and ensuring the correct chromosome number.
- 🔬 During prophase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up (synapsis) and may exchange genetic material (crossing over), increasing genetic variation.
- 🧭 Metaphase I is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes at the cell's equator, introducing further genetic variation through random arrangement.
- 📏 Anaphase I involves the separation of homologous chromosomes, effectively halving the chromosome number in the cell.
- 📚 Telophase I concludes with the separation of cytoplasm and the formation of two distinct, non-identical cells via cytokinesis.
- 🧬 Crossing over during prophase I results in recombinant chromatids, which are new combinations of genetic material from the original chromosomes.
- 🌱 The terms diploid and haploid describe cells with full and half sets of chromosomes, respectively, with meiosis producing haploid cells from diploid ones.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between mitosis and meiosis?
-Mitosis results in two identical cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the original cell, while meiosis results in four non-identical cells, each with half the number of chromosomes, making them haploid.
What is the main purpose of interphase in the cell cycle?
-Interphase is the phase where the cell spends the majority of its time and is primarily dedicated to DNA replication, ensuring each chromosome is duplicated into sister chromatids.
How does the process of meiosis contribute to genetic variation?
-Meiosis contributes to genetic variation through crossing over during prophase I, where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, and through random assortment during metaphase I, where chromosomes align at the equator in a random order.
What structures are essential for identifying a cell in interphase?
-In interphase, essential structures for identification include the chromatin network, which appears as a long spaghetti-like structure, and the presence of a visible nuclear membrane.
What is the significance of the term 'bivalent' in meiosis?
-A bivalent refers to a pair of homologous chromosomes that have come together and are touching each other during crossing over in prophase I, exchanging genetic information.
What is the role of chiasmata in meiosis?
-Chiasmata are the points where homologous chromosomes are connected during crossing over in prophase I, and they are the sites where genetic material is exchanged.
How does metaphase I in meiosis differ from metaphase in mitosis?
-In metaphase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes align at the equator in a random arrangement, which introduces genetic variation. In mitosis, chromosomes align at the equator, but they do not involve homologous pairs.
What is the purpose of anaphase I in meiosis?
-Anaphase I in meiosis separates the homologous chromosomes (bivalents), reducing the chromosome number by half and ensuring each daughter cell receives a unique set of chromosomes.
What is cytokinesis and when does it occur in the cell cycle?
-Cytokinesis is the process by which the cytoplasm of a cell is divided, forming two separate cells. It occurs at the end of telophase I in meiosis.
What is the term for the process where homologous chromosomes move towards each other before crossing over?
-The process where homologous chromosomes move towards each other before crossing over is called synapsis.
How can you identify a cell in telophase I of meiosis?
-A cell in telophase I of meiosis can be identified by the presence of cell cleavage, the reformation of the nuclear membrane, and the disappearance of spindle fibers.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)