Mitosis vs Meiosis
Summary
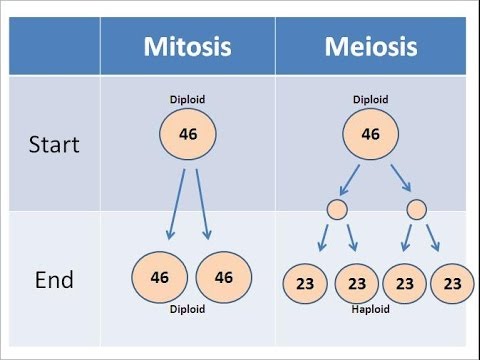
TLDRThis video script delves into the differences between mitosis and meiosis, two vital cell division processes. Mitosis, occurring in somatic cells throughout the body, results in two genetically identical diploid daughter cells. In contrast, meiosis, exclusive to the reproductive cells in gonads, undergoes two stages—meiosis I and II—yielding four genetically unique haploid gametes. While mitosis maintains genetic consistency, meiosis introduces genetic diversity, essential for sexual reproduction.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Mitosis and meiosis are two types of cell division with distinct functions.
- 📍 Mitosis occurs in somatic cells throughout the body, whereas meiosis is specific to reproductive cells in gonads.
- 🌟 Both processes begin with a diploid cell, containing two sets of chromosomes.
- 📈 Mitosis involves a single cell division, while meiosis includes two stages: meiosis I and meiosis II.
- 🤖 Mitosis results in two genetically identical diploid daughter cells.
- 🌈 Meiosis produces four haploid gametes, each genetically unique.
- 🔄 Mitotic daughter cells are clones of the parent cell and each other, maintaining genetic stability.
- 🌀 Meiosis introduces genetic diversity through the formation of distinct gametes.
- 🧬 The genetic variation in gametes from meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction and evolution.
- 🎵 The script includes music, suggesting a multimedia presentation or educational video format.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between mitosis and meiosis?
-Mitosis occurs in somatic cells all over the body, while meiosis occurs only in the reproductive cells of the gonads to form gametes.
What is the starting cell type for both mitosis and meiosis?
-The original cell in both mitosis and meiosis is diploid.
How many stages of cell division are there in meiosis?
-Meiosis consists of two stages of cell division called meiosis 1 and meiosis 2.
What is the outcome of mitosis in terms of cell number and type?
-Mitosis results in two diploid daughter cells.
How many daughter cells are produced by meiosis, and what is their genetic status?
-Meiosis results in four haploid daughter cells, which are gametes.
Are the daughter cells resulting from mitosis genetically identical?
-Yes, the two daughter cells resulting from mitosis are genetic duplicates of each other and the original cell.
How is the genetic variation in gametes produced through meiosis?
-Each haploid gamete resulting from meiosis is genetically different from every other gamete ever formed, introducing genetic variation.
Why is meiosis important for sexual reproduction?
-Meiosis is important for sexual reproduction because it produces genetically diverse gametes, which when combined during fertilization, create offspring with a unique genetic makeup.
What is the significance of having haploid gametes in sexual reproduction?
-Having haploid gametes ensures that when they fuse during fertilization, the resulting zygote is diploid, maintaining the correct chromosome number across generations.
Can you explain the role of meiosis in maintaining genetic diversity?
-Meiosis plays a crucial role in maintaining genetic diversity by creating gametes with different combinations of genetic material through processes like crossing over and independent assortment.
What is the main function of mitosis in an organism?
-The main function of mitosis in an organism is to enable growth, repair, and asexual reproduction by producing identical diploid cells.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)