The Mesolithic Age
Summary
TLDRThe Mesolithic Period in ancient Egypt marked a pivotal transition from the Paleolithic to the Neolithic eras, spanning from 10,000 to 5,000 B.C. As the Ice Age ended, climate change led to the expansion of the Sahara, forcing human societies to adapt to dwindling resources. Mesolithic Egyptians shifted to fishing, gathering, and hunting smaller game, leading to innovations in toolmaking and subsistence strategies. This era laid the groundwork for the Neolithic revolution, where advancements in technology, settlement patterns, and cultural expressions paved the way for the development of agriculture and complex societies.
Takeaways
- 🏺 The Mesolithic Period in Ancient Egypt was a critical transitional phase between the Paleolithic and Neolithic eras.
- 🌍 It spanned from approximately 10,000 to 5,000 B.C., witnessing significant cultural and societal changes.
- 🌳 The end of the last Ice Age led to increased aridity and the expansion of the Sahara Desert, affecting resource availability.
- 🐘 Large game and wild plant species became scarce, necessitating a shift in human subsistence strategies.
- 🏜️ Human settlements during the Mesolithic period were concentrated in areas like river valleys, oases, and coastal regions due to environmental pressures.
- 🎣 Innovations in toolmaking and an increased reliance on fishing and gathering of smaller resources were key adaptations.
- 🛠️ The development of new fishing technologies such as hooks, harpoons, and nets from organic materials improved subsistence strategies.
- 🌱 The environmental changes during the Mesolithic period forced humans to adapt their hunting, gathering, and fishing practices.
- 🏘️ The Mesolithic period laid the groundwork for the Neolithic Revolution in Egypt, with changes in subsistence strategies and cultural expressions.
- 🌟 The Mesolithic Egyptians' adaptations to their environment set the stage for the emergence of settled agriculture and complex societies.
Q & A
What is the Mesolithic Period in Ancient Egypt?
-The Mesolithic Period in Ancient Egypt represents a crucial phase of cultural transition between the Paleolithic and Neolithic eras, spanning roughly from 10,000 to 5,000 B.C.
What were the significant changes witnessed during the Mesolithic Period in Egypt?
-The era witnessed significant changes in human settlement patterns, subsistence strategies, technological advancements, and social structures.
How did the end of the last Ice Age affect Egypt?
-The climate in the region underwent a gradual shift towards increased aridity, resulting in the expansion of the Sahara Desert and impacting the availability and distribution of natural resources.
How did the environmental changes affect the resources relied upon by Paleolithic hunter-gatherer societies?
-The resources became increasingly scarce, with large game like mammoths decreasing in numbers or migrating, and the abundance of wild plant species and water sources diminishing.
What were the impacts of the Sahara Desert expansion on human settlement patterns during the Mesolithic period?
-Human groups began to concentrate in areas that still provided access to vital resources, such as river valleys, oases, and coastal regions.
How did the environmental changes necessitate adaptations in hunting, gathering, and fishing practices?
-Mesolithic populations had to develop new strategies to exploit the remaining resources and make efficient use of the limited available food sources, leading to innovations in toolmaking.
What were the advancements in fishing technology during the Mesolithic period?
-Mesolithic Egyptians expanded their fishing activities, utilizing hooks, harpoons, and nets made from organic materials such as bone, wood, and plant fibers.
How did the Mesolithic period act as a transitional phase for Egypt?
-The changes in subsistence strategies, technological advancements, and cultural expressions laid the foundation for the shift towards settled agriculture and the emergence of complex societies.
What role did fishing play in the subsistence strategies of Mesolithic communities?
-Fishing activities were expanded, utilizing advanced technology, which facilitated the exploitation of aquatic resources and enhanced their subsistence strategies.
How did the adaptations during the Mesolithic period set the stage for future cultural developments?
-These adaptations exemplify the dynamic relationship between human societies and their environment, paving the way for the Neolithic revolution in Egypt.
What was the impact of the arid landscapes on the subsistence strategies of Mesolithic communities?
-The arid landscapes forced human communities to adapt their subsistence strategies, leading to an increased reliance on fishing and the gathering of smaller game, edible plants, and shellfish.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Stone Age | Prehistoric age | Paleolithic | Mesolithic | Neolithic | Stone Age Humans

The Three Stone Age Eras

A Complete Timeline of The Mesolithic Period | Early Humans Documentary
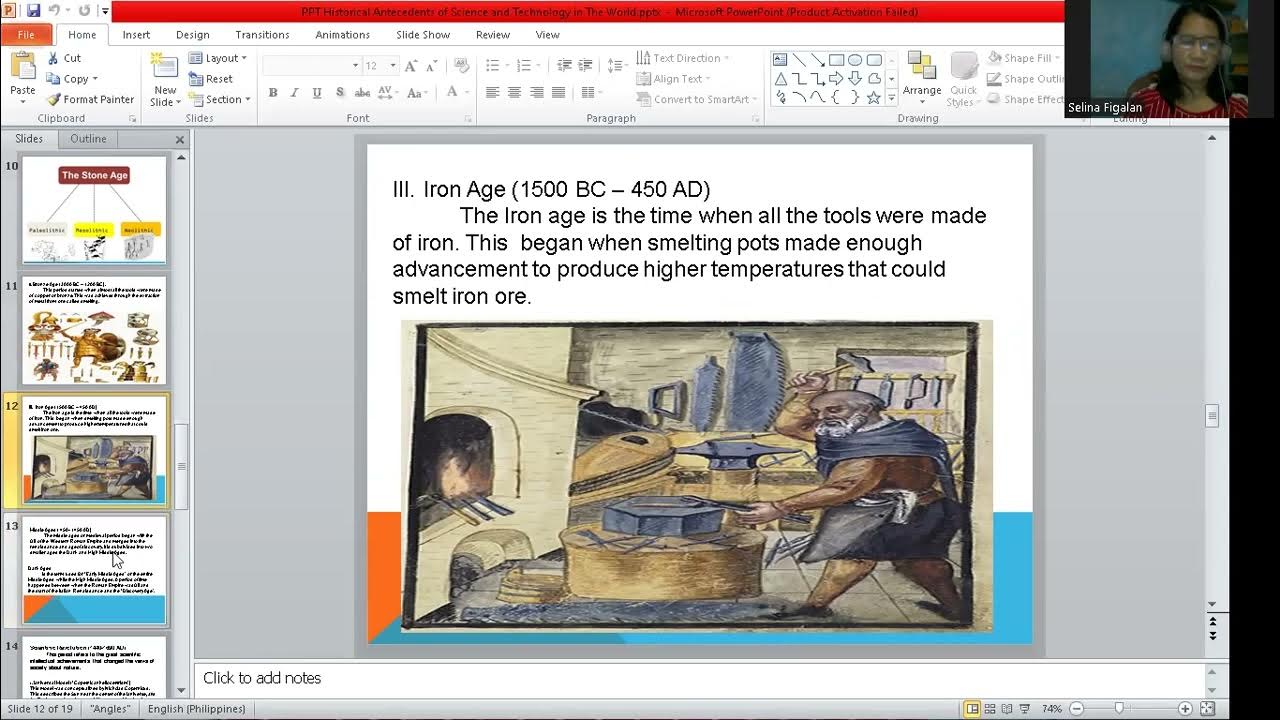
Historical Antecedents of Science and Technology in the World

Science, Technology and Society - In the World: Ancient, Middle and Modern Ages

A Pré-História - Paleolítico, Neolítico, Mesolítico e Idade dos Metais
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)