B2 Reflection Solutions
Summary
TLDRThis video script outlines a lesson on data analysis, focusing on creating frequency tables and histograms. The instructor demonstrates how to determine interval width by dividing the range of data by the number of intervals and rounding up to the nearest whole number. The script also covers the creation of a stem plot for ordered data and discusses the importance of starting intervals at logical points. Further topics include identifying different types of samples, such as voluntary response and stratified samples, and the process of taking a random sample from a larger population.
Takeaways
- 📊 The lesson focuses on frequency tables and histograms for data analysis.
- 📋 The data in the example is quantitative, specifically tracking total absences over 30 days.
- ✂️ Interval width is calculated as the range divided by the number of intervals, rounded up to the nearest integer.
- 🔢 The range of the data is calculated as the maximum value minus the minimum value (49 - 3 = 46).
- ➗ The interval width is determined to be 10 (range of 46 divided by 5 intervals, rounded up).
- ⏳ The first interval starts at 0, with subsequent intervals using a width of 10.
- 📐 The histogram and stem plot are used to visualize the data and identify patterns.
- 💡 A voluntary response sample involves participants who choose to respond, rather than being randomly selected.
- 🔄 A random sample is drawn from a population by assigning numbers and selecting based on a table of random digits.
- 🔀 Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into groups and taking samples from each group.
Q & A
What is the first step the speaker takes when analyzing the data?
-The first step the speaker takes is to copy the data and paste it into a statistical tool for analysis.
What type of data is being analyzed in the script?
-The data being analyzed is quantitative data, specifically total absences.
What is a stem plot and how does it help in data analysis?
-A stem plot is a graphical way to display data by sorting it into categories and displaying the data in order, which helps in quickly visualizing the distribution of the data.
What is the purpose of determining the interval width in creating a histogram?
-The purpose of determining the interval width is to decide the size of each bar in the histogram, which helps in categorizing the data into meaningful groups for analysis.
How is the interval width calculated according to the script?
-The interval width is calculated by dividing the range (maximum value minus minimum value) by the number of intervals and then rounding up to the nearest whole number.
What is the range of the data in the script?
-The range of the data is 46, calculated by subtracting the minimum value (3) from the maximum value (49).
Why does the speaker round the interval width up to 10 instead of using 9.2?
-The speaker rounds the interval width up to 10 because interval widths should not be decimals, and even if it was exactly 9, it would not be sufficient for the data set.
What is the best place to start the first interval according to the script?
-The best place to start the first interval is at zero, which is a more natural place to start and aligns with the minimum value of the data.
How many data points would be in the first bar of the histogram with a start at zero and a width of 10?
-There would be three data points in the first bar of the histogram.
What is a voluntary response sample as mentioned in the script?
-A voluntary response sample is a type of sample where individuals self-select to participate in a survey or poll, as opposed to being randomly selected.
What is a stratified sample as discussed in the script?
-A stratified sample is a type of sample where the population is divided into subgroups or strata, and random samples are taken from each subgroup.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
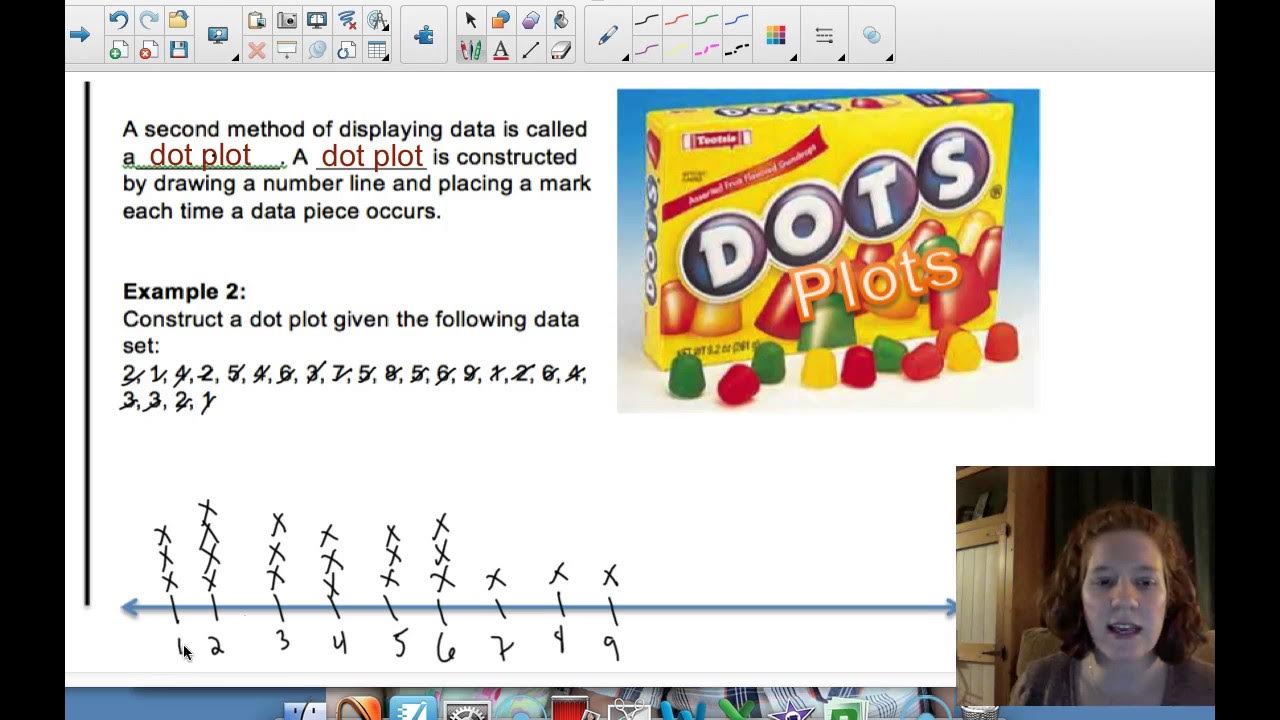
6 - 3 Part 1 Frequency Tables, Dot Plots, HIstograms

Statistik : Penyajian Data - Part 5
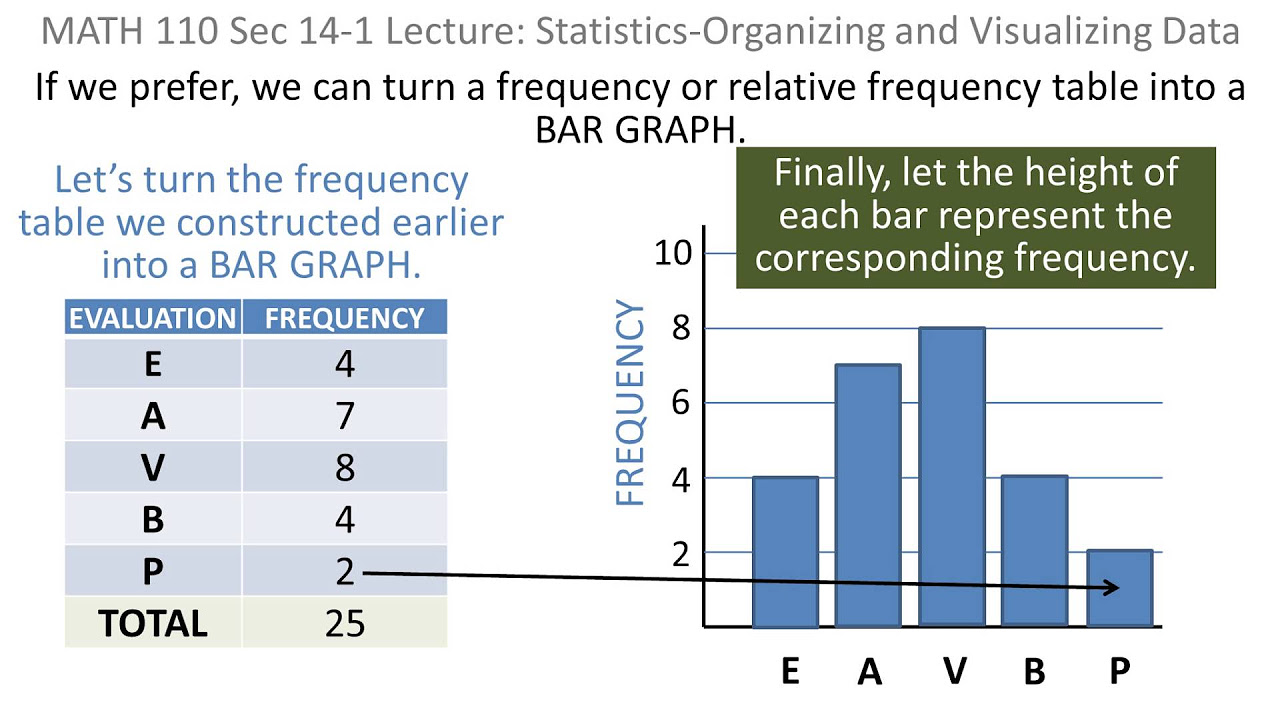
Statistics: 01 Organizing and Visaulizing Data

4.2 | DATA COLLECTION & PRESENTATION | DATA MANAGEMENT | MATHEMATICS IN THE MODERN WORLD | ALOPOGS

Statistika - Membaca dan Menyajikan data, Poligon Histogram Ogive

KONSEP DASAR STATISTIKA DAN DISTRIBUSI FREKUENSI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)