Kurikulum Merdeka Matematika Kelas 7 Bab 4 Bentuk Aljabar
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script covers algebraic concepts for 7th graders, focusing on algebraic terms like coefficients, variables, and constants. It explains how to simplify expressions by combining like terms and demonstrates addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of algebraic expressions. The script also clarifies the rules for multiplying and dividing terms with variables, including handling of exponents and expressions within parentheses. The aim is to make algebra more accessible and engaging for students.
Takeaways
- 🔢 Algebra involves understanding terms like coefficients, variables, and constants.
- 📐 A term in algebra is a mathematical expression separated by addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.
- 🔄 Coefficients are the numbers preceding variables, while constants are standalone numbers.
- 🧩 Like terms in algebra can be combined by adding or subtracting their coefficients.
- ➕ To add algebraic expressions, combine like terms by adding their coefficients.
- ➖ When subtracting, only like terms with the same variables can be simplified.
- 🔄 Multiplication in algebra involves multiplying coefficients and variables separately.
- 📚 When multiplying a variable by a number, the result is a new term with the variable's exponent increased.
- 📉 Division in algebra requires dividing both the coefficients and the variables.
- 📘 Exponents in division are reduced by subtracting the exponents of like bases.
- 👉 Parentheses indicate that the expression inside must be multiplied by the expression outside.
Q & A
What are the basic components of an algebraic expression?
-The basic components of an algebraic expression are terms, coefficients, variables, and constants. Terms are separated by addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Coefficients are the numbers preceding variables, variables are represented by letters, and constants are numbers not followed by letters.
How do you combine like terms in algebra?
-Like terms are terms that have the same variables raised to the same power. To combine them, you add or subtract their coefficients while keeping the variable part unchanged.
What happens when you try to add terms with different variables?
-Terms with different variables cannot be combined through addition or subtraction because they are not like terms.
Can you give an example of how to add algebraic expressions?
-Yes, for example, to add 2A + 3A, you add the coefficients (2 + 3) to get 5A.
How do you subtract algebraic expressions with the same variable?
-Subtraction of algebraic expressions with the same variable involves subtracting their coefficients. For instance, 5A - 3A results in 2A.
What is the rule for multiplying algebraic expressions?
-When multiplying algebraic expressions, you multiply the coefficients and the variables separately. If a variable is multiplied by another variable of the same kind, you add their exponents.
What does it mean when there is no number written before a variable in an algebraic expression?
-If there is no number written before a variable, it means the coefficient is 1. For example, in the expression 7A - A, the second term is equivalent to 1A, which simplifies to 6A.
How do you handle parentheses in algebraic expressions?
-Parentheses indicate that the expression inside them should be treated as a single entity. When multiplying, every term inside the parentheses is multiplied by the term outside.
Can you explain the process of dividing algebraic expressions?
-Division of algebraic expressions involves dividing the coefficients and the variables separately. If you divide a variable by itself, the result is 1, and any exponents are subtracted from one another.
What is the significance of exponents in algebraic division?
-When dividing expressions with the same base, you subtract the exponents. For example, if you divide a^5 by a^3, the result is a^2.
How do you simplify an expression like 3(a + b)?
-To simplify 3(a + b), you distribute the 3 to both a and b, resulting in 3a + 3b.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Aljabar | Matematika Kelas 7 Kurikulum Merdeka - Lengkap

Materi Aljabar Kelas 7
PT3 KSSM Mathematics Form 1 (Algebraic Expressions) Chapter 5 Complete Revision

Hlm 124 - 132 Part 1 BENTUK ALJABAR MATEMATIKA SMP KELAS 7 KURIKULUM MERDEKA

PERKALIAN ALJABAR (ALJABAR PART #2)
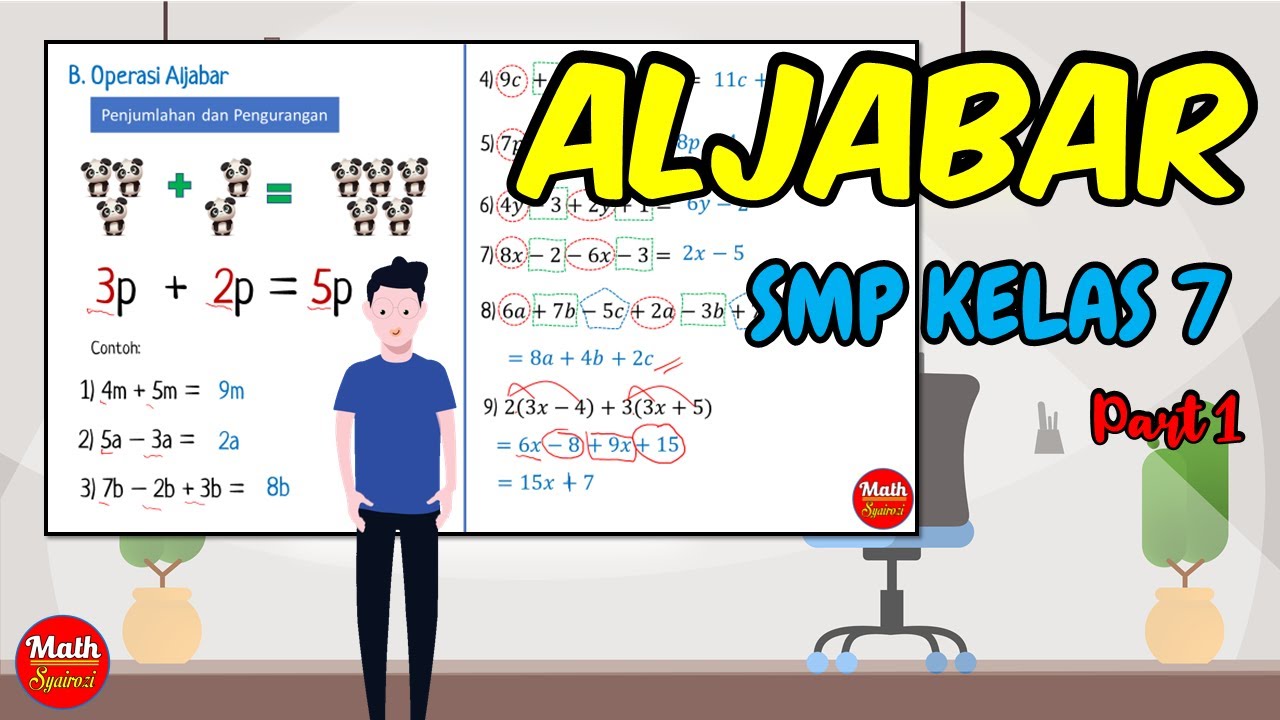
ALJABAR PART 1 (PENJUMLAHAN DAN PENGURANGAN)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)