Tejidos Básicos del Cuerpo Humano | Tipos y Clasificación | Histología
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Andrés Gálvez explains the fundamental types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. He describes their functions and characteristics, such as the protective role of epithelial tissue, the supportive nature of connective tissue, the movement function of muscle tissue, and the information processing of nervous tissue. The video also touches on tissue classification, cell organization, and embryological development, offering a comprehensive overview of these essential biological components.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video introduces the basic types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective (conjunctive), muscle, and nervous.
- 🔍 Epithelial tissue covers both external surfaces like the skin and internal surfaces such as the lining of the digestive tract, and it also forms glands like sweat and salivary glands.
- 🤔 Connective tissue acts as a 'filler' in spaces where other tissues are not present, like underneath the epithelial layer of the skin.
- 💪 Muscle tissue is responsible for movement and is easily identifiable with structures like the biceps and quadriceps.
- 🧠 Nervous tissue is involved in receiving and transmitting information both internally and externally, coordinating responses based on this information.
- 👀 The video uses a cross-section of the skin to illustrate the presence of all four basic types of tissues.
- 📖 Epithelial tissue is classified by the shape of its cells and the number of cell layers, such as simple or stratified, and can be squamous, cubic, or columnar.
- 🧬 Connective tissue is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix, which includes a ground substance and fibers like collagen and elastin.
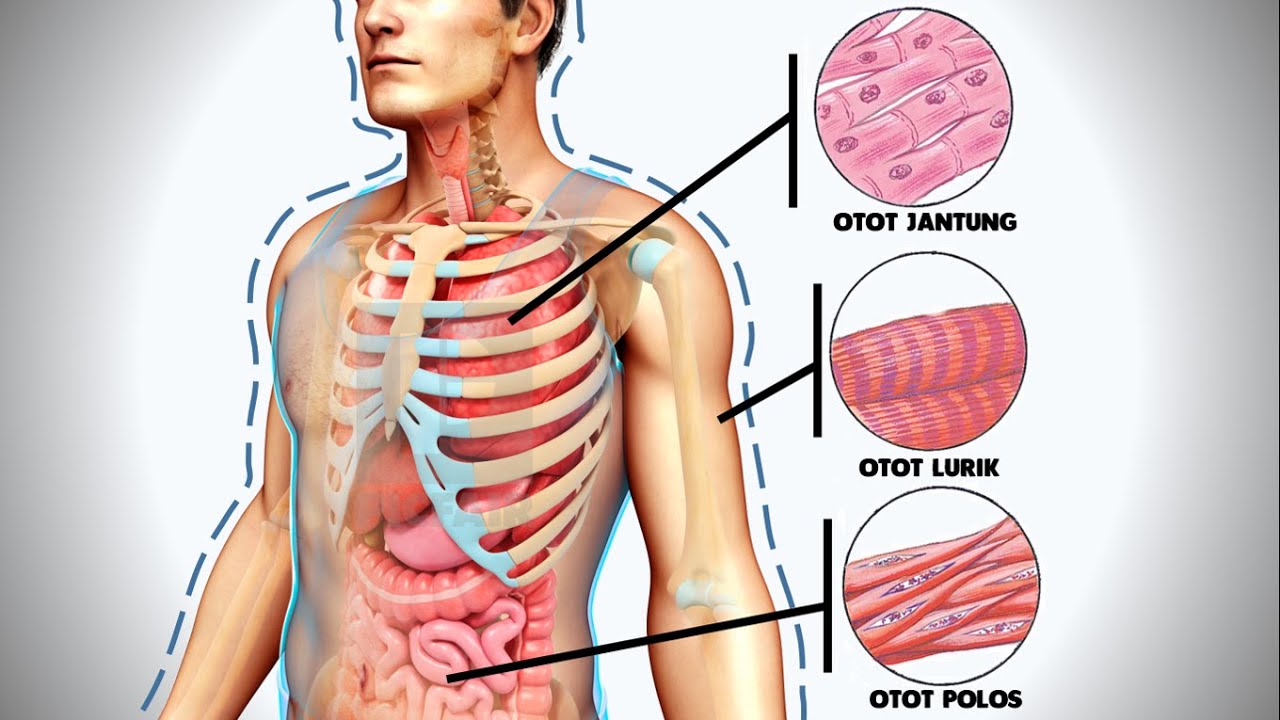
- 🌱 Muscle tissue is made up of contractile cells containing proteins that enable movement, and it is classified as smooth or striated based on the presence of striations.
- ⚡ Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and supporting cells known as glial cells, with neurons being responsible for receiving and transmitting nerve impulses.
- 🤰 The embryological development of tissues is briefly touched upon, explaining how the germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm) give rise to different types of tissues.
Q & A
What are the four basic types of tissues in the human body?
-The four basic types of tissues in the human body are epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue.
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue primarily functions as a protective barrier and covers surfaces, both externally like the skin, and internally like the lining of the digestive tract. It also forms glands such as sweat and salivary glands.
How is connective tissue different from other tissues?
-Connective tissue is different as it fills spaces between other tissues, acting as a 'filler'. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix, which includes substances like the ground substance and fibers such as collagen and elastin.
What role does muscle tissue play in the body?
-Muscle tissue is responsible for movement. It is made up of contractile cells that contain proteins which give them the ability to contract and relax.
What is the main component of nervous tissue?
-The main components of nervous tissue are neurons, which are specialized cells responsible for receiving and transmitting information throughout the body.
Can you describe the structure of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue is composed of tightly packed cells that form a layered pattern. These cells are connected by junctions and are supported by a basal lamina, which helps them adhere to the underlying connective tissue.
How is epithelial tissue classified?
-Epithelial tissue can be classified based on the shape of its cells and the number of cell layers. Cell shapes can be squamous, cuboidal, or columnar. The tissue can be simple, with a single layer, or stratified, with multiple layers.
What is the function of the basal lamina in epithelial tissue?
-The basal lamina in epithelial tissue serves as a support structure that allows the tissue to adhere to the underlying connective tissue, preventing it from separating like a sheet of plastic.
What are the specialized types of connective tissue mentioned in the script?
-Specialized types of connective tissue include blood, cartilage, and bone. These tissues are composed of cells and an extracellular matrix, with bone's matrix being mineralized, giving it its rigidity.
How is muscle tissue classified?
-Muscle tissue is classified as either smooth (without striations) or striated (with striations). Striated muscle tissue is further divided into skeletal muscle, which is voluntary and attached to bones, and cardiac muscle, which is involuntary and found in the heart.
What is the role of the neuron's axon and dendrites?
-The axon of a neuron is responsible for transmitting nerve impulses, while dendrites receive these impulses. Together, they facilitate the flow of information within the nervous system.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

MATERI MARTIKULASI | JARINGAN TUBUH MANUSIA

what are tissues in human body, what are tissues made of, what are tissues class 9, Human tissues,

Tissues of Human Body | Animation | Simple Explanation
Media Pembelajaran Jaringan Hewan - Kelas Daring Biologi SMA Kelas XI

Animal Tissues

Clase 1 aCelula e introducción a tejidos
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)