Probability Concepts for Data Analysis and Data Science | Statistics for Data Science
Summary
TLDRThis script discusses the concept of probability, using examples like coin tosses and dice rolls to explain the sample space and events. It defines probability as the likelihood of an event occurring, ranging from 0% to 100%. The script introduces basic probability functions and explores complementary events, emphasizing how to calculate the probability of an event by dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total outcomes. It also touches on different types of events, such as dependent and independent events.
Takeaways
- 📝 The concept of probability is discussed, ranging between zero and one, with zero meaning an impossible event and one indicating a certain event.
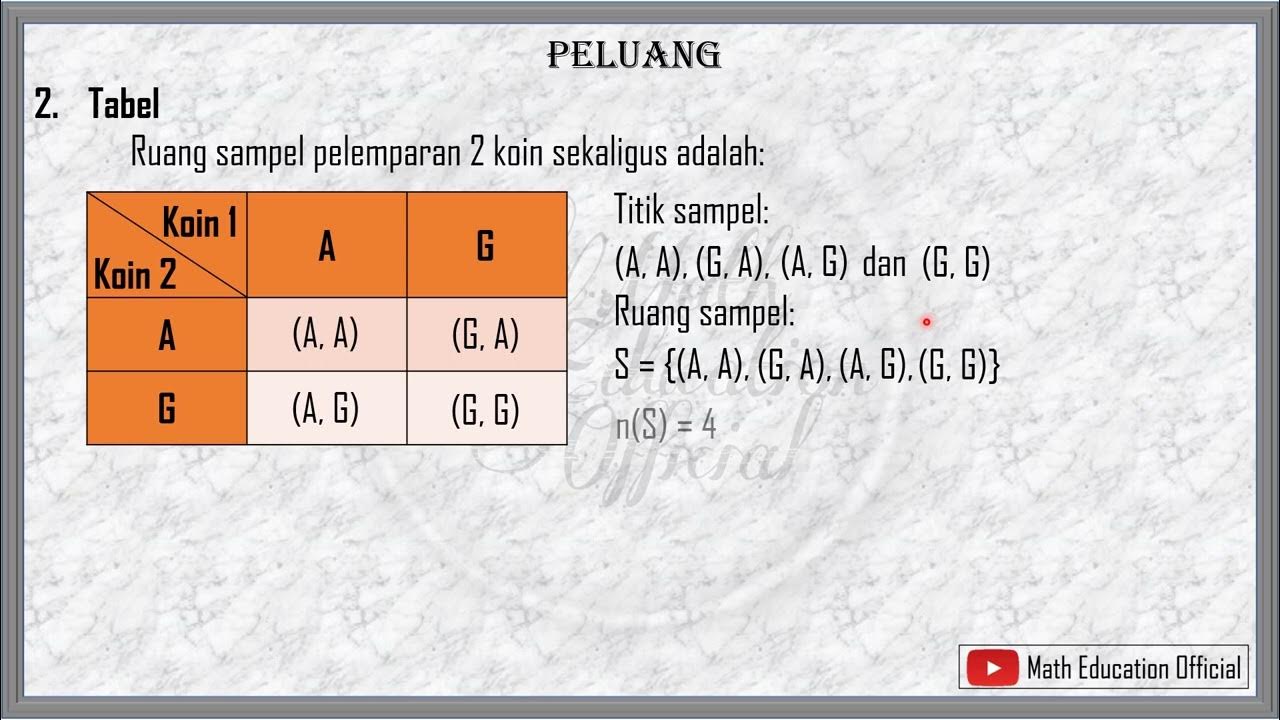
- 📝 The term 'sample space' is introduced, referring to the set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment.
- 📝 Random experiments are processes where outcomes cannot be predicted with certainty.
- 📝 Examples of random experiments include tossing a coin, rolling a die, and the outcomes are part of the sample space.
- 📝 The probability function is explained, which assigns a likelihood (chance) to each event within the sample space.
- 📝 The formula for calculating probability is presented: Number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of outcomes.
- 📝 The concept of complementary events is introduced, which consists of all outcomes not in a specific event.
- 📝 The formula for complementary events is explained, which is one minus the probability of the event.
- 📝 Different types of events are mentioned, such as joint events, dependent events, and independent events.
- 📝 The video script provides examples to illustrate the calculation of probability, such as getting a head when tossing a coin.
Q & A
What does the term 'probability' refer to?
-Probability refers to the measure of the likelihood that a particular event will occur, expressed as a number between 0 and 1 (or as a percentage between 0% and 100%).
How is probability calculated between zero and one?
-Probability is calculated as the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes.
What is meant by 'sample space' in probability?
-The sample space is the set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment.
What is a random experiment?
-A random experiment is a process in which the outcome cannot be predicted.
Can you provide an example of a sample space for tossing a coin?
-When tossing a coin, the sample space consists of two outcomes: heads (H) and tails (T).
What is the sample space when rolling a die?
-The sample space for rolling a die is the set of all possible outcomes, which are the numbers 1 through 6.
What is an event in probability?
-An event is a subset of the sample space that consists of specific outcomes.
How is the probability of getting an even number when rolling a die calculated?
-The probability of getting an even number when rolling a die is calculated by dividing the number of favorable outcomes (2, 4, 6) by the total number of outcomes (1 through 6), which gives a probability of 3/6 or 1/2.
What is meant by the complement of an event?
-The complement of an event is the set of all outcomes in the sample space that are not included in the event.
How do you calculate the complement of getting an even number when rolling a die?
-The complement of getting an even number (which would be getting an odd number) is calculated by subtracting the probability of getting an even number from 1. So, if the probability of getting an even number is 1/2, the complement would be 1 - 1/2 = 1/2.
What are the different types of events discussed in the script?
-The script discusses different types of events such as disjoint events, joint events, dependent events, and independent events.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)