Estados de la Materia [CARACTERÍSTICAS]
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script explains the concept of states of matter, focusing on the solid, liquid, and gaseous states. It describes how solids have a fixed shape and volume due to tightly bound particles, liquids lack a fixed shape but maintain a constant volume as they flow and take the shape of their containers, and gases have neither a fixed shape nor volume, being highly compressible. The script hints at the kinetic molecular theory for further explanation, suggesting it will be covered in a future video.
Takeaways
- 🔋 A battery is defined by its mass and volume.
- 🌐 Mass is the measure of the amount of matter in a body.
- 📦 Volume is the space that matter occupies.
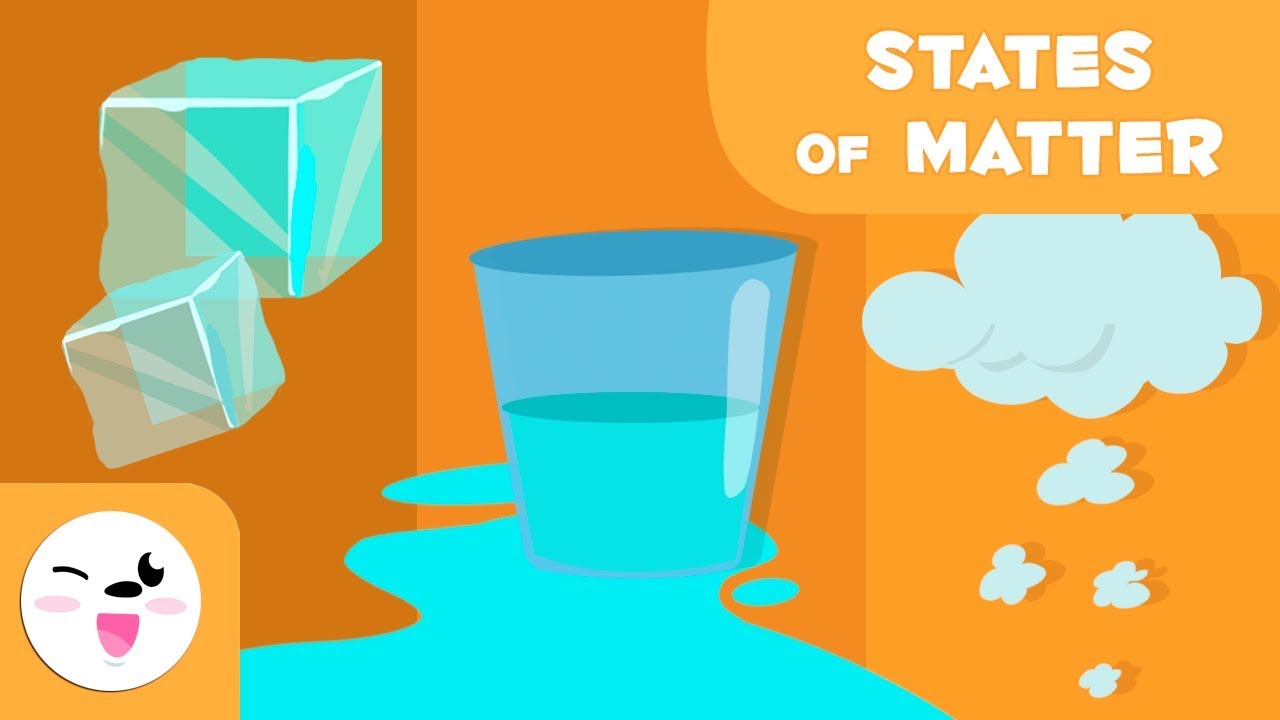
- 🔲 There are three physical states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
- 🏔 Solids have a definite shape and volume; their particles are tightly bound and cannot be compressed.
- 💧 Liquids have a definite volume but no fixed shape; they take the shape of their container and can flow due to weaker intermolecular forces.
- 🌀 Gases have neither a fixed shape nor volume; their particles move freely and are highly compressible.
- 🔄 The behavior of liquids and gases is due to the balance of attractive and repulsive forces between particles.
- 🔬 The kinetic molecular theory can explain the characteristics of different states of matter.
- 🎥 Further exploration of the kinetic molecular theory will be covered in a future video.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

CHANGES IN STATES OF MATTER || FREEZING, MELTING, CONDENSATION, EVAPORATION, SUBLIMATION, DEPOSITION

Kurikulum Merdeka IPA Kelas 7 Bab 2 Zat dan Perubahannya

3 States of Matter - Solid, Liquid, Gas

Science 5 Quarter 1 Week 5 Revised K-12 - Temperature And Its Effect On The State Of Matter
States of matter for kids - What are the states of matter? Solid, liquid and gas

Matter In Our Surroundings | One Shot | Class 9 Science
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)