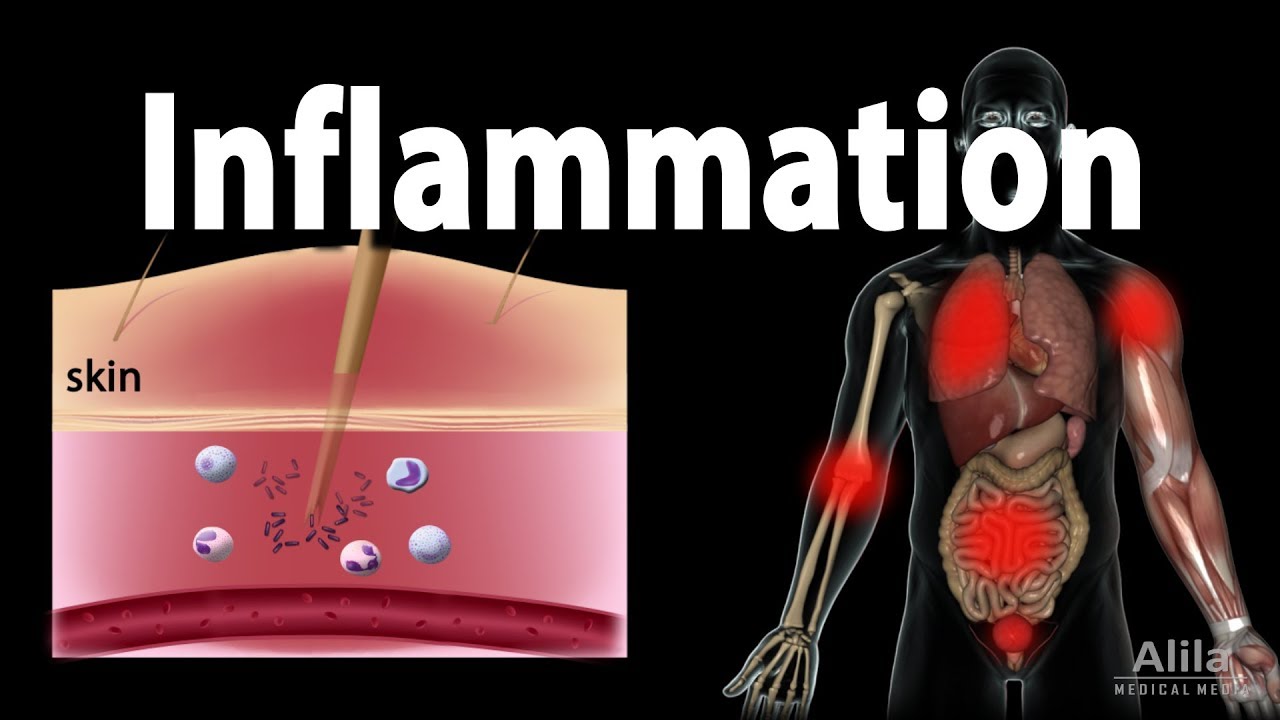
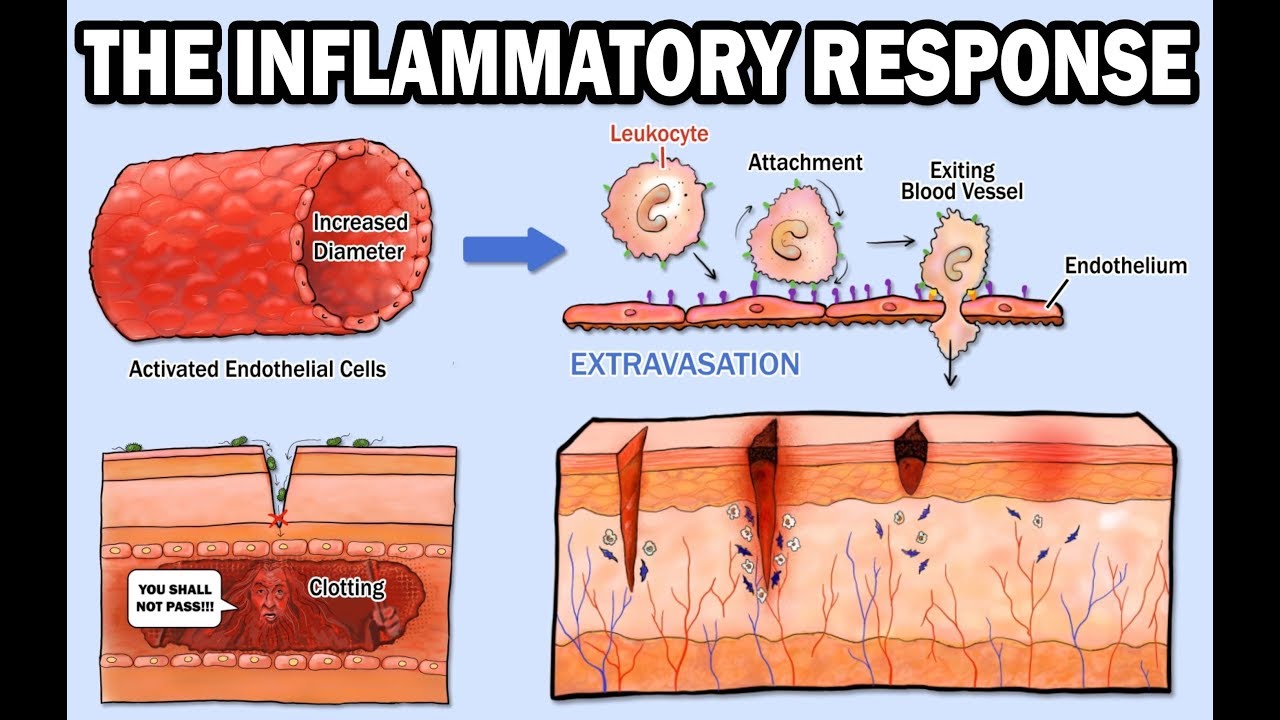
Inflammation: Immune Response to Tissue Injury or Infection
Summary
TLDRInflammation is a vital immune response to tissue injury or infection, characterized by heat, redness, swelling, pain, and loss of function. It initiates with vasoconstriction to minimize blood loss, followed by vasodilation due to chemicals like prostaglandins and histamine, increasing blood flow and capillary permeability. Neutrophils, immune cells, migrate to the injury site through chemotaxis and diapedesis, where they phagocytose pathogens. Tissue repair commences with fibroblast activity and collagen production. Anti-inflammatory drugs like NSAIDs reduce inflammation by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, thus decreasing prostaglandins and other inflammatory chemicals.
Takeaways
- 🔴 Inflammation is a local immune response to tissue injury or infection, characterized by heat, redness, swelling, pain, and loss of function.
- 🩸 The initial response to injury involves vasoconstriction to reduce blood loss and clot formation to stop bleeding.
- 🌡️ Vasoactive chemicals like prostaglandins and histamine are released, leading to vasodilation and increased blood flow to the affected area.
- 💧 Increased capillary permeability allows fluid and proteins to leak into the tissue, causing edema.
- 🔍 Chemotaxis is a multi-stage process where neutrophils are drawn to the site of injury to destroy pathogens and damaged cells.
- 🔗 Chemoattractants released by injured cells initiate the process of neutrophils sticking to endothelial cells and moving towards the injury site.
- 🚶♂️ Diapedesis is the process where neutrophils squeeze through the endothelial gaps to reach the injury site.
- 🌀 Neutrophils follow a chemotactic gradient to migrate to the injury site, where they engulf and digest bacteria through phagocytosis.
- 🛠️ Tissue repair begins after the destruction of bacteria and removal of cellular waste, with fibroblasts dividing and producing collagen to reinforce the wound.
- 💊 Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as NSAIDs (e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen), work by inhibiting the production of inflammatory chemicals, reducing vasodilation, edema, and pain.
Q & A
What is inflammation and what are its typical symptoms?
-Inflammation is a local immune response to tissue injury or infection, characterized by heat, redness, edema, pain, and loss of function.
How does the initial vasoconstriction during inflammation help the body?
-Vasoconstriction of local blood vessels at the site of injury helps to reduce blood loss and facilitates the formation of a clot to stop bleeding.
What role do vasoactive chemicals like prostaglandins and histamine play in inflammation?
-Vasoactive chemicals such as prostaglandins and histamine dilate local blood vessels, increasing blood flow to the area and causing endothelial cells in small blood vessels to contract, thereby increasing capillary permeability.
What is chemotaxis and how does it relate to the immune response during inflammation?
-Chemotaxis is a multi-stage process where immune cells called neutrophils move from the bloodstream to the site of injury, guided by chemoattractants released by cells at the injury site.
Describe the process of diapedesis in the context of inflammation.
-Diapedesis is the process where neutrophils squeeze through the endothelial gaps in the blood vessels to reach the site of injury.
How do neutrophils contribute to the resolution of inflammation?
-Neutrophils contribute to resolving inflammation by migrating to the injury site, encountering bacteria, and engulfing and digesting them through a process called phagocytosis.
What is the role of fibroblasts in tissue repair after inflammation?
-Fibroblasts play a role in tissue repair by dividing rapidly and secreting large quantities of collagen to reinforce the wound, which is initiated by locally produced growth factors.
How do anti-inflammatory drugs like NSAIDs work to reduce inflammation?
-Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as NSAIDs, work by inhibiting the production of inflammatory chemicals. They contain an enzyme called cyclooxygenase (Cox) that inhibits the production of prostaglandins and other inflammatory chemicals, thus reducing vasodilation, edema, and pain.
What are the common types of drugs used to treat inflammation?
-The most common drugs used to treat inflammation are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin and ibuprofen.
How does the release of chemoattractants influence neutrophils during inflammation?
-The release of chemoattractants by cells at the injury site causes local endothelial cells and circulating neutrophils to stick together, which is a crucial step in the process of chemotaxis.
What is the significance of increased capillary permeability during inflammation?
-Increased capillary permeability allows fluids and proteins to pass from the blood into the tissue, which aids in the delivery of immune cells and nutrients to the site of injury and helps in the removal of waste products.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)