الخواص الجامعة للمحاليل كيمياء ثالث ثانوي 1445
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script discusses the concept of colligative properties in chemistry, focusing on how the properties of a solution are affected by the number of solute particles rather than their nature. It explains the relationship between solute particles and the solution's boiling point elevation and vapor pressure lowering. The script differentiates between electrolytes and non-electrolytes, highlighting the greater impact of electrolytes like sodium chloride on colligative properties due to their ability to dissociate into more ions. The video aims to clarify these properties and their significance in understanding solution behavior.
Takeaways
- 😀 The main concept discussed is the colligative properties of solutions, which depend on the number of solute particles in a solution rather than the nature of the solute.
- 🔬 Colligative properties are physical properties of solutions that are affected by the number of solute particles present, not by the nature of the solute itself.
- 🧪 Solutions can be classified into two main types: electrolytes, which dissociate into ions and conduct electricity, and non-electrolytes, which do not dissociate into ions and do not conduct electricity.
- 📚 Electrolytes are further divided into strong and weak electrolytes. Strong electrolytes dissociate completely in water, producing a large number of ions, while weak electrolytes produce only a small number of ions.
- 🌡 One of the key colligative properties discussed is the lowering of the vapor pressure of a solvent when a non-volatile solute is added to it.
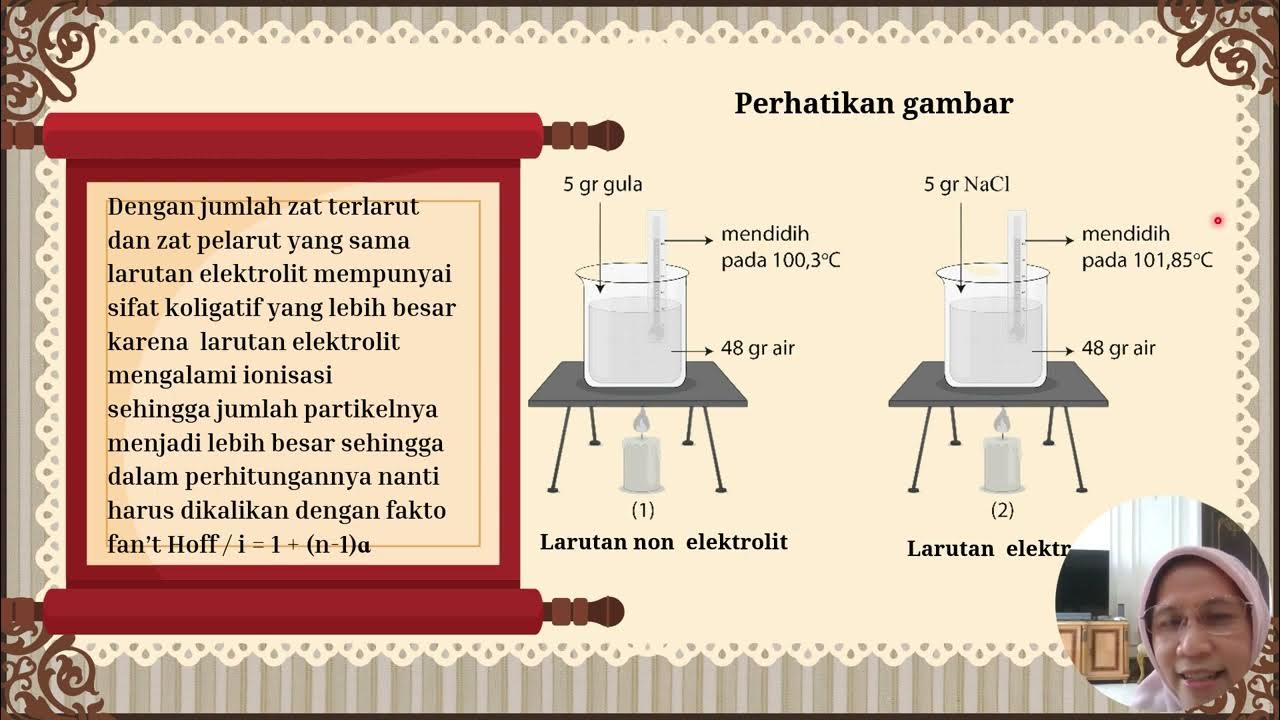
- 🔍 The boiling point of a solution increases when a non-volatile solute is added, due to the need to increase the pressure to match the atmospheric pressure, as the solute lowers the vapor pressure.
- ⚖️ The effect of electrolytes on colligative properties, such as lowering the vapor pressure, is greater than that of non-electrolytes because they produce more particles per mole of solute.
- 📉 The freezing point depression is another colligative property that will be discussed in a subsequent video, as it relates to the lowering of the freezing point of a solvent due to the presence of a solute.
- 📈 The concept of molality, which is the amount of solute per kilogram of solvent, is introduced as a factor in determining the extent of changes in colligative properties.
- 🔗 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding the fundamental principles of colligative properties for solving related problems in chemistry.
Q & A
What is the main concept discussed in the first lesson of the chemistry chapter?
-The main concept discussed is the properties of solutions, specifically how the properties of a solution are affected by the number of solute particles in the solvent, rather than the nature of the solute itself.
What are the physical properties of solutions that are affected by the number of solute particles?
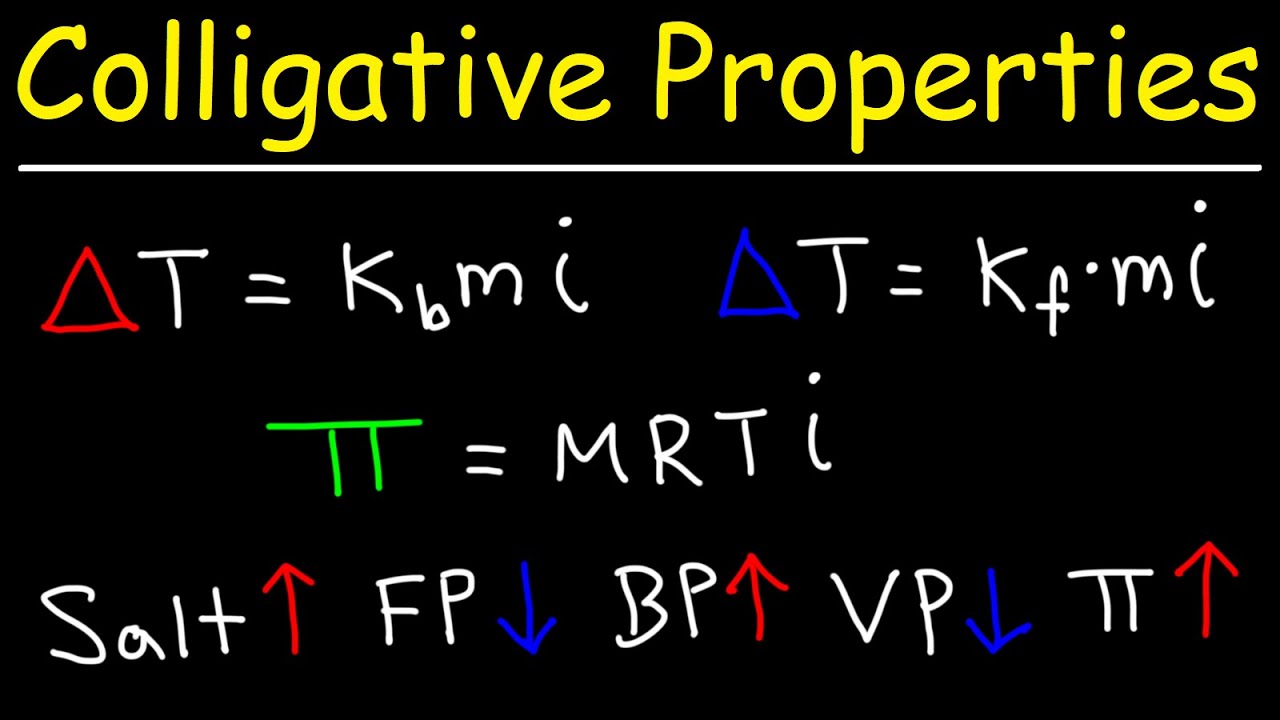
-The physical properties of solutions that are affected by the number of solute particles include the lowering of vapor pressure, the elevation of boiling point, the lowering of freezing point, and the osmotic pressure.
What is the definition of a strong electrolyte in the context of this lesson?
-A strong electrolyte is a substance that completely dissociates into ions in an aqueous solution, producing a large number of ions, such as sodium chloride (NaCl).
How does the presence of a solute affect the vapor pressure of a solvent?
-The presence of a non-volatile solute in a solvent reduces the vapor pressure of the solvent because it increases the number of particles in the solution, which slows down the rate of evaporation.
What is the relationship between the boiling point elevation and the amount of solute particles in a solution?
-The boiling point elevation is directly proportional to the number of solute particles in the solution. As the number of solute particles increases, the boiling point of the solution also increases.
What is the significance of the term 'colligative properties' in the context of this chemistry lesson?
-Colligative properties are those properties of a solution that depend on the number of solute particles present in the solvent, not on the nature of the solute. Examples include vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure.
How does the type of solute (electrolyte vs. non-electrolyte) affect the colligative properties of a solution?
-Electrolytes, which dissociate into ions, have a greater effect on colligative properties than non-electrolytes because they produce more particles in solution. For instance, sodium chloride (NaCl) as an electrolyte produces more particles than sucrose (a non-electrolyte), thus having a more significant impact on properties like vapor pressure and boiling point.
What is the difference between a strong and a weak electrolyte as explained in the lesson?
-A strong electrolyte is a substance that completely dissociates into a large number of ions in solution, while a weak electrolyte only partially dissociates, producing a smaller number of ions.
How does the presence of a solute like sodium chloride (NaCl) affect the freezing point of a solution compared to a solution with sucrose?
-Sodium chloride (NaCl), being an electrolyte, will lower the freezing point of a solution more significantly than sucrose because it produces more particles in the solution, which interferes more with the solvent's ability to freeze.
What is the practical implication of understanding colligative properties in chemistry?
-Understanding colligative properties is crucial in various fields such as medicine, where osmotic pressure is important for understanding cell behavior, and in industrial processes like distillation, where vapor pressure is a key factor.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Sifat Koligatif 2Penurunan Tekanan Uap

Colligative Properties Explained

🧪 PROPRIEDADES COLIGATIVAS - APRENDA RÁPIDO!

SIFAT KOLIGATIF LARUTAN - KIMIA - MATERI UTBK SBMPTN DAN SIMAK UI

ruangbelajar - Kimia XII SMA - Pendahuluan Sifat Koligatif
Colligative Properties - Boiling Point Elevation, Freezing Point Depression & Osmotic Pressure
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)