Barisan dan deret Geometri kelas 10
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script introduces the concept of geometric sequences and series. It explains the difference between arithmetic and geometric progressions, highlighting the constant ratio (r) in geometric sequences. The script demonstrates how to calculate the nth term (UN) using the formula UN = a * r^(n-1) and the sum of the first n terms (SN) using SN = a * (r^n - 1) / (r - 1). Examples are provided to illustrate the calculation of specific terms and the total sum, aiming to clarify these mathematical concepts for viewers.
Takeaways
- 🔢 The script discusses geometric sequences, which are series where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous term by a constant called the common ratio (r).
- 📐 It provides an example of a geometric sequence: 2, 4, 8, 16, and so on, where each term is twice the previous one.
- 📈 The script differentiates between arithmetic and geometric series, highlighting that in arithmetic series, the difference between consecutive terms is constant, while in geometric series, the ratio is constant.
- 🧮 The formula for the nth term of a geometric sequence is given as UN = a * r^(n-1), where 'a' is the first term and 'r' is the common ratio.
- 🔑 The script explains that to find any term in the sequence, you can use the formula UN = a * r^(n-1), and provides examples to demonstrate its use.
- 🌐 The script introduces the concept of the sum of the first 'n' terms of a geometric sequence, denoted as SN.
- 📘 The formula for the sum of the first 'n' terms of a geometric sequence is given as SN = a * (1 - r^n) / (1 - r), provided 'r' is not equal to 1.
- 🔍 An example calculation is provided to find the sum of the first three terms of a geometric sequence, using the formula mentioned above.
- 💡 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding the basic concepts of geometric series, such as the first term, common ratio, and how to calculate any term or the sum of terms.
- 🙏 The presenter encourages repetition and practice for better understanding, suggesting that prayer and perseverance can aid in learning complex mathematical concepts.
Q & A
What is a geometric sequence?
-A geometric sequence is a sequence of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous one by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio.
What is the difference between a geometric sequence and an arithmetic sequence?
-In an arithmetic sequence, each term is found by adding a constant difference to the previous term. In contrast, a geometric sequence involves multiplying by a constant ratio.
What is the common ratio in the example given in the script?
-The common ratio in the example is 2, as each term is twice the previous term (e.g., 4 is 2 times 2, 8 is 2 times 4, and so on).
How do you calculate the nth term of a geometric sequence?
-The nth term (UN) of a geometric sequence can be calculated using the formula UN = a * r^(n-1), where 'a' is the first term and 'r' is the common ratio.
What is the first term (U1) in the geometric sequence mentioned in the script?
-The first term (U1) in the geometric sequence mentioned in the script is 2.
How can you find the third term (U3) in the geometric sequence without knowing the common ratio?
-To find the third term (U3) without knowing the common ratio, you can use the formula U3 = U1 * r^2, where U1 is the first term and 'r' is the common ratio.
What is the sum of the first n terms of a geometric sequence?
-The sum of the first n terms of a geometric sequence (SN) can be calculated using the formula SN = a * (1 - r^n) / (1 - r), where 'a' is the first term and 'r' is the common ratio, provided that r ≠ 1.
What is the formula to find the sum of the first three terms (S3) of a geometric sequence?
-The formula to find the sum of the first three terms (S3) of a geometric sequence is S3 = U1 + U2 + U3, or using the sum formula, S3 = a * (1 - r^3) / (1 - r).
How does the script suggest finding the common ratio if it's not given?
-The script suggests finding the common ratio by using the relationship between consecutive terms, such as dividing the second term by the first term or the third term by the second term.
What is the significance of the term 'r' in the context of geometric sequences?
-The term 'r' represents the common ratio in a geometric sequence, which is the factor by which each term is multiplied to get the next term.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Sequences and Series (Arithmetic & Geometric) Quick Review
Arithmetic Sequences and Arithmetic Series - Basic Introduction

Pembahasan BARISAN DAN DERET (Aritmetika & Geometri) KELAS 11 | #MatematikAsik

Pola Bilangan (5) | Barisan dan Deret Geometri

Barisan dan Deret Bagian 3 - Barisan Geometri Matematika Wajib Kelas 11
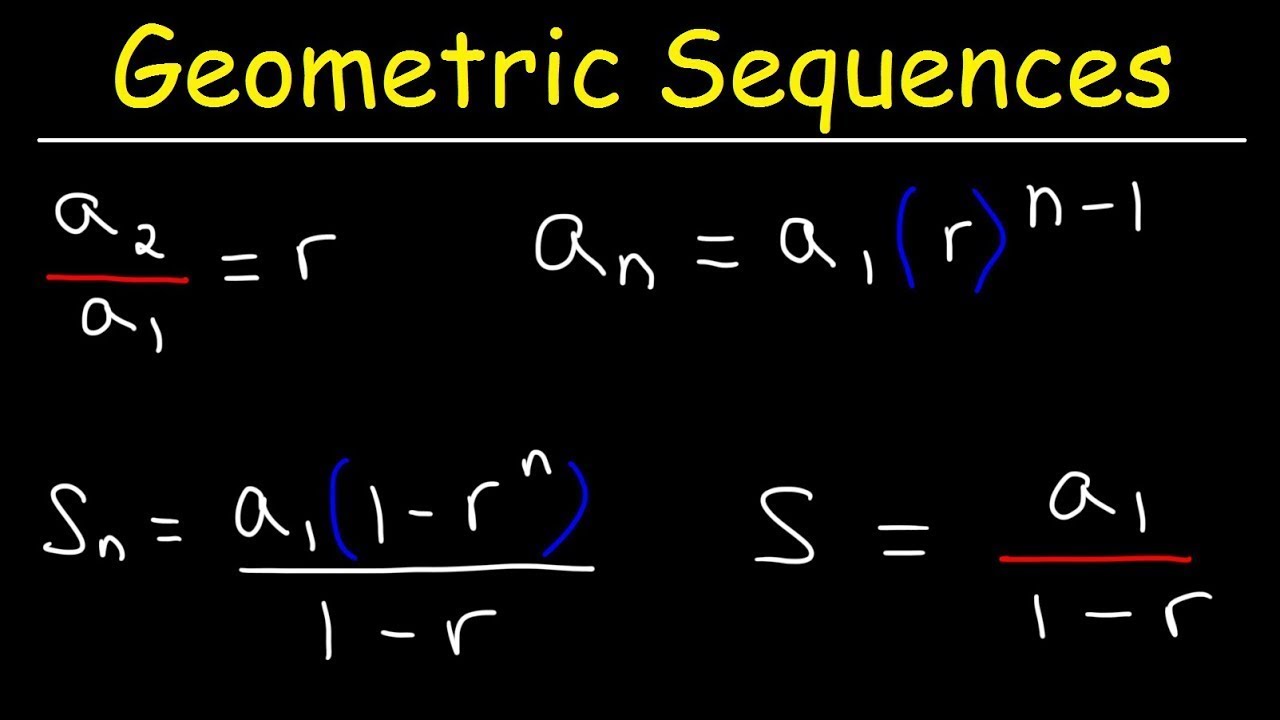
Geometric Series and Geometric Sequences - Basic Introduction
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)