Mitosis in Onion Root tip Experiment
Summary
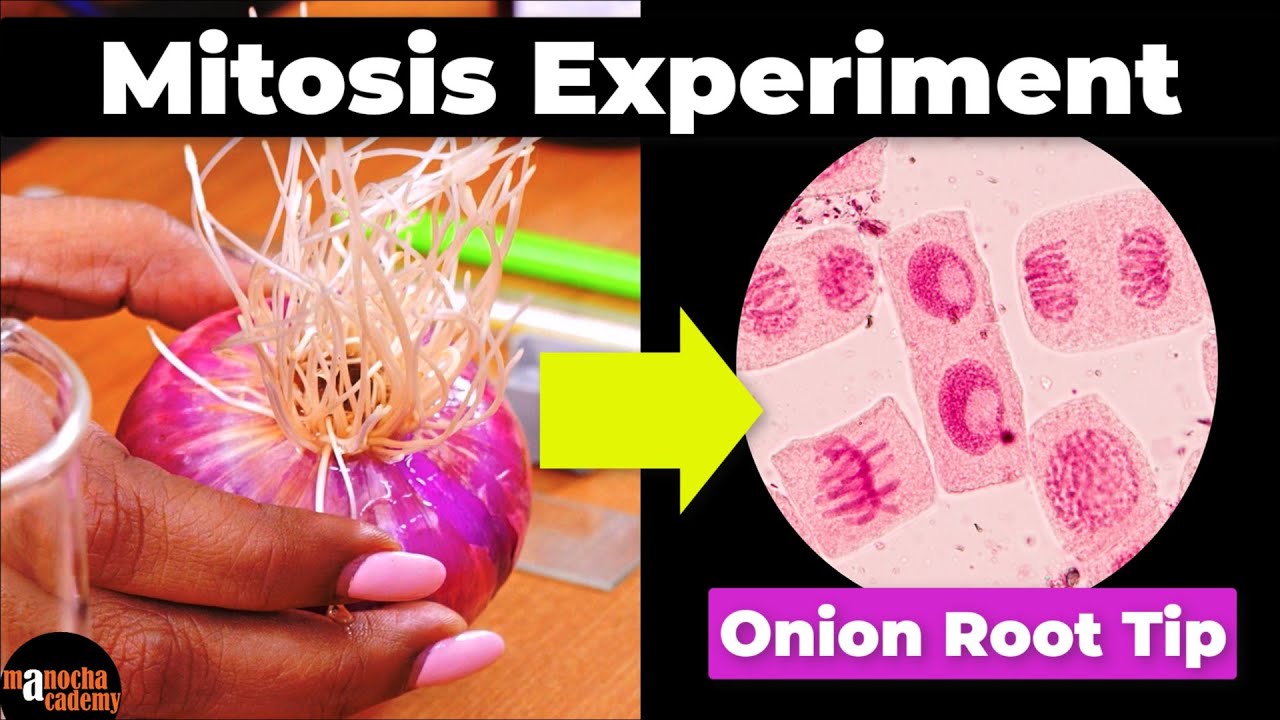
TLDRThis video guides viewers through the process of preparing root tips of Allium species to observe mitosis under a microscope. Mitosis is a cell cycle stage where chromosomes replicate and separate to form two identical cells. The experiment requires an onion or garlic bulb, various chemicals, and lab equipment. After growing root tips, they are fixed, preserved, and stained to highlight chromosomes. The stained root tips are then squashed on a slide for microscopic observation. The video demonstrates steps to prepare, squash, and observe the cells under different magnifications, capturing various stages of mitotic division.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Mitosis is a cell cycle stage where chromosomes replicate and separate to form two genetically identical cells.
- 🧅 The experiment requires an onion or garlic bulb, beakers, toothpicks, and various chemicals and tools.
- 🌱 Allow roots to grow by submerging the base of the bulb in water for a few days.
- 🔪 Cut out root tips and place them in Carnoy fixative fluid to preserve the DNA.
- ⏳ Leave the root tips in the fixative for 48 hours for proper fixation.
- 💧 If storing for future use, transfer fixed root tips to 70% ethanol for dehydration and preservation.
- 🔬 Use 1N hydrochloric acid to soften cell walls and facilitate squashing of root material.
- 🌈 Stain the root tips with acetyl carbine or acido-orcin stain to color the nuclear material for observation.
- 📚 Create a slide by squashing the root tips between a slide and a coverslip, avoiding air bubbles.
- 🔍 Observe the slide under a compound light microscope, using different magnifications to view mitotic stages.
- 📸 Capture images of the cells using a mobile phone and a tripod for documentation.
Q & A
What is the purpose of preparing root tips of Allium species?
-The purpose is to observe cells in various stages of mitotic division, where chromosomes replicate and separate to form two genetically identical cells.
What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis?
-In mitosis, the chromosome number is maintained in both daughter cells, whereas in meiosis, the chromosome number is halved.
What materials are needed for the experiment described in the script?
-Materials needed include an onion or garlic bulb, beakers, toothpicks, Carnoy's fixative fluid, 70% ethanol, one normal hydrochloric acid, acetyl carbine or aceto-orcein stain, glass slides and cover slips, a blade or scalpel, watch glasses or petri dishes, spirit lamp or Bunsen burner, blotting paper, droppers, thumb forceps, scissors, a compound light microscope, and immersion oil.
Why is it necessary to keep the base of the bulb in contact with water?
-The base of the bulb needs to touch the water level to facilitate root growth for the experiment.
How long should the root tips be left in Carnoy's fixative fluid?
-The root tips should be left in Carnoy's fixative fluid for about 48 hours.
What is the purpose of using 70% ethanol after fixing the root tips?
-70% ethanol is used to dehydrate the root tissue, which helps preserve the DNA for potential future genetic studies.
Why is the root material softened with one normal hydrochloric acid?
-Hydrochloric acid softens the cell walls and weakens cellular connections, making it easier to squash the root material for slide preparation.
What is the role of acetyl carbine or aceto-orcein stain in the experiment?
-These stains are used to color the nuclear material of the root cells, making it easier to observe the cells under a microscope.
How long should the root tips be left in the stain before microscopic observation?
-The root tips should be left in the stain for about 5 to 10 minutes.
What is the significance of squashing the root tips between the slide and the coverslip?
-Squashing the root tips helps to spread out the cells evenly, allowing for clear observation of individual cells without overlapping.
Why is immersion oil used during high-power microscopic observation?
-Immersion oil is used to reduce light refraction and improve the resolution of the image when observing under high magnification, such as with a 100x oil immersion lens.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)