Comment utiliser la loi de Beer-Lambert ? Première Spécialité Physique Chimie Lycée
Summary
TLDRThe video script discusses the concept of absorbance in solutions, explaining how it relates to the depth of light penetration in liquids like seawater. It defines absorbance as the ratio of incident to transmitted light, with a focus on how it increases with solution concentration and path length. The script explores the relationship between absorbance, solution color, and the colors absorbed or transmitted, emphasizing that the color of a solution is complementary to the most absorbed color. It introduces the use of a spectrophotometer to measure absorbance and explains the Beer-Lambert Law, which states absorbance is proportional to both solute concentration and path length. The script concludes with an exercise on determining the concentration of a red dye in grenadine syrup using a spectrophotometer, illustrating the practical application of these principles.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Absorbance is the capacity of a solution to absorb light that passes through it, which is crucial in understanding how light interacts with substances.
- 🌊 Light absorption increases with the depth of the sea due to water's absorption properties, leading to less light penetration.
- 🔍 The absorbance is calculated as the ratio of incident light to transmitted light, indicating the proportion of light absorbed by the solution.
- 🎨 The color of a solution is related to the light it absorbs and transmits, with colors being complementary on the color wheel.
- 🌈 Absorbance depends on the wavelength of light, with different colors (wavelengths) being absorbed to varying degrees by a solution.
- 📊 The color of a solution is the color that is most absorbed by it, which is opposite on the color wheel, known as the complementary color.
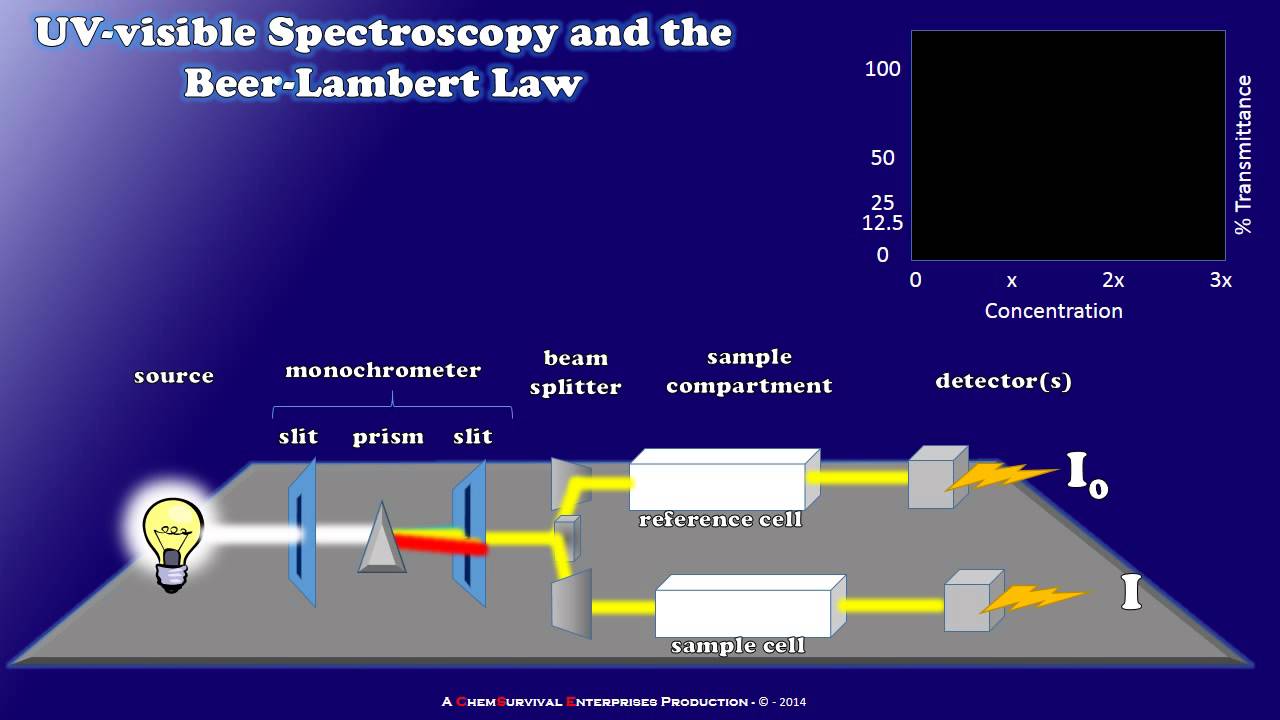
- 🔬 A spectrophotometer is used to study the content of a solution by analyzing the light absorbed, which is based on the Beer-Lambert Law.
- ⚖️ The Beer-Lambert Law states that absorbance is proportional to the concentration of the solution and the length of the light path (cuvette).
- 📉 A calibration curve can be created by plotting absorbance against concentration, which is linear for low concentrations but may deviate at higher concentrations.
- 🧪 Dilution of solutions may be necessary for accurate measurement, especially when the concentration is too high, to fit within the measurable range of the spectrophotometer.
Q & A
What is absorbance and how is it related to the color of a solution?
-Absorbance is the capacity of a solution to absorb light that passes through it. It is calculated as the ratio of incident light to transmitted light. A higher absorbance indicates a darker solution because more light is being absorbed.
How does the depth in the ocean affect the amount of light that penetrates?
-The deeper in the ocean, the less light penetrates because water absorbs sunlight, and as the thickness of the liquid increases, more light is absorbed, resulting in less light transmission.
What is the relationship between absorbance and the concentration of a solution?
-According to the Lambert-Beer law, absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration of solutes in a solution and the length of the light path through the solution, given a fixed wavelength.
Why does the color of a solution affect its absorbance?
-The color of a solution affects its absorbance because different colors correspond to different wavelengths of light, and each wavelength is absorbed to varying degrees by the solution.
What are complementary colors in relation to light absorption?
-Complementary colors are those that are diametrically opposite each other on the color wheel. A solution's color is the least absorbed, and its complementary color is the most absorbed.
What is meant by 'lambda max' in spectrophotometry?
-Lambda max refers to the wavelength at which a solution absorbs light most strongly. It is the maximum point of absorption and is used for precise measurements in spectrophotometry.
How does the length of the light path in a cuvette affect the absorbance measurement?
-The absorbance is directly proportional to the length of the light path. If the path length is increased, the absorbance will also increase, assuming the concentration and wavelength are constant.
Why is it necessary to dilute some solutions before measuring their absorbance?
-Some solutions need to be diluted before measuring their absorbance to ensure that the absorbance values fall within the linear range of the spectrophotometer, preventing the solution from being too concentrated and opaque.
What is the purpose of a spectrophotometer in chemical analysis?
-A spectrophotometer is used to analyze the content of a solution by measuring the light absorbed by the solution, which can then be used to determine the concentration of solutes within the solution.
How can you determine the concentration of a solute in an unknown solution using a spectrophotometer?
-By measuring the absorbance of the unknown solution at lambda max and comparing it to a calibration curve created from solutions of known concentration, one can determine the concentration of the solute in the unknown solution.
What is the significance of the linear relationship between absorbance and concentration in the context of the Lambert-Beer law?
-The linear relationship between absorbance and concentration, as described by the Lambert-Beer law, allows for the creation of a calibration curve. This curve is used to determine the concentration of unknown solutions by measuring their absorbance.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)