PHOTOSYNTHESIS: LIGHT_INDEPENDET REACTION or CALVIN CYCLE Tagalog
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the light-independent stage, or Calvin cycle, of photosynthesis. It reviews the light-dependent stage and introduces the process of converting light energy into chemical energy, primarily glucose. The video explains the roles of chloroplasts, thylakoids, and stroma, and outlines the chemical reactions involved in producing glucose and oxygen. It details the Calvin cycle's three phases: carbon dioxide fixation, reduction, and regeneration of RuBP, emphasizing the cycle's dependency on ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent stage.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Photosynthesis is a process that converts light energy into chemical energy, primarily stored as glucose (sugar).
- 🌿 The process occurs in chloroplasts, which are found in plant cells but not in animal cells.
- 🔬 Photosynthesis has two stages: the light-dependent stage and the light-independent stage (Calvin cycle).
- ☀️ The light-dependent reaction requires light energy and water, producing oxygen and high-energy molecules ATP and NADPH.
- 🌿 The Calvin cycle (light-independent reaction) does not require light energy but uses carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADPH to produce glucose.
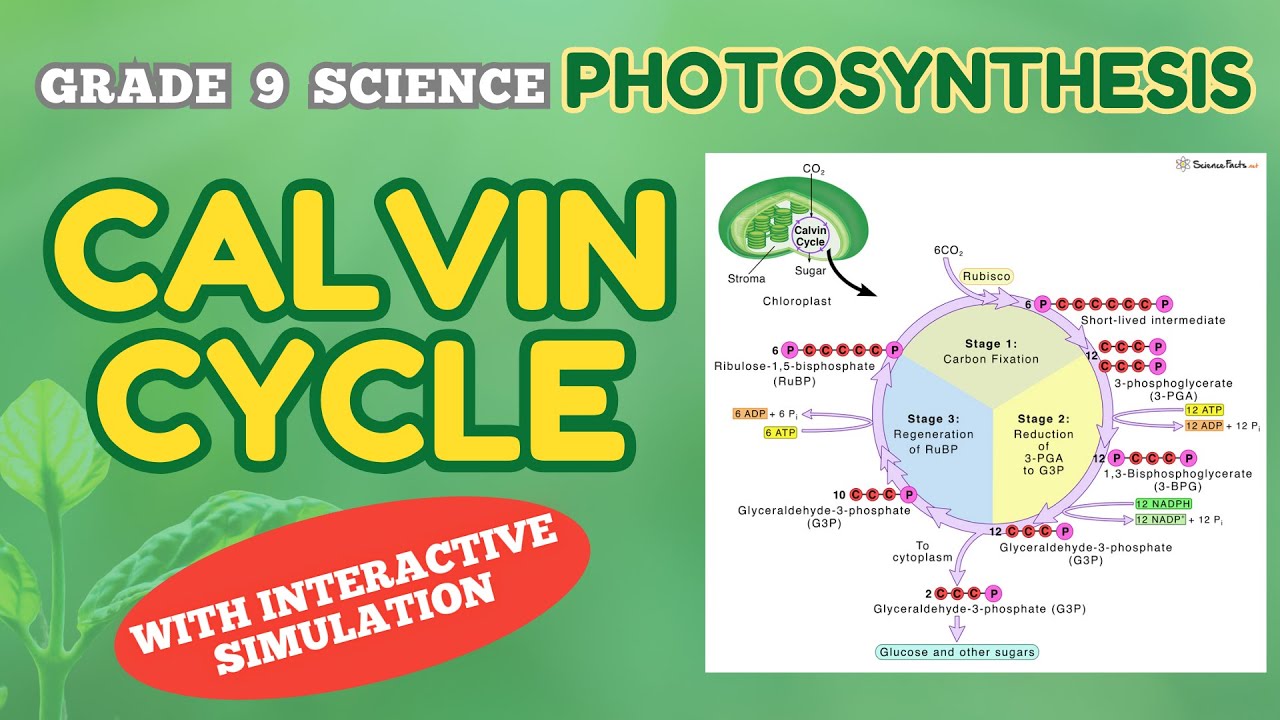
- 🔄 The Calvin cycle consists of three phases: carbon dioxide fixation, carbon dioxide reduction, and regeneration of RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate).
- 🧬 Carbon dioxide fixation involves the enzyme RuBisCO, which combines CO2 with a five-carbon molecule (RuBP) to form two three-carbon molecules (3-phosphoglycerate).
- 🔋 Carbon dioxide reduction converts 3-phosphoglycerate into carbohydrates (G3P) using ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reaction.
- 🔁 RubP regeneration uses G3P from the second phase to regenerate RuBP, enabling the cycle to start again.
- 🌐 It takes six turns of the Calvin cycle to produce one molecule of glucose, highlighting the efficiency of photosynthesis.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is the light-independent stage or Calvin cycle of photosynthesis.
What is the role of chloroplasts in photosynthesis?
-Chloroplasts are the organelles in plant cells where photosynthesis takes place. They are responsible for converting light energy into chemical energy.
What are the two stages of photosynthesis mentioned in the script?
-The two stages of photosynthesis mentioned are the light-dependent stage and the light-independent stage, also known as the Calvin cycle.
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis as described in the script?
-The chemical equation for photosynthesis is 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2.
What are the products and byproducts of photosynthesis according to the script?
-The products of photosynthesis are glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen (O2), while the byproduct is water.
What is the role of the thylakoid in the light-dependent reaction?
-The thylakoid is where the light-dependent reaction occurs, which involves the splitting of water molecules to release oxygen and produce high-energy molecules like ATP and NADPH.
What is the function of the stroma in the Calvin cycle?
-The stroma is where the light-independent reactions or Calvin cycle take place, where carbon dioxide is fixed and reduced to form glucose using ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent stage.
What are the three phases of the Calvin cycle mentioned in the script?
-The three phases of the Calvin cycle are carbon dioxide fixation, carbon dioxide reduction, and the regeneration of RuBP.
How does carbon dioxide fixation occur in the Calvin cycle?
-Carbon dioxide fixation occurs when carbon dioxide reacts with RuBP (a five-carbon molecule) with the help of the enzyme RuBisCO to form two three-carbon phosphoglycerate molecules.
What happens during the carbon dioxide reduction phase in the Calvin cycle?
-During the carbon dioxide reduction phase, phosphoglycerate is converted into carbohydrates or G3P using NADPH and ATP from the light-dependent reaction.
How is RuBP regenerated in the Calvin cycle, and what is its role in the cycle?
-RuBP is regenerated using G3P from the second phase of the Calvin cycle, with the help of ATP. One G3P molecule is left to become a building block for glucose, and the rest are used to regenerate RuBP, allowing the cycle to start again.
Why is the Calvin cycle considered a cycle, and how many turns are needed to produce one molecule of glucose?
-The Calvin cycle is considered a cycle because it repeats the same process to produce glucose. It requires six turns of the cycle to produce one molecule of glucose.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
PHOTOSYNTHESIS: CALVIN CYCLE || Grade 9 Science _ BIOLOGY

Photosynthesis - Light-dependent Stage - Post 16 Biology (A Level, Pre-U, IB, AP Bio)

Photosynthesis - Light Dependent Reactions and the Calvin Cycle

BIOLOGI Kelas 12 - Metabolisme Part 3 (Anabolisme) | GIA Academy

Reaksi Terang Fotosintesis

Photosynthesis: Crash Course Biology #8
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)