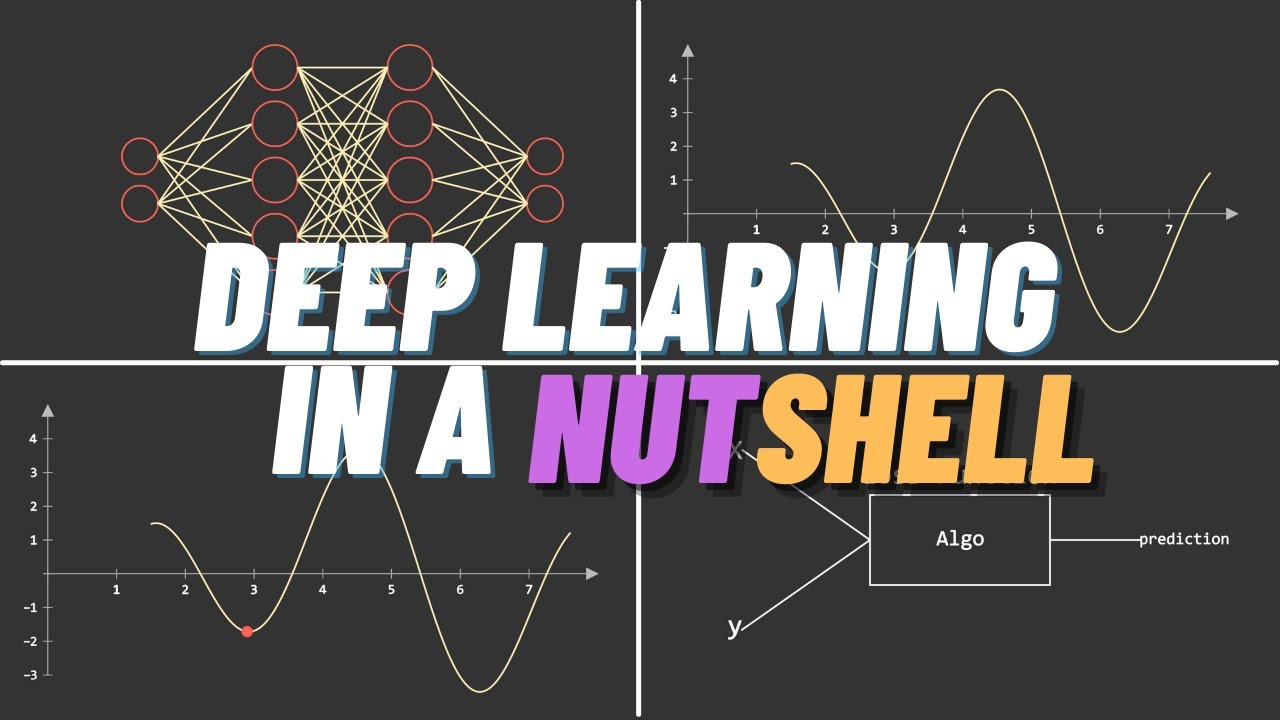
Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
Summary
TLDRThis video script creatively explains the difference between machine learning and deep learning using pizza as an analogy. It outlines the hierarchy from artificial intelligence to deep learning, emphasizing deep learning as a subset of machine learning. The script simplifies the concept by discussing how machine learning algorithms use structured data and weights to make decisions, exemplified by a pizza ordering model. It contrasts this with deep learning's ability to process unstructured data and learn from patterns without human intervention, highlighting the role of neural networks with more than three layers. The video concludes by inviting viewers to explore more on the topic and engage with the content.
Takeaways
- 🍕 The video uses pizza as a metaphor to explain the difference between machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL).
- 📊 Deep learning is a subset of machine learning, which in turn is a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI).
- 🧠 Machine learning algorithms use structured, labeled data to make predictions, whereas deep learning can process unstructured data without the need for human labeling.
- 🔢 The script introduces a simple model with inputs (X1, X2, X3) and weights (W1, W2, W3) to determine whether to order pizza, illustrating how ML algorithms work.
- 🤖 The concept of a neural network is fundamental to both ML and DL, with deep learning involving networks that have more than three layers, including input and output layers.
- 🏋️♂️ Human intervention is more critical in classical machine learning, where experts define features for the model to learn from, compared to deep learning which can discover features automatically.
- 🌟 Deep learning models can perform unsupervised learning, identifying patterns and clustering data without explicit human guidance.
- 🔄 Back-propagation is a technique used in training deep learning models, allowing for the calculation of error and adjustment of the model in the opposite direction of the feed-forward process.
- 📉 The video emphasizes that while ML and DL are part of the same field of study, the key differences lie in the depth of the neural network and the level of human involvement in the learning process.
- 🎥 The IBM technology channel offers more videos on these topics, encouraging viewers to subscribe for further insights into AI, ML, and DL.
Q & A
What is the relationship between deep learning and machine learning?
-Deep learning is a subset of machine learning. Machine learning is a broader field that includes deep learning as one of its methods.
How does the hierarchy of AI, ML, and DL look like?
-The hierarchy goes from AI (Artificial Intelligence) at the top, with ML (Machine Learning) as a subfield of AI, and DL (Deep Learning) as a subset of ML that relies on neural networks.
What are the three main factors considered for the decision to order pizza in the script?
-The three main factors are: whether ordering pizza will save time, whether it will help in losing weight, and whether it will save money.
What does X1, X2, and X3 represent in the pizza ordering model?
-X1 represents whether ordering pizza will save time (1 for yes, 0 for no). X2 represents whether it will help in losing weight (1 for yes, 0 for no). X3 represents whether it will save money (1 for yes, 0 for no).
How are weights assigned in the machine learning model for pizza ordering?
-Weights are assigned based on the importance of each input factor. For example, W1 is given a weight of 5 for time, W2 is given a weight of 3 for weight loss, and W3 is given a weight of 2 for money savings.
What is the threshold used in the pizza ordering model and why is it important?
-The threshold used is 5. It is important because it helps determine the output of the model; if the weighted sum of inputs exceeds the threshold, it indicates a positive decision to order pizza.
What is the difference between classical machine learning and deep learning in terms of human intervention?
-Classical machine learning often requires human intervention to label and structure data, while deep learning can process unstructured data and learn from it without the need for manual labeling.
How does deep learning handle unstructured data?
-Deep learning can ingest unstructured data such as text and images, and automatically determine the features that distinguish different types of data, a process known as unsupervised learning.
What is back-propagation and how does it help in training deep learning models?
-Back-propagation is a method of training where the model is adjusted by calculating the error associated with each neuron and moving in the opposite direction from output to input. It helps in fitting the algorithm more accurately.
What is the main distinction between machine learning and deep learning algorithms?
-The main distinction lies in the number of layers in a neural network (more than three layers indicate deep learning) and whether human intervention is required to label data.
What does the term 'feed forward' mean in the context of neural networks?
-In the context of neural networks, 'feed forward' means that data flows in one direction, from the input layer through the hidden layers to the output layer, without any loops or backward connections.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)