454 Sequencing
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial from Shaman's Biology delves into the advanced technology of 45 for DNA sequencing, a fast and reliable method belonging to next-generation sequencing. It outlines the process involving genome fragmentation, adapter ligation, and attachment to beads, followed by amplification and loading into wells. The video explains how fluorescence data is used to sequence DNA, with a focus on larger genomes like the human genome. It concludes with the interpretation of data to achieve the complete genome sequence, offering viewers insight into modern DNA sequencing techniques.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Next-generation sequencing technology, 454 sequencing, is fast and reliable, using fluorescence data to sequence DNA.
- 🧬 454 Sequencing is particularly effective for large genomes, such as the human genome, for whole genome sequencing.
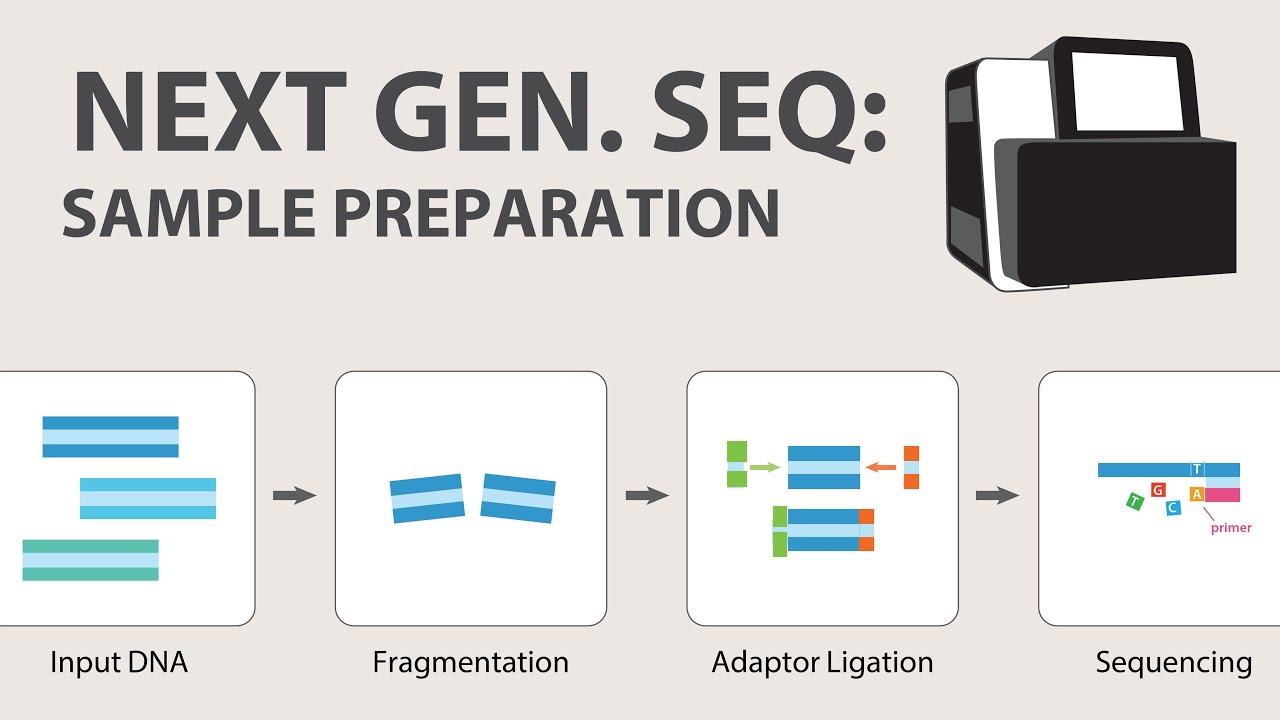
- 🔬 The process begins with the fragmentation of the genome, typically using physical shearing to break down the DNA into smaller pieces.
- 🔗 Adapter ligation is a crucial step, involving two different adapters attached to the ends of the DNA fragments to facilitate sequencing.
- 🧵 The DNA strands need to be separated into single-stranded DNA to prepare for the sequencing process.
- 📿 Beads play a key role as a solid surface for attaching single-stranded DNA sequences with the help of adapter A.
- 🔄 Amplification of DNA is achieved without PCR, by using the complementary strand to produce more target DNA strands for sequencing.
- 🧬 The amplification process creates multiple copies of the DNA, which are then attached to the beads, facilitating the sequencing of multiple fragments.
- 🚀 The actual sequencing begins once the beads, loaded with DNA fragments, are placed into the sequencing machine's wells.
- 🔍 Fluorescently tagged nucleotides are added sequentially, and the fluorescence generated indicates the presence of specific nucleotides in the DNA sequence.
- 🖥️ Data interpretation involves processing the fluorescence measurements to determine the sequence of the DNA fragments and ultimately assemble the whole genome sequence.
Q & A
What is 454 sequencing and why is it considered a next-generation sequencing technology?
-454 sequencing, also known as pyrosequencing, is a high-throughput DNA sequencing method that is part of the next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies. It is known for its speed and reliability, and it uses fluorescence data to sequence DNA. It is particularly effective for whole genome sequencing of larger genomes, such as the human genome.
What is the first stage in the 454 sequencing process?
-The first stage in 454 sequencing is the fragmentation of the genome. This is typically done using physical shearing to break down the genome into smaller pieces without using any chemical processes.
Why is adapter ligation an important step in 454 sequencing?
-Adapter ligation is crucial in 454 sequencing because it involves attaching two different adapters to the ends of the fragmented DNA. These adapters are single-stranded DNA sequences that facilitate the subsequent steps of sequencing by providing a binding site for the sequencing process.
How does the process of making DNA single-stranded relate to the 454 sequencing method?
-After genome fragmentation, the DNA obtained is double-stranded. In 454 sequencing, it is necessary to separate the strands to make them single-stranded. This is important because the adapters are ligated to the single-stranded DNA fragments, which are then used in the sequencing process.
What role do beads play in the 454 sequencing process?
-In 454 sequencing, beads are used as a solid surface to which the single-stranded DNA fragments, with adapters ligated at both ends, attach. The beads are constructed to allow a section of nucleotide sequence to bind to them, facilitating the attachment of the DNA fragments.
How is DNA amplified in the 454 sequencing process without using PCR?
-DNA amplification in 454 sequencing is achieved through a process where the nucleotide sequences are added to produce complementary structures. This is done repeatedly to generate multiple copies of the target DNA strands, which are then attached to the beads, without the need for a PCR process.
What is the purpose of loading the beads into wells in the 454 sequencing process?
-Loading the beads into wells is a preparatory step before the actual sequencing begins. The wells are small volumetric areas where the beads, now filled with DNA fragments, are placed. This allows for the organized and controlled sequencing of multiple DNA samples simultaneously.
How does the addition of primers and nucleotide sequences contribute to the sequencing process in 454 sequencing?
-Primers are added to bind with the adapter B region on the DNA fragments attached to the beads. The addition of nucleotide sequences generates a specific fluorescence each time a nucleotide is incorporated. This fluorescence is used to determine the sequence of the DNA, as each nucleotide corresponds to a different color.
What is the significance of fluorescence in determining the DNA sequence in 454 sequencing?
-Fluorescence is key in 454 sequencing as it allows for the detection of incorporated nucleotides. Each type of nucleotide is tagged with a different fluorescence color. The intensity and color of the fluorescence generated indicate the presence and number of specific nucleotides in the sequence, which helps in determining the DNA sequence.
How does the 454 sequencing process interpret the fluorescence data to obtain the DNA sequence?
-The fluorescence data obtained during the sequencing process is analyzed by software programs. These programs process the data for each fragment, overlap the sequences, and assemble the complete sequence of the whole genome based on the fluorescence intensity and color patterns.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)