The Earth and Its Geological Processes
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the Earth's geological processes, distinguishing between endogenic and exogenic forces. It explains how internal thermal energy drives tectonic activity and how radioactive decay fuels Earth's heat. The script covers the rock cycle, geological stress types, and the impacts of weathering, erosion, mass wasting, and sedimentation on the landscape. It concludes by reflecting on the inevitability of destruction as a creative force, encouraging viewers to embrace challenges for personal growth.
Takeaways
- 🌏 Geological processes on Earth can be categorized into endogenic and exogenic processes, each with distinct origins and effects.
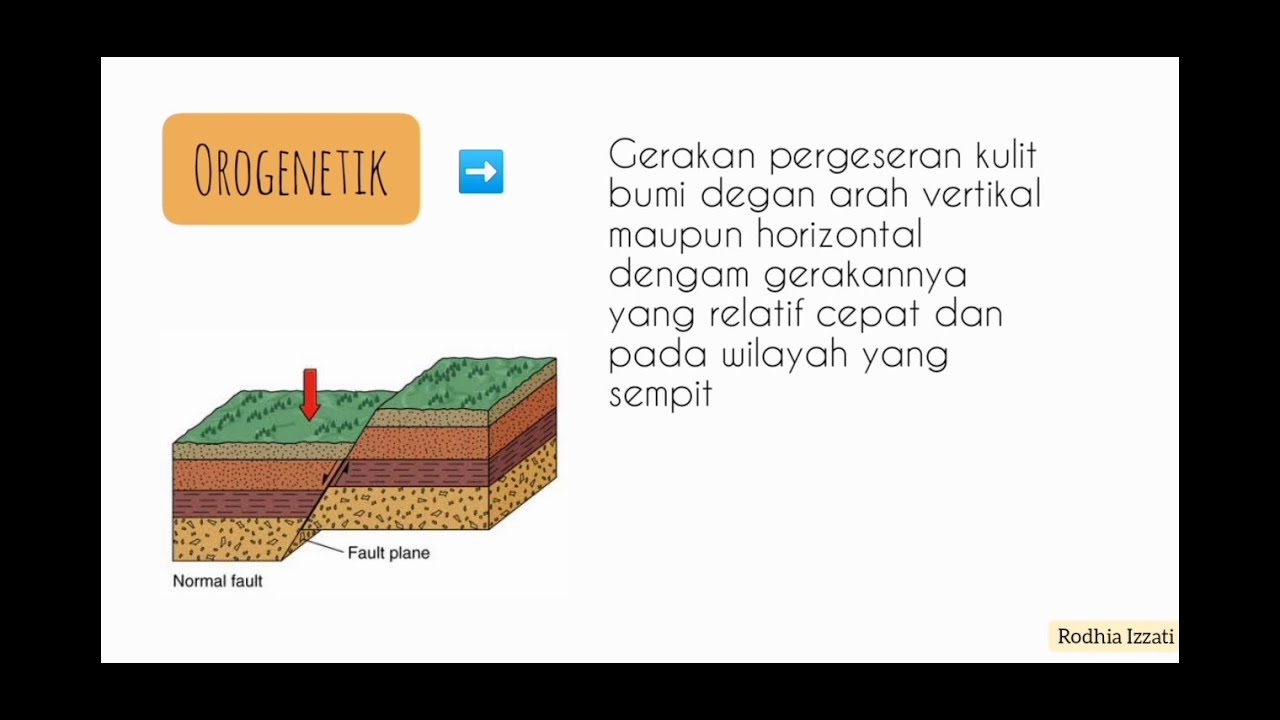
- 🔥 Endogenic processes are driven by thermal energy from the Earth's interior, causing the ground to move through tectonic activity.
- 🌌 The Earth's geosphere is divided into the core, mantle, and crust, with the lithosphere including the crust and uppermost solid mantle.
- 🌋 Volcanism and magmatism are endogenic processes that lead to the formation of igneous rocks, both intrusive and extrusive.
- 🔥🪨 Metamorphism is an endogenic process that alters the chemical composition and geological characteristics of rocks due to changes in heat and pressure.
- 🌐 Earth's internal heat primarily comes from the decay of radioactive elements in the core, which release energy as they decay.
- 📏 Geological stress, including compressional, tensional, shearing, and confining stress, can reshape the Earth's crust through various mechanisms.
- 🌧️ Exogenic processes occur on or near the surface and are influenced by gravity, water, wind, and organisms, often leading to significant landscape changes.
- 💥 Weathering, a form of exogenic process, involves the disintegration of rocks and minerals through physical, biological, and chemical means.
- 🌊 Erosion is the movement of rock debris or soil due to natural agents like water and wind, which can lead to the formation of new landforms.
- 🏔️ Mass wasting is the destructive movement of large masses of material down a slope due to gravity, often exacerbated by increased water flow.
- 🛤️ Sedimentation is the accumulation of materials that settle over time, potentially forming new layers of ground or ocean basins.
Q & A
What are the two main types of geological processes discussed in the script?
-The two main types of geological processes discussed in the script are endogenic processes, which originate from the energy within the Earth, and exogenic processes, which occur on or near the Earth's surface and are influenced by gravity, water, wind, and organisms.
What is the lithosphere and what does it consist of?
-The lithosphere is the rigid outermost layer of the Earth, consisting of the crust and the uppermost solid part of the mantle. It rests on the asthenosphere, which is a more ductile layer where the Earth's molten material is located.
What are the three main layers of the geosphere?
-The three main layers of the geosphere are the core, the mantle, and the crust. The core is further divided into the inner and outer cores, both made up of iron and nickel alloy.
What is the source of the Earth's internal heat?
-The Earth's internal heat primarily comes from the thermal energy of the mantle, which is mostly generated by the decay of radioactive elements in the Earth's core.
What are the three significant endogenic processes that contribute to the evolution of the Earth's platforms?
-The three significant endogenic processes are magnetism (formation of magma and igneous rocks), volcanism (eruption of magma through volcanoes or cracks), and metamorphism (chemical and structural changes in rocks due to heat and pressure).
What are the four types of geological stress?
-The four types of geological stress are compressional stress (rocks pushing against each other), tensional stress (rocks being pulled apart), shearing stress (rocks sliding past each other), and confining stress (uniform pressure causing the crust to compact).
What is weathering and what are its three main types?
-Weathering is the process of disintegration of rocks, soil, and minerals due to contact with the Earth's subsystems. The three main types are physical or mechanical weathering, biological weathering, and chemical weathering.
How does chemical weathering affect rocks?
-Chemical weathering involves chemical reactions that break down rocks, often resulting in the formation of new minerals and sometimes altering the original properties of the rock or soil. Examples include oxidation, hydrolysis, and reactions with acid rain.
What is erosion and how does it occur?
-Erosion is the process where rock debris or soil is transported from one place to another, typically due to natural agents like rainfall, surface runoff, flooding, freezing, or wind.
What is mass wasting and what are its effects?
-Mass wasting is the movement of large masses of material down the slope of a hill or mountain due to gravity. It can be very destructive, causing significant changes to the landscape and potentially damaging ecosystems.
What is sedimentation and how does it contribute to the formation of new ground layers?
-Sedimentation is the build-up of materials such as soil, rock fragments, and particles that settle on the ground over time. This layer of sediment can become thick and eventually form a new layer of ground, such as ocean basins, through a process called cementation.
What is the conclusion the script draws about the inevitability of destruction and its role in creation?
-The script concludes that destruction is inevitable and not necessarily a bad thing. It suggests that destruction can lead to creation, and in the context of personal growth, the challenges we face that cause 'destruction' within us can serve as a catalyst for becoming better versions of ourselves.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

TENAGA ENDOGEN DAN EKSOGEN

Tenaga Endogen - Dinamika Litosfer - Materi Geografi

Endogenic and Exogenic Forces | Learn with LEAD | LEAD

Geografi Kelas X (20) Tenaga Pembentuk Muka Bumi | Tenaga Endogen dan Eksogen

Endogenic and Exogenic Processes - Earth and Life Science
Tenaga Endogen Part 1 : TEKTONISME
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)