Kuliah Fisiologi Respirasi - dr. Yose Ramda Ilhami, Sp.JP
Summary
TLDRThis educational script delves into the physiology of respiration, detailing the structure of the respiratory system from the nasal cavity to the alveoli. It explains the process of ventilation, gas exchange between the lungs and blood, and the five main functions of respiration. The script also discusses the mechanics of breathing, including inspiration and expiration, and the importance of compliance and elasticity in the lungs. It highlights the role of surfactant produced by Type 2 alveolar cells in preventing alveolar collapse, providing a foundational understanding of respiratory physiology.
Takeaways
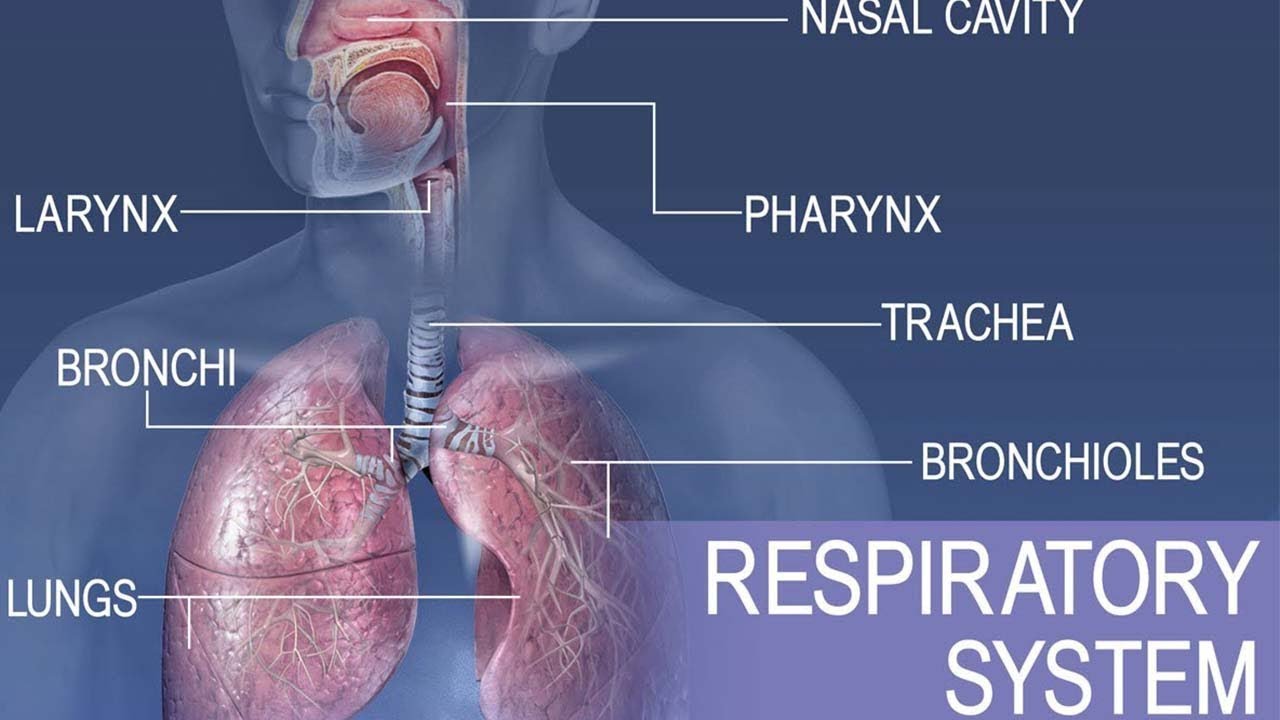
- 🌟 The respiratory system involves a complex structure starting from the nasal cavity, mouth, pharynx, epiglottis, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and ending at the alveoli.
- 🔍 The process of respiration is composed of four main components: ventilation, external respiration (gas exchange between the lungs and blood), internal respiration (gas exchange between blood and tissues), and production of sound.
- 🏗️ The thoracic cavity consists of the ribcage, vertebrae, and sternum, which house vital organs for respiration and cardiovascular functions.
- 💨 Ventilation is the active process of inhaling air into the lungs and exhaling it out, driven by the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
- 🔄 The diaphragm and intercostal muscles play a crucial role in the active inhalation process by increasing the thoracic volume, thus decreasing the intrathoracic pressure and allowing air to enter the lungs.
- 🔻 Expiratory process is generally passive, relying on the recoil of the lungs due to their elasticity, which pushes air out when intra-alveolar pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure.
- 💧 The role of respiration includes gas exchange, maintaining acid-base balance, and also involves the production of sound and metabolic functions.
- 🌀 The respiratory system is divided into two zones: the conducting zone, which does not exchange gases, and the respiratory zone, where gas exchange occurs.
- 🌐 The alveoli are the primary site of gas exchange, with a large surface area and thin barriers between the alveolar cells and the capillaries, facilitating rapid diffusion.
- 🛡️ Surfactant, produced by type II alveolar cells, reduces surface tension and prevents the alveoli from collapsing, which is critical for the respiratory function, especially in premature infants.
- 🌿 Understanding the mechanics of the respiratory system is essential for grasping the overall physiology of respiration, including the role of compliance and elasticity in lung function.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video script?
-The main topic discussed in the video script is the physiology of respiration, including the structure of the respiratory system, the process of breathing, and the gas exchange mechanism.
What are the components of the respiratory system mentioned in the script?
-The components of the respiratory system mentioned include the nasal cavity, mouth, pharynx, epiglottis, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveolar sacs, and alveoli.
What is the function of the epiglottis in the respiratory system?
-The epiglottis functions to prevent food and liquids from entering the trachea during swallowing, thus protecting the airway.
How many lobes are there in the right lung and what are they called?
-The right lung has three lobes, which are the upper lobe, middle lobe, and lower lobe.
What are the two main processes of breathing mentioned in the script?
-The two main processes of breathing mentioned are inspiration (inhalation) and expiration (exhalation).
What is the significance of the diaphragm in the process of inspiration?
-The diaphragm plays a crucial role in inspiration by contracting and moving downward, which increases the volume of the thoracic cavity and decreases the pressure, allowing air to be drawn into the lungs.
What is the role of surfactant in the alveoli?
-Surfactant, produced by type II alveolar cells, reduces surface tension in the alveoli, preventing them from collapsing and making it easier for the lungs to expand during inhalation.
What is the primary process that occurs in the alveoli for gas exchange?
-The primary process that occurs in the alveoli for gas exchange is diffusion, where oxygen moves from the air into the blood, and carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli.
What is the term used to describe the remaining air in the lungs after a full exhalation?
-The term used to describe the remaining air in the lungs after a full exhalation is residual volume.
How does the script describe the process of gas exchange in the respiratory system?
-The script describes the process of gas exchange as involving external respiration (gas exchange between the lungs and blood) and internal respiration (gas exchange between the blood and body tissues).
What are the two zones mentioned in the script for the respiratory tract?
-The two zones mentioned for the respiratory tract are the conducting zone, which includes structures that air passes through before reaching the area of gas exchange, and the respiratory zone, where the actual gas exchange occurs.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Anatomi Fisiologi Sistem Respirasi

Układ oddechowy! Drogi oddechowe i płuca, budowa i funkcje narządów. Głęboki wdech...i zaczynamy!!!

The Respiratory System CRASH COURSE

Anatomy & Physiology of Respiratory System

BIOLOGI SMA Kelas 11 - Sistem Pernapasan | GIA Academy
Anatomy and physiology of Respiratory system
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)