Signals Indicating Coherence
Summary
TLDRThis video script offers a comprehensive guide to enhancing coherence in writing through the strategic use of transition signals. It categorizes these signals into four types: additive, adversative, causal, and sequential, providing examples for each to illustrate their role in logically connecting ideas. The presentation emphasizes the importance of these 'bridges' in creating a clear and compelling narrative, suggesting that understanding and applying them effectively can be achieved through continuous reading and writing practice.
Takeaways
- 📝 Writing can be challenging, and coherence is key to logically connecting ideas in sentences and paragraphs.
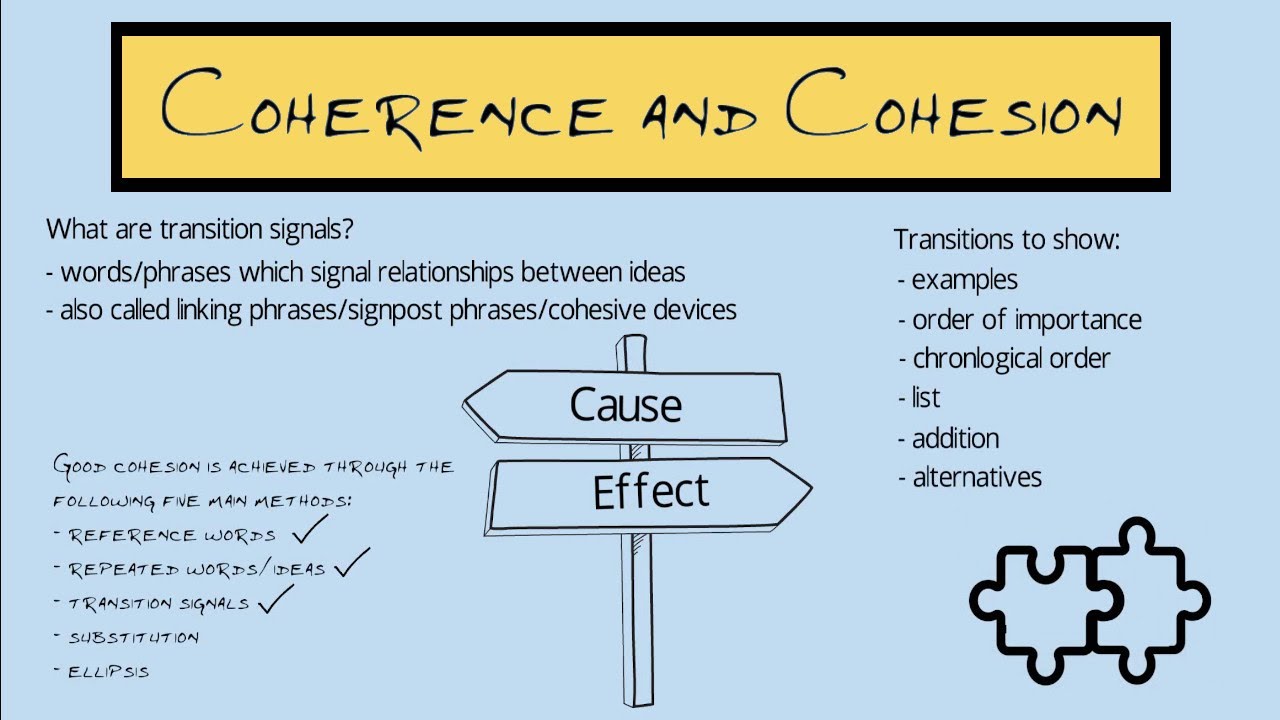
- 🔗 Coherence is established through the use of transition signals that signify different meanings and contexts.
- 🔄 Four main classifications of transition signals were discussed: additive, adversative, causal, and sequential.
- 🚀 Additive transitions are used to add similar ideas, introduce additional thoughts, provide examples, restate or explain, and summarize.
- 🔄 Adversative transitions introduce opposition or contrast to an idea, emphasizing or clarifying a point.
- ⚠️ Causal transitions indicate a consequence or result, linking actions to their outcomes.
- 🔄 Sequential transitions show the order of ideas, events, or actions, providing a clear sequence.
- 🌐 Examples of transition signals were provided for each classification, demonstrating their use in sentences.
- 📚 Learning to use transition signals effectively can improve writing and speaking by creating clearer, more coherent messages.
- 📈 Constant reading and writing practice can help in understanding and applying transition signals correctly.
- 📢 The importance of using transition signals as 'bridges' to link ideas was emphasized for better coherence.
- 👏 The video lecture encourages viewers to subscribe for more content and to practice using the discussed transition signals.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video lecture?
-The main topic of the video lecture is the use of transition signals to establish coherence in writing and speaking.
Why are transition signals important in writing and speaking?
-Transition signals are important because they help to establish a systematic logical connection or consistency in sentences and text, making the presentation of information clear and comprehensible.
How many classifications of transition signals are discussed in the video?
-The video discusses four classifications of transition signals: additive, adversative, causal, and sequential.
What are additive transitions used for?
-Additive transitions are used to add a similar idea, introduce an additional idea, provide an example or illustration, offer a restatement or explanation, or draw to a close or summarize.
Can you give an example of an additive transition signal and its use in a sentence?
-An example of an additive transition signal is 'likewise'. In a sentence: 'We should be careful with the coronavirus disease that makes our respiratory system weak, likewise the HIV/AIDS that makes our immune system frail.'
What is the purpose of adversative transitions?
-Adversative transitions are used to introduce an opposition to an idea, contrast, or to emphasize or clarify a point.
How can 'even though' be used as an adversative transition signal in a sentence?
-'Even though' can be used to introduce a contrast between two opposing situations, such as: 'Even though the country is experiencing great economic loss due to this pandemic, it has continued helping other countries by sending our medical frontliners and other essential materials.'
What does the video say about causal transitions?
-Causal transitions indicate a consequence or a result, and are used to show the outcome of an action or event.
Can you provide a sentence example using the causal transition 'as a result'?
-A sentence example using 'as a result' could be: 'The students reviewed their lessons well before their exams, as a result they passed the school's assessment process.'
What is the role of sequential transitions in writing or speaking?
-Sequential transitions indicate the order of ideas, events, or actions, helping to lay down a clear sequence from the first to the last one.
How can 'firstly', 'then', and 'lastly' be used in a sentence to show sequence?
-These sequential transition signals can be used in a sentence like this: 'My mother cooked our favorite breakfast, after eating she washed the dishes and other utensils, then she swept the floor and cleaned the whole house, lastly she took a well-deserved rest.'
What is the final advice given in the video regarding the use of transition signals?
-The final advice is that learning to use transition signals can be challenging, but understanding their uses can be gradually achieved through constant reading and writing practices.
Who is acknowledged as the content source for the video lecture?
-Pivot 4a learner's material for English 8 is acknowledged as the content source for the video lecture.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)