ANIMATED CONIC SECTION
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial video delves into the fascinating world of conic sections, exploring their generation from the intersection of a plane with two cones. It explains the formation of an ellipse when the plane is not parallel to the cone's base, a parabola when it cuts through one cone's base, and a hyperbola when slicing through both. Special attention is given to the degenerate cases, including points, lines, and intersecting lines, formed under specific cutting conditions. The video concludes by summarizing the four primary conic sections and their unique characteristics.
Takeaways
- 📚 The script introduces the concept of conic sections and their generation from the intersection of a plane with two cones.
- 📏 The figure formed by the intersection of a vertical line and another line is called a double knob right, circular cone, with the vertical line being the axis and the point of intersection the vertex.
- 🔍 The two distinct lines on the cone are known as the generators, and the two circles formed are the bases of the cone.
- 🌀 The parts of the cone referred to as 'lowering up' and 'upper nap' are described, though the exact terms may be misheard or misspoken in the script.
- 🔪 The conic sections are formed by the intersection of a plane with the cones, with different results depending on the orientation and position of the plane relative to the cones.
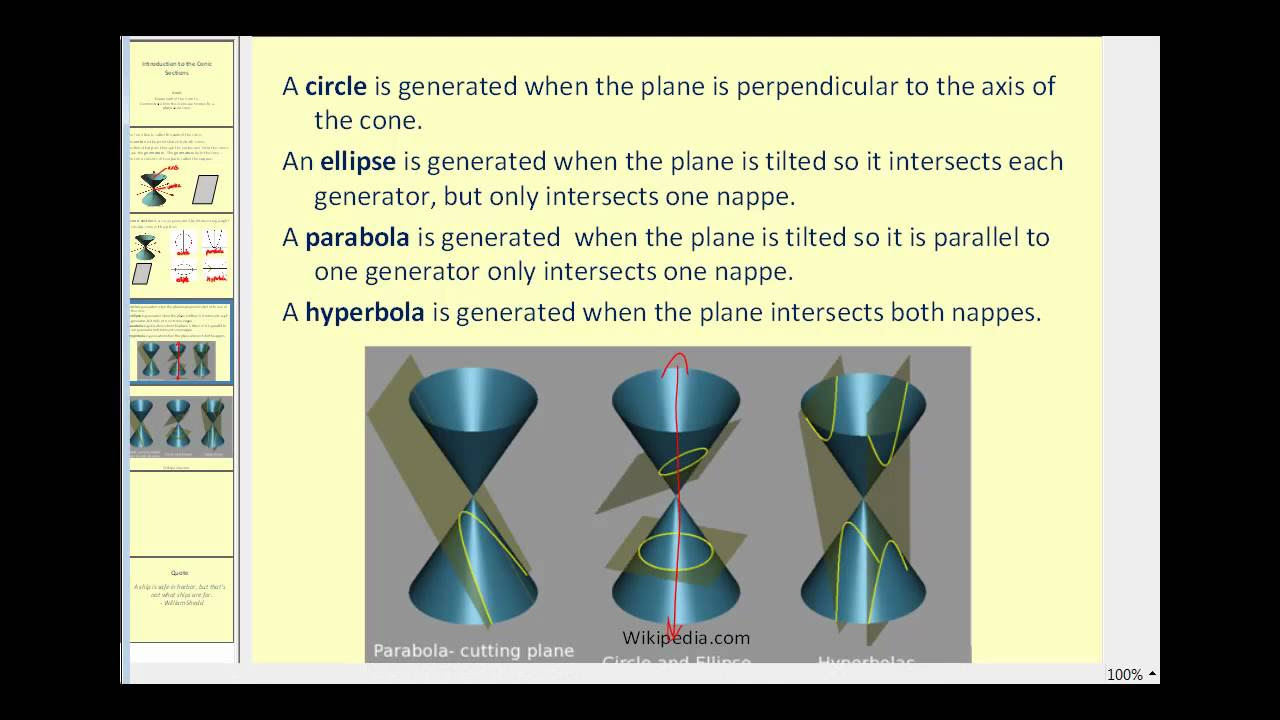
- 🌕 A circle is formed when the plane is parallel to the cone's base and passes through both cones.
- 🥚 An ellipse is created when the plane is not parallel to the base and does not pass through both bases.
- 🚀 A parabola is the result of a plane cutting through only one nap of the cone and passing through that cone's base.
- 🌌 A hyperbola is formed when the plane cuts through both naps of the cones and passes through the bases of both.
- 📝 The script summarizes the four conic sections as ellipse, circle, parabola, and hyperbola, with the circle being a special case of an ellipse.
- 📐 Degenerate cases are also discussed, where the plane's orientation and position relative to the cones result in figures such as a single point, a line, or intersecting lines.
Q & A
What is a conic section?
-A conic section is a curve obtained by intersecting a cone with a plane. It can result in an ellipse, a circle, a parabola, or a hyperbola, depending on the angle and position of the intersecting plane.
What are the four types of conic sections?
-The four types of conic sections are ellipse, circle, parabola, and hyperbola.
What is the special relationship between a circle and an ellipse?
-A circle is a special type of ellipse where the two axes of the ellipse are of equal length, making it perfectly round.
What is the term used for the line that intersects the vertical line to form a double-knob right circular cone?
-The line that intersects the vertical line to form a double-knob right circular cone is called the axis of the cone.
What are the generators of a cone?
-The generators of a cone are the two distinct lines that form the sides of the cone, connecting the vertex to the edges of the base circles.
What is the term for the part of the cone that is referred to as the 'lowering up' in the script?
-The term 'lowering up' seems to be a mispronunciation or error in the script; it likely refers to the 'lower nap' or the lower half of the cone.
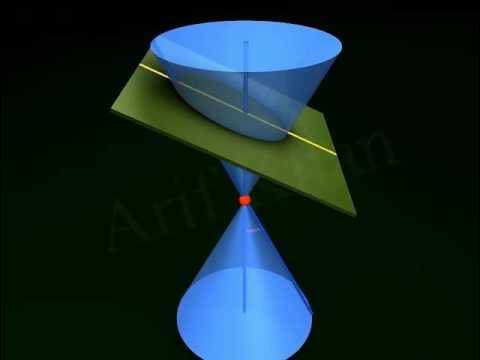
What happens when a plane is parallel to the bases of the cone and passes through the cones?
-When a plane is parallel to the bases of the cone and passes through the cones, it forms a circle.
What figure is formed when a cutting plane is not parallel to the base of the cone and does not pass through the bases?
-When a cutting plane is not parallel to the base of the cone and does not pass through the bases, an ellipse is formed.
What is a parabola?
-A parabola is a conic section formed when a plane cuts only one nap of the cone and passes through the base of that cone.
What is a hyperbola?
-A hyperbola is a conic section formed when a plane cuts both naps of the two cones and passes through the bases of the two cones.
What are the degenerate cases of conic sections?
-The degenerate cases of conic sections occur when the cutting plane is in a specific position relative to the cone, resulting in figures such as a point, a line, or two intersecting lines, instead of the typical conic sections.
What figure is formed when the cutting plane is parallel to the base of the cone and passes exactly at the vertex?
-When the cutting plane is parallel to the base of the cone and passes exactly at the vertex, the figure formed is just a point.
What happens when the cutting plane is parallel to the generator of the cone and passes through the vertex?
-When the cutting plane is parallel to the generator of the cone and passes through the vertex, the figure formed is a line.
What is the result when the plane cuts both naps of the cones and passes through the vertex?
-When the plane cuts both naps of the cones and passes through the vertex, the result is two intersecting lines.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Introduction to Conic Sections

Conic Section 3D Animation | explain conic section one shot | hyperbola and parabola
Conic Section 3D Animation

Irisan Kerucut Matematika Kelas 11 • Part 1: Macam-Macam (Lingkaran, Parabola, Elips, Hiperbola)

Intro to Conic Sections | Pre Calculus | STEM Math

What are Conic Sections? | Don't Memorise
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
