Conic Section 3D Animation | explain conic section one shot | hyperbola and parabola
Summary
TLDRThis educational script introduces conic sections, which are two-dimensional curves formed when a plane intersects a double right circular cone. It explains the cone's structure, including the vertex, axis, and generator, and defines the three main types of conic sections: ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. The summary also touches on the special case of a circle, a type of ellipse, and degenerate conics, which occur when the plane intersects at the cone's vertex. The module aims to provide a foundational understanding of these geometric figures and their formation.
Takeaways
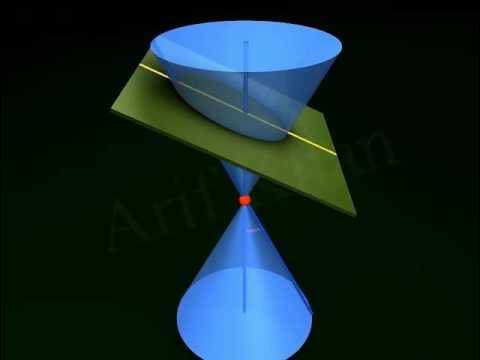
- 📚 Conic sections are two-dimensional curves formed when a plane intersects a double right circular cone.
- 🔄 The double right circular cone is made up of two cones joined at a fixed point called the vertex.
- 📐 The line that rotates around the vertex is known as the generator, and the fixed line is the axis.
- 🌐 A right circular cone has a circular base with its axis perpendicular to a line from the base's center to the vertex.
- 🔶 The perimeter of the cone's base is referred to as the directrix.
- 💭 The lateral surface of a right circular cone is called a nap, with the upper and lower naps being distinct sections.
- 📐 The angle between the generator and the axis is termed the vertex angle.
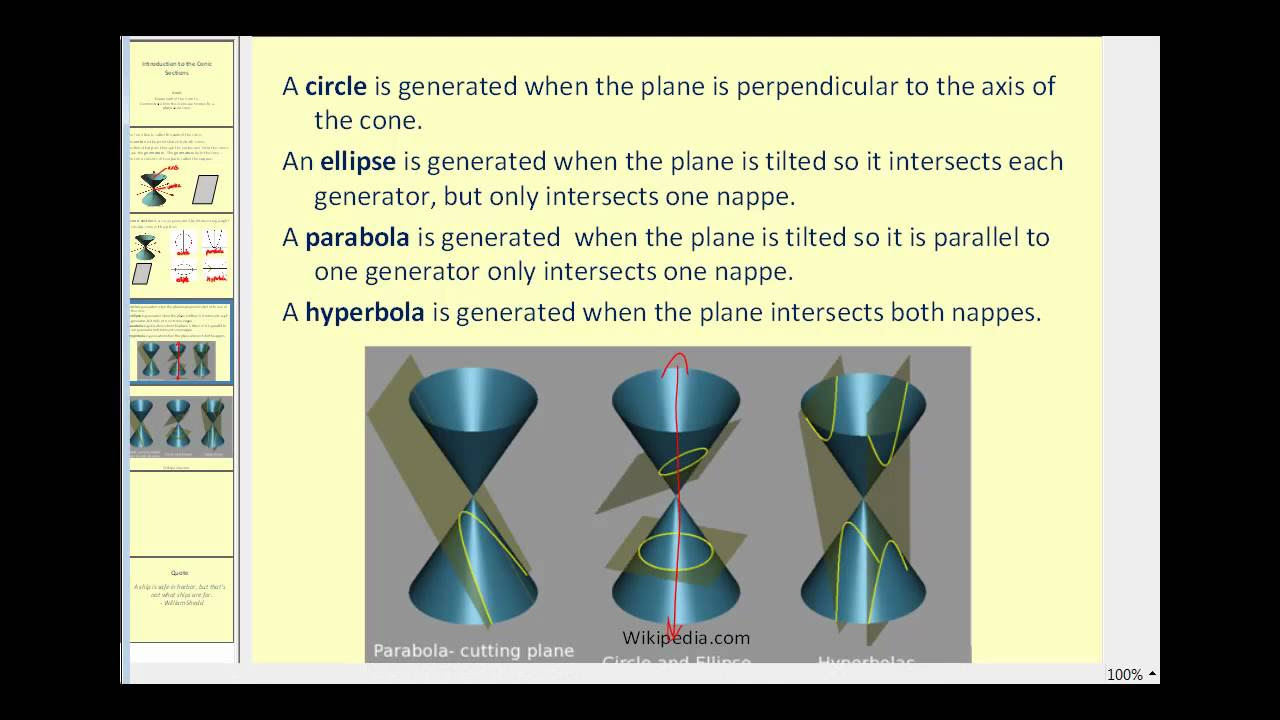
- 🌍 Depending on the angle of intersection with the cone's axis, the plane can create three types of conic sections: ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola.
- 🔶 An ellipse is formed when the plane intersects the cone at an angle greater than the vertex angle but not perpendicular to the axis.
- ⭕ A circle is a special case of an ellipse, occurring when the intersecting plane is perpendicular to the axis.
- 📈 A parabola is created when the plane's angle with the vertical axis is exactly equal to the vertex angle.
- 📉 A hyperbola results when the plane intersects at an angle less than the vertex angle, or only one nap of the cone if the angle is greater than or equal to the vertex angle.
- 🚫 Degenerate conics occur when the plane intersects the cone at its vertex, resulting in a point for an ellipse, a line for a parabola, and two intersecting lines for a hyperbola.
Q & A
What is a conic section?
-A conic section is a two-dimensional curve formed when a plane intersects a double right circular cone.
What is a double right circular cone?
-A double right circular cone consists of two cones joined at a fixed point called the vertex. The line that rotates about the vertex is called the generator, and the line that remains fixed is called the axis.
What is the significance of the vertex in a double right circular cone?
-The vertex is the fixed point at which the two cones of a double right circular cone are joined. The line that rotates about the vertex is called the generator.
What is the axis of a right circular cone?
-The axis of a right circular cone is the line that passes from the center of the base to the vertex, and it is always perpendicular to the base.
What is the directrix in the context of a right circular cone?
-The directrix is the perimeter of the base of a right circular cone.
What is the lateral surface of a right circular cone called?
-The lateral surface of a right circular cone is called a nap.
How many types of naps does a double right circular cone have?
-A double right circular cone has two naps: the upper nap above the vertex and the lower nap below the vertex.
What is the vertex angle in relation to a conic section?
-The vertex angle is the angle between the generator and the axis of the cone.
What type of conic section is formed when the plane intersects the cone with an angle greater than the vertex angle?
-An ellipse is formed when the plane intersects the cone with an angle greater than the vertex angle.
What happens when the plane is perpendicular to the axis of the cone?
-When the plane is perpendicular to the axis, the ellipse becomes a circle, which is a special type of ellipse.
What is a parabola and how is it formed?
-A parabola is an open curve formed when the plane intersects the cone with an angle equal to the vertex angle.
What is a hyperbola and under what condition is it formed?
-A hyperbola is an open curve formed when the plane intersects the cone with an angle less than the vertex angle, intersecting both naps of the cone.
What are degenerate conics and how do they form?
-Degenerate conics are figures formed when a plane intersects the double right circular cone at its vertex. They include a point (from an ellipse), a line (from a parabola), and two intersecting lines (from a hyperbola).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)