Capillary Electrophoresis (Part 2): Instrumentation & Electroosmotic Flow
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of capillary electrophoresis (CE) is explored, focusing on its instrumentation and key mechanisms. The CE setup involves silica capillaries, buffer reservoirs, and electrodes, with samples introduced at one end and detected at the other. The video highlights two main principles: electroosmotic flow (EOF) and electrophoretic mobility. EOF governs the movement of solutions in the capillary, driven by charged layers at the silica surface, while electrophoretic mobility facilitates the separation of ions and neutral species. The unique flat flow profile in CE ensures higher separation efficiency and resolution compared to HPLC, making it a powerful technique for analysis.
Takeaways
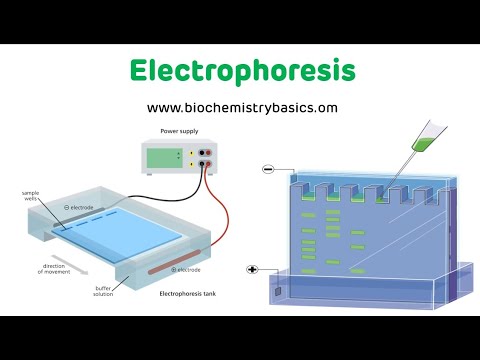
- 😀 Capillary electrophoresis (CE) uses a silica capillary between two buffer reservoirs to separate samples based on their charge.
- 😀 The process is powered by a high-voltage power supply, and a detector is placed at the opposite end of the capillary.
- 😀 The separation mechanism involves two key processes: electroosmotic flow and electrophoretic mobility.
- 😀 Electroosmotic flow refers to the movement of buffer solution through the capillary, driven by the charge interactions between the buffer and the silica surface.
- 😀 The electroosmotic flow is influenced by the zeta potential at the solvent-silica interface, which affects the movement of the solution inside the capillary.
- 😀 The capillary walls are coated with silica, which has silanol groups that are pH-dependent, leading to a negatively charged surface when pH is high.
- 😀 At pH values above 9, the silanol groups are mostly deprotonated, creating a negatively charged capillary surface that attracts positively charged ions from the buffer.
- 😀 The electroosmotic flow is directed toward the cathode when a voltage is applied, as positively charged ions are drawn toward the negatively charged electrode.
- 😀 The electroosmotic flow results in a flat flow profile, unlike the parabolic flow observed in pressure-driven systems like HPLC.
- 😀 The flat flow profile in CE minimizes band broadening, improving peak resolution and separation efficiency compared to traditional HPLC methods.
- 😀 The next step in capillary electrophoresis will involve understanding how electrophoretic mobility contributes to the separation of ions, cations, and neutral species.
Q & A
What is Capillary Electrophoresis (CE)?
-Capillary Electrophoresis (CE) is an analytical technique used for separating charged species, such as ions, cations, and neutral molecules, by applying an electric field in a narrow silica capillary.
What are the main components of the instrumentation used in CE?
-The main components of CE include a silica capillary, buffer reservoirs with platinum electrodes, a high voltage power supply, a sample valve, and a detector placed at the other end of the capillary.
What is Electroosmotic Flow (EOF) in CE?
-Electroosmotic Flow (EOF) is the movement of the buffer solution through the silica capillary, driven by the attraction of cations towards the negatively charged cathode, which drags the bulk solution along with it.
How does the electroosmotic flow contribute to the separation process in CE?
-The electroosmotic flow drives the movement of the solution in the capillary, creating a flat flow profile that reduces band broadening and increases separation resolution and efficiency compared to pressure-driven flow systems like HPLC.
Why does the silica surface play a key role in EOF?
-The silica surface is negatively charged due to deprotonation of silanol groups at higher pH levels. This negative charge attracts positively charged cations, forming a fixed layer, which facilitates the electroosmotic flow when a voltage is applied.
What happens when a voltage is applied across the capillary in CE?
-When a voltage is applied across the capillary, the cations in the diffuse layer move toward the cathode, pulling the bulk solution with them, resulting in electroosmotic flow.
How does the flow profile in CE differ from that of HPLC?
-In CE, the flow profile is flat due to electroosmotic flow, whereas in HPLC, the flow is parabolic due to pressure-induced flow, leading to better resolution and efficiency in CE.
What is the role of electrophoretic mobility in CE?
-Electrophoretic mobility is responsible for the separation of charged species (ions and cations) in CE. It separates analytes based on their size and charge under the influence of an electric field.
How does the unique flat flow profile of EOF improve separation in CE?
-The flat flow profile minimizes band broadening, leading to sharper peaks and better resolution in the separation of analytes, which increases the efficiency of the CE process.
What are the differences in the surface chemistry of silica at different pH levels?
-At pH levels below 3, the silanol groups on the silica surface are protonated, while at pH above 9, the silanol groups are deprotonated, making the surface negatively charged. This negative charge is crucial for generating electroosmotic flow.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)