Electrophoresis
Summary
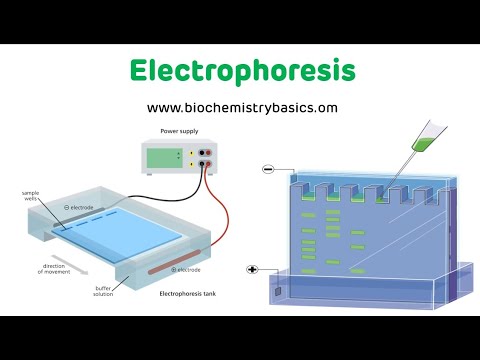
TLDRElectrophoresis is a laboratory technique used to separate charged molecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins under an electric field. The process depends on factors like voltage, current, electric field strength, and the type of buffer used. Key techniques include paper electrophoresis, agarose gel electrophoresis for nucleic acids, capillary electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE, 2D gel electrophoresis for proteins, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for large DNA fragments. Heat generation is a critical concern, controlled by adjusting current to ensure optimal separation without damaging the samples.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electrophoresis is the movement of charged particles in a liquid medium under an electric field, first discovered by a Russian professor studying clay particles.
- 😀 This technique is commonly used for the separation of biomolecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins, as they often carry a charge.
- 😀 DNA and RNA have a net negative charge, while proteins can have either a positive or negative charge depending on their amino acids.
- 😀 During electrophoresis, an electric field is applied using electrodes connected to a power pack, which also displays voltage (potential difference) and current (electricity flow).
- 😀 The electric field strength is determined by the voltage and the distance between the electrodes, measured in volts per centimeter.
- 😀 The distance between electrodes affects the speed of electrophoresis—larger distances result in a weaker electric field and longer separation times.
- 😀 Heat generated during electrophoresis is influenced by voltage, current, and the duration of the process, with the heat increasing if the current is high.
- 😀 The heat formula is H = I² R T, meaning heat increases exponentially with current, necessitating low current settings to avoid excess heat.
- 😀 Common types of electrophoresis include paper electrophoresis, agarose gel electrophoresis, capillary electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE, 2D gel electrophoresis, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis.
- 😀 Paper electrophoresis is a simple method where sample molecules are separated on a filter paper strip based on their charge.
- 😀 Agarose gel electrophoresis is primarily used for DNA and RNA separation, where molecules move from the negative to positive electrodes.
- 😀 Capillary electrophoresis involves a capillary tube and is used for small sample analyses, with sample detection via UV or IR absorption.
- 😀 SDS-PAGE is used to separate proteins by size using a vertical electrophoresis setup.
- 😀 Two-dimensional electrophoresis (2D) separates proteins in two steps: isoelectric focusing (based on pH) followed by SDS-PAGE for size-based separation.
- 😀 Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis is used for separating large DNA fragments or chromosomes by applying alternating electric fields at specific angles.
Q & A
What does the term 'electrophoresis' mean?
-Electrophoresis refers to the movement of charged particles dispersed in a liquid medium under the influence of an electric field.
Who discovered the movement of particles under an electric field?
-The movement of particles under an electric field was first discovered by a Russian professor while studying the effect of electric fields on dispersed clay particles.
Why is electrophoresis widely used for separating biomolecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins?
-Electrophoresis is used to separate biomolecules because many biomolecules, including DNA, RNA, and proteins, carry either a positive or negative charge, which allows them to migrate under an electric field.
How do the voltage and current readings relate to the electrophoresis process?
-The voltage represents the potential difference across the electrodes, and the current indicates the flow of electricity across the electrodes, both of which are crucial for regulating the electrophoresis process.
Why is the distance between electrodes important in electrophoresis?
-The distance between the electrodes is important because it affects the electric field. The electric field is calculated as the ratio of the potential difference to the distance between the electrodes, which influences the separation process.
How does the size of the electrophoresis apparatus impact the electric field?
-The electric field is inversely proportional to the distance between the electrodes. A larger distance results in a lower electric field, which can affect the time it takes for electrophoresis to be completed.
What formula relates to the heat generated during electrophoresis?
-The heat generated during electrophoresis is given by the formula H = VIT, where H is the heat, V is the voltage, I is the current, and T is the time for which electrophoresis is carried out.
Why is it important to carry out electrophoresis at a low current?
-Electrophoresis should be carried out at a low current to avoid excessive heat generation, which could interfere with the process and affect the results.
What are the types of electrophoresis mentioned in the script?
-The types of electrophoresis mentioned include paper electrophoresis, capillary electrophoresis, agarose gel electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE, pulsed field electrophoresis, and two-dimensional electrophoresis.
How does agarose gel electrophoresis separate DNA and RNA?
-In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA and RNA, which carry a negative charge, migrate towards the positive electrode. Smaller DNA fragments move faster through the gel, while larger fragments move slower.
What is the principle behind SDS-PAGE?
-SDS-PAGE is used to separate proteins based on their size. The proteins are coated with SDS to impart a uniform negative charge, and then they are separated in a gel matrix based on their molecular weight.
What is isoelectric focusing in two-dimensional electrophoresis?
-Isoelectric focusing is the first step in two-dimensional electrophoresis, where proteins are separated based on their isoelectric point (pI) in a gel with a pH gradient before undergoing separation by SDS-PAGE.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)