8. Pembebanan Pelat 2 Arah
Summary
TLDRIn this tutorial, Agus Setiawan explains the distribution of loads in a two-way plate system, a crucial concept in reinforced concrete structures. He covers the basics of a two-way plate, its load distribution to supporting beams, and how to calculate the load for different plate shapes. Using a hands-on example, the process of determining the load distribution for triangular and trapezoidal beam shapes is explained. The session also highlights practical application, including calculating reactions and total axial loads on columns. This is an essential guide for understanding load calculation in structural design.
Takeaways
- 😀 The two-way plate system is supported by beams on each side and distributes load in both directions.
- 😀 A two-way plate system is characterized by a span ratio (long l / short l) smaller than 2.0.
- 😀 In a two-way plate, load distribution is shaped like triangles for equal span lengths, and trapezoids when spans are unequal.
- 😀 When both span lengths (L1 and L2) are the same, load is distributed in a triangular pattern to each beam.
- 😀 For unequal spans (L2 > L1), load distribution changes, with beam AB bearing a triangular load and beam BD a trapezoidal load.
- 😀 The load intensity on each beam is determined by the size of the plate and the span lengths, impacting the beam’s load-bearing area.
- 😀 Load calculations involve determining both dead and live loads, with the inclusion of cement mortar and ceramics affecting the total load.
- 😀 Load distribution involves calculating reactions at each beam support, considering factors like symmetry and plate dimensions.
- 😀 The total load transferred to columns is calculated by summing up the reactions from the beams, considering the axial load at each point.
- 😀 The example structure shows a 4m by 6m plate module, with load calculations for beams AB and BD considering specific live and dead loads.
- 😀 The calculation process follows the SNI 1727 standard, considering factors like load combination and structural safety for various applications, like gym or library rooms.
Q & A
What is a two-way plate system in reinforced concrete structures?
-A two-way plate system is a type of slab supported by beams on all sides, where the load is distributed in both the short and long directions of the slab. If the ratio of the long span to short span is less than 2.0, it is considered a two-way system.
How is the load on a two-way plate system distributed to the supporting beams?
-The load on a two-way plate system is distributed in a triangular or trapezoidal shape depending on the span of the slab. For example, when the spans are equal, the load is distributed evenly, while if the spans differ, the load distribution varies between the supporting beams.
What happens when the span lengths of a two-way plate system are unequal?
-When the span lengths are unequal, the load distribution between the supporting beams changes. The load distribution on one beam may form a triangle, while the other forms a trapezoid, with the short span determining the intensity of the load.
How do you calculate the load distribution on the beams in a two-way plate system?
-To calculate the load distribution, you must analyze the shape of the load distribution (triangular or trapezoidal) and the span lengths. You then multiply the load intensity by the appropriate factor for each beam (using the short or long span lengths) to calculate the load borne by each beam.
What is the importance of the ratio between the long and short span in a two-way plate system?
-The ratio between the long and short span determines whether the system is a one-way or two-way plate. A ratio smaller than 2.0 indicates a two-way system, meaning the load is distributed in both directions. A larger ratio typically indicates a one-way plate system where the load is distributed in one direction.
How is the dead load of a two-way plate calculated?
-The dead load is calculated by considering the thickness of the concrete slab, the density of the concrete, and any additional layers such as cement mortar and ceramics. These are multiplied by the thickness or area to get the total dead load.
What factors are considered when calculating live loads for a two-way plate system?
-Live loads are calculated based on the intended use of the building (e.g., library, gym, etc.), and factors such as the weight of the ceiling, ducting, and other systems that contribute to the load must also be accounted for.
What is a load combination in the context of structural design?
-A load combination is a method used to account for different types of loads (such as dead loads and live loads) acting simultaneously on a structure. These combinations are selected to ensure the structure can withstand the greatest possible load scenarios.
How is the reaction force calculated for a beam in a two-way plate system?
-The reaction force for a beam is calculated by determining the load intensity on the beam and multiplying it by the length of the span. This reaction is then divided according to the distribution pattern (triangular or trapezoidal) and used to find the support reactions at the beam’s ends.
How does the load distribution affect the columns in a two-way plate system?
-The load distributed to the beams ultimately reaches the columns, which must bear the axial loads. The total axial load on each column is the sum of the loads from the beams connected to that column. This must be accounted for to ensure the columns are adequately sized.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

3. Metode Direct Design Method

1. Kupas Tuntas Teknologi Beton

Desain Pelat 2 Arah Beton Bertulang - Part 1 Konsep SNI 2847-2019

Desain Balok Beton Bertulang Tulangan Tunggal | Penampang Persegi | Konsep dan Prosedur Desain

Basics of Structural Design Load Calculations | One-Way Vs Two-Way Slab
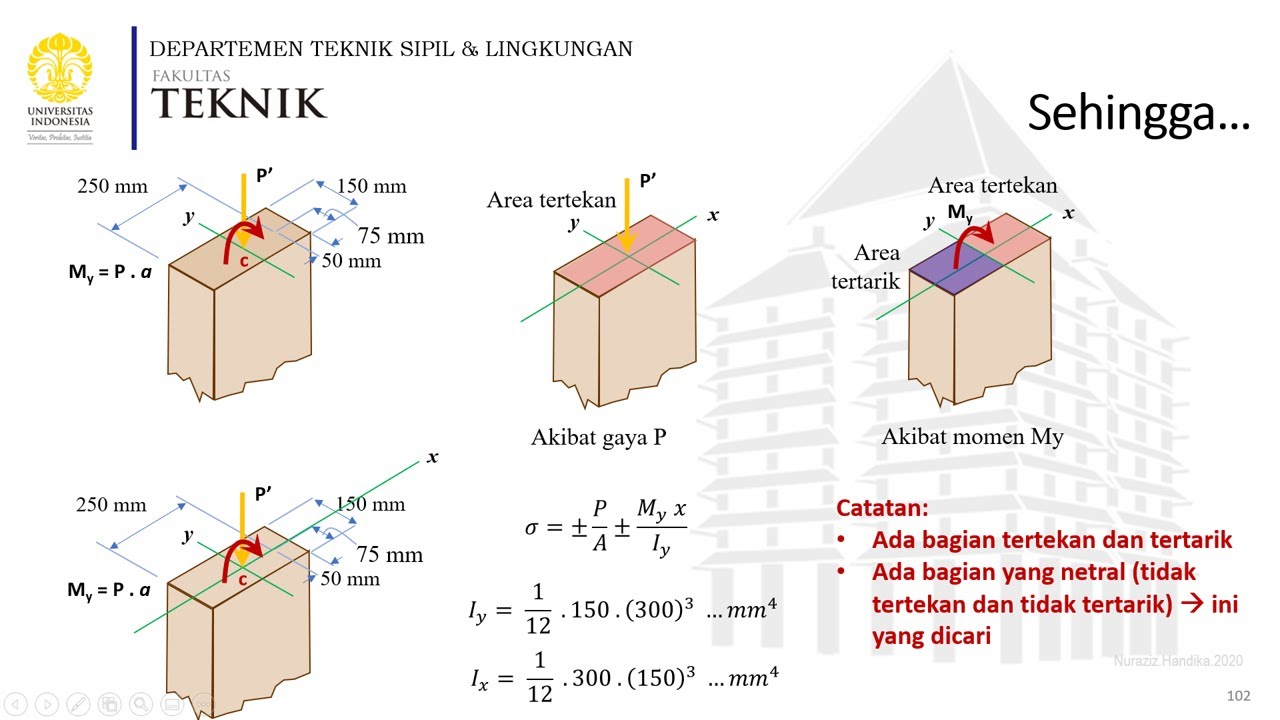
Normal stress due to axial and bending moment - Tegangan normal akibat gaya dalam momen lentur - 7
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
