Exponential growth and epidemics
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the concept of exponential growth, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. It explains how exponential growth leads to rapid increases in cases, driven by the multiplication of existing cases. Through the lens of mathematical modeling, the script discusses the logistic curve, which eventually caps exponential growth. The video also highlights the significance of growth factors and how small changes in infection rates can drastically alter projections. The narrative emphasizes the importance of understanding these dynamics to predict when the growth will slow down and the critical role of preventative measures like social distancing and handwashing.
Takeaways
- 😀 Exponential growth can be hard to grasp intuitively, as small numbers can quickly escalate into very large ones.
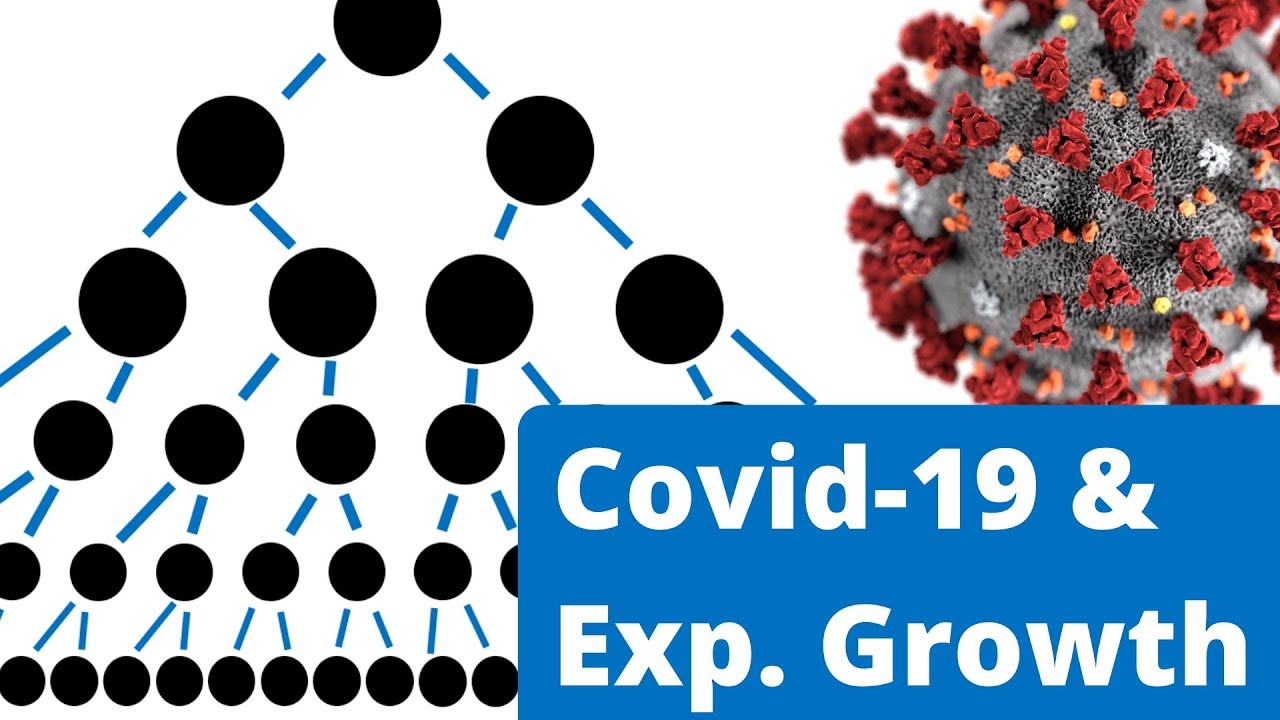
- 😀 COVID-19 is a perfect example of exponential growth, where each day's new cases are a multiple of the previous day's cases.
- 😀 Viruses spread through exponential growth because new infections come from existing cases, causing rapid escalation.
- 😀 In exponential growth, a constant factor (e.g., the multiplication factor between days) causes the numbers to increase at an accelerating rate.
- 😀 A logarithmic scale on a graph can help visualize exponential growth, turning it into a straight line and revealing the growth rate.
- 😀 In exponential models, it took just 20 days to increase from 100 to 1000 cases and 13 more days to reach 10,000, demonstrating rapid escalation.
- 😀 Exponential growth can make countries with smaller case numbers seem fine, but they could be a month behind larger countries experiencing the same trend.
- 😀 If the exponential trend continues, cases could escalate to billions in a short period, but growth will inevitably slow down eventually.
- 😀 Exponential growth models eventually transition into logistic growth curves when the population reaches a saturation point and growth begins to slow.
- 😀 The inflection point, where the growth rate transitions from increasing to decreasing, is a key moment in epidemic models and indicates when growth will begin to plateau.
- 😀 The growth factor is a key indicator of whether exponential growth is continuing or if it has reached an inflection point, where the growth rate is slowing down.
- 😀 Changes in exposure and infection rates (e.g., through behavioral changes like reducing gatherings or better hygiene) can significantly alter the trajectory of an epidemic.
Q & A
What is exponential growth, and why is it difficult for people to recognize?
-Exponential growth refers to a situation where a quantity grows by a consistent multiplicative factor over time. It can be difficult for people to recognize because they often anchor on small numbers and fail to notice how quickly the numbers can grow as the process accelerates.
How does exponential growth relate to the spread of viruses like COVID-19?
-Exponential growth in viruses occurs because the number of new cases is proportional to the number of existing cases. Each infected person exposes others to the virus, multiplying the number of cases by a constant factor each day.
What is the basic formula for exponential growth in the context of a virus outbreak?
-The number of new cases each day is calculated by multiplying the number of existing cases by a constant factor, which is the product of the average number of people each infected person is exposed to and the probability of those exposures leading to new infections.
How can a logarithmic scale help visualize exponential growth?
-On a logarithmic scale, each step on the y-axis represents a multiplication by a constant factor. This allows exponential growth to appear as a straight line, making it easier to see the consistent multiplicative increase over time.
What does a linear regression of exponential growth data tell us?
-A linear regression of exponential growth data helps quantify the rate at which cases are multiplying. It can show the average factor by which cases increase (e.g., multiplying by 10 every 16 days) and provide a better understanding of the overall growth trend.
What is the significance of the growth factor in tracking the spread of a virus?
-The growth factor is the ratio between the number of new cases one day and the number of new cases the previous day. A growth factor consistently above 1 indicates exponential growth, while a value close to 1 suggests the growth rate is slowing, possibly indicating the start of the inflection point.
What is the inflection point in exponential growth, and why is it important?
-The inflection point is when the growth rate of new cases starts to slow down and eventually levels off. It marks the shift from exponential growth to the saturation phase, where the number of new cases stops increasing and begins to decrease.
How does a logistic curve differ from pure exponential growth?
-A logistic curve starts off looking like exponential growth but eventually levels off as the total population becomes saturated. The growth rate slows down because the number of uninfected individuals decreases, limiting new infections.
Why do exponential growth models eventually slow down, even in the worst-case scenarios?
-Exponential growth slows down because, over time, a larger proportion of the population becomes infected, reducing the number of susceptible individuals. This leads to a decrease in the probability of further infections and ultimately slows the spread.
How can human actions, like social distancing and handwashing, impact the rate of exponential growth?
-Human actions, such as reducing exposure by social distancing and improving hygiene by washing hands, can significantly lower the infection rate. These actions decrease the constant factor (the exposure and infection rate), potentially preventing the growth from continuing at exponential rates.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Fungsi Eksponen Matematika Peminatan Kelas X - Apersepsi Masalah COVID-19

CARA PENULARAN DAN PENCEGAHAN PANDEMI COVID 19 DALAM MATEMATIKA

Ini Kata Jerinx Soal Konspirasi Corona

How the advancement of technology is affecting community | Chris Stamatopoulos | TEDxHopeCollege

Sustainability Hub: SDG3 – Health and Wellbeing
Algebra 5.1 (Version A) - Exponential Growth
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
