Hambatan Pengganti Rangkaian Seri, Paralel Dan Campuran
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial offers a clear and step-by-step guide to calculating equivalent resistance in electrical circuits, focusing on both series and parallel configurations. It explains how to add resistances in series (simply by summing them) and how to calculate equivalent resistance in parallel circuits using the reciprocal formula. The video also covers more complex combinations of series and parallel circuits, offering practical examples with detailed solutions. Viewers will learn to solve various circuit problems, making this tutorial an invaluable resource for anyone seeking to understand the basics of electrical resistance calculations.
Takeaways
- 😀 In a series circuit, the equivalent resistance is found by simply adding up the individual resistances (R = R1 + R2).
- 😀 For a series circuit with resistances of 2 Ohm and 3 Ohm, the total resistance is 5 Ohms (R = 2 + 3).
- 😀 In a series circuit with resistances of 3 Ohm, 4 Ohm, and 6 Ohm, the total resistance is 13 Ohms (R = 3 + 4 + 6).
- 😀 For parallel circuits, the reciprocal formula 1/Rp = 1/R1 + 1/R2 is used to calculate the equivalent resistance.
- 😀 To calculate the equivalent resistance of a parallel circuit with 2 Ohm and 3 Ohm resistances, find a common denominator for the fractions: 1/2 + 1/3 = 5/6, then invert the fraction to get Rp = 6/5, or 1.2 Ohm.
- 😀 When calculating the equivalent resistance of a parallel circuit with 3 resistances (3 Ohm, 4 Ohm, and 6 Ohm), use the reciprocal formula 1/Rp = 1/3 + 1/4 + 1/6, and find the least common multiple (LCM) for the fractions.
- 😀 In a parallel circuit with resistances of 3 Ohm, 4 Ohm, and 6 Ohm, the equivalent resistance is 4/3 or 1.33 Ohms after simplifying the reciprocal sum.
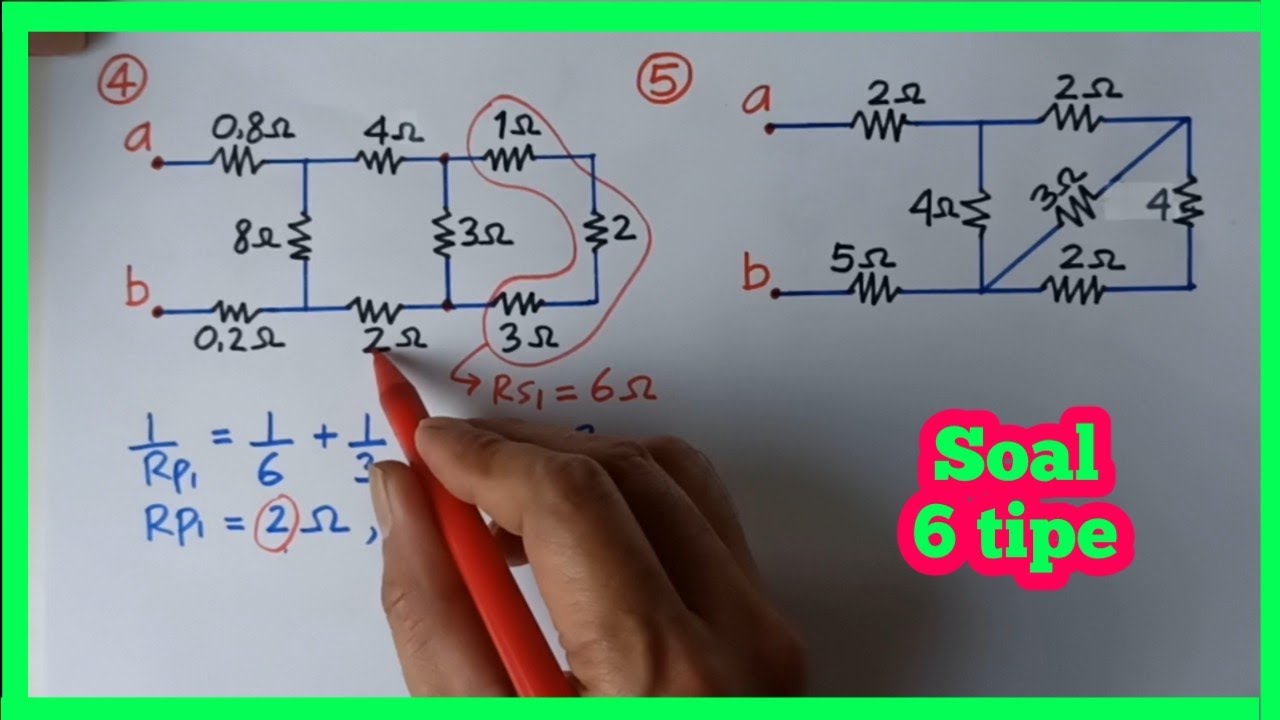
- 😀 For a parallel circuit with two series circuits connected, first calculate the resistance of each series part (e.g., R1 + R2 = 6 Ohms, R3 + R4 = 9 Ohms), then apply the parallel formula 1/Rp = 1/Rs1 + 1/Rs2.
- 😀 When two series circuits with 6 Ohm and 9 Ohm resistances are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance is 3.6 Ohms after applying the parallel formula.
- 😀 In a combination of series and parallel circuits, first calculate the parallel resistance, then add the series resistances to get the total equivalent resistance (e.g., R1 + R_parallel + R4 = 12.8 Ohms).
Q & A
What is the method to calculate the equivalent resistance in a series circuit?
-In a series circuit, the equivalent resistance is found by simply adding up the individual resistances. For example, if two resistors are 2 Ohms and 3 Ohms, the equivalent resistance (Rs) is 2 + 3 = 5 Ohms.
How do you calculate the equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit?
-For parallel circuits, the formula used is 1/Rp = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ... For example, for two resistors of 2 Ohms and 3 Ohms, 1/Rp = 1/2 + 1/3. After finding the common denominator, you calculate the reciprocal to find Rp.
What is the method to calculate the equivalent resistance of multiple resistors in parallel?
-When there are multiple resistors in parallel, you use the formula 1/Rp = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3... After calculating the sum of the reciprocals of each resistor, you take the reciprocal of the result to find the equivalent resistance.
What is the equivalent resistance when two resistors of 2 Ohms and 3 Ohms are connected in parallel?
-For two resistors of 2 Ohms and 3 Ohms in parallel, you first find the reciprocal of each, 1/2 + 1/3, then find the common denominator (6), resulting in 1/Rp = 5/6. Taking the reciprocal gives Rp = 6/5, or 1.2 Ohms.
How do you calculate the equivalent resistance when three resistors are connected in parallel?
-For three resistors in parallel, the formula is 1/Rp = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3. After calculating the reciprocals, you find the common denominator and calculate the total reciprocal to find the equivalent resistance.
What is the equivalent resistance of three resistors (3 Ohms, 4 Ohms, and 6 Ohms) connected in parallel?
-For three resistors of 3 Ohms, 4 Ohms, and 6 Ohms in parallel, you calculate 1/Rp = 1/3 + 1/4 + 1/6. The least common denominator is 12, and after simplifying, the equivalent resistance is 4/3 Ohms or approximately 1.33 Ohms.
How is the total resistance calculated when two series circuits are connected in parallel?
-When two series circuits are connected in parallel, you first calculate the equivalent resistance of each series circuit, then apply the parallel formula. For example, if the first series circuit has 2 Ohms and 4 Ohms and the second has 3 Ohms and 6 Ohms, calculate each series circuit's resistance first, then find the parallel equivalent.
What is the total resistance for two series circuits (6 Ohms and 9 Ohms) connected in parallel?
-For two series circuits with resistances of 6 Ohms and 9 Ohms, you first find the total resistance for each series circuit, then apply the parallel formula. For this case, 1/Rp = 1/6 + 1/9. Simplifying gives 1/Rp = 5/18, so the total resistance is 18/5 or 3.6 Ohms.
How do you calculate the equivalent resistance for a complex combination of series and parallel resistors?
-To calculate the equivalent resistance for a complex circuit, break down the circuit into simpler parts. Calculate the resistance for series connections first by adding resistances, then for parallel connections by using the reciprocal formula. Repeat this process step by step until you find the overall equivalent resistance.
What is the equivalent resistance when a 3 Ohm resistor and a 5 Ohm resistor are in series with a parallel combination of 8 Ohm and 12 Ohm resistors?
-First, calculate the parallel resistance for 8 Ohms and 12 Ohms: 1/Rp = 1/8 + 1/12 = 5/24, so Rp = 24/5 or 4.8 Ohms. Then, add this result to the series resistors: 3 + 4.8 + 5 = 12.8 Ohms.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (18 of 31) Finding the Equivalent Resistor Ex. 3

[NEW VERSION!] RANGKAIAN PARALEL DAN SERI PARALEL | Rangkaian Listik Arus Searah - Fisika Kelas 12

Capacitors in Series and Parallel Explained!
Menghitung Hambatan total / pengganti rangkaian listrik seri paralel majemuk

Petunjuk Praktikum Membuat Rangkaian Listrik dan Pengukuran dengan Basicmeter

Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (16 of 31) NOTE ERROR! Finding the Equivalent Resistor Ex. 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
