Potential Transformer (PT) | control Transformer; use
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive overview of Potential Transformers (PTs), explaining their function as step-down transformers that maintain correct voltage magnitude and phase. It covers both electromagnetic and capacitor PT types, their design, and construction. Key applications include voltage measurement, protection, synchronization, control, and isolation. The video also delves into PT specifications, such as system voltage, accuracy, temperature range, and VA rating, as well as essential testing procedures like accuracy and insulation checks. Overall, the content emphasizes the importance of PTs in electrical systems for reliable operation and protection.
Takeaways
- 😀 PT (Potential Transformer) is a step-down transformer that provides voltage in the correct magnitude and phase for accurate measurements.
- 😀 Correct phase means the secondary voltage aligns with the primary voltage without any delay or phase shift.
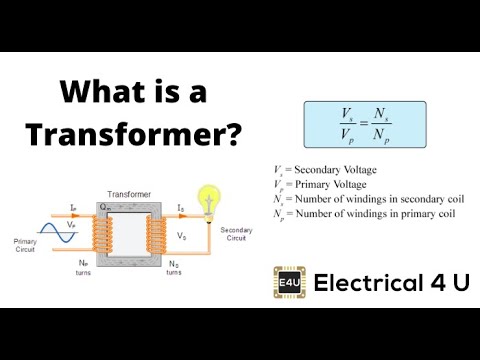
- 😀 The voltage ratio between the secondary and primary is proportional to the turn ratio of the transformer windings (V2/V1 = N2/N1).
- 😀 There are two main types of PTs: electromagnetic type (with windings) and capacitor type (with voltage dividers).
- 😀 Capacitor-type PTs are more cost-effective and don't require high-voltage windings, using capacitors to divide the voltage.
- 😀 PTs are commonly used in high-voltage systems (e.g., 10KV, 50KV, 100KV) for voltage measurement, protection, and control applications.
- 😀 PTs are used for synchronization in systems with thyristors, providing accurate gate pulses in relation to incoming voltages.
- 😀 PTs also serve as isolating transformers, ensuring safety and reducing electrical noise in the system.
- 😀 Key specifications of PTs include system voltage, voltage ratio, accuracy class, ambient temperature, and voltage factor (over-voltage handling).
- 😀 Tests for PTs include accuracy, dielectric insulation, temperature rise, terminal marking & polarity, and response time tests, ensuring proper performance.
- 😀 Special requirements can be specified by the user, including specific standards (e.g., IS, IEC) and testing for faster response in control applications.
Q & A
What is a potential transformer (PT)?
-A potential transformer (PT) is a step-down transformer that provides secondary voltage in the correct magnitude and phase, ensuring it is proportional to the primary voltage and maintains no phase shift.
What is the difference between correct magnitude and correct phase in a PT?
-Correct magnitude means that the secondary voltage is proportional to the primary voltage, while correct phase means there is no delay or phase shift between the primary and secondary voltages.
What are the two types of potential transformers mentioned in the transcript?
-The two types of potential transformers mentioned are the electromagnetic type PT and the capacitor type PT, also known as the capacitor voltage transformer.
How does a capacitor type PT differ from an electromagnetic type PT?
-A capacitor type PT uses capacitors for voltage division instead of high-voltage windings. This makes it more cost-effective for high-voltage applications.
What is the role of an isolating PT?
-An isolating PT is used for isolation purposes, particularly in capacitor type PTs, where lower voltage is generated without isolation. The isolating transformer provides this isolation.
What are the primary applications of potential transformers in industry?
-Potential transformers are primarily used for measuring voltage, protection (such as over-voltage, under-voltage, and unbalance relays), synchronization in thyristor-based systems, control applications, and isolation.
What does the voltage ratio of a potential transformer represent?
-The voltage ratio of a potential transformer (V2/V1) represents the turn ratio (N2/N1), indicating how the secondary voltage is proportional to the primary voltage.
What is the typical accuracy range for potential transformers?
-The accuracy range for potential transformers is typically between 80% to 120% of the specified voltage, ensuring accurate voltage measurement over a wide range.
What is the significance of the VA rating in potential transformers?
-The VA rating, or burden, of a potential transformer refers to the total VA capacity of all its windings, which determines the load it can handle and ensures proper performance under specified conditions.
What types of tests are conducted on potential transformers?
-Two types of tests are conducted on potential transformers: routine tests, which are performed on all units, and type tests, which are done on a select few. These tests include accuracy checks, dielectric insulation, temperature rise, terminal marking and polarity, and special tests such as response time and surge resistance.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Materi Kuliah Transformer #1

Video Animasi tentang Cara Kerja Transformator / Trafo versi English
What is a Transformer And How Do They Work? | Transformer Working Principle | Electrical4U
CAMBRIDGE IGCSE PHYSICS - transformer

How does a Transformer work - Working Principle electrical engineering

IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (part 5 : Transformator)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
