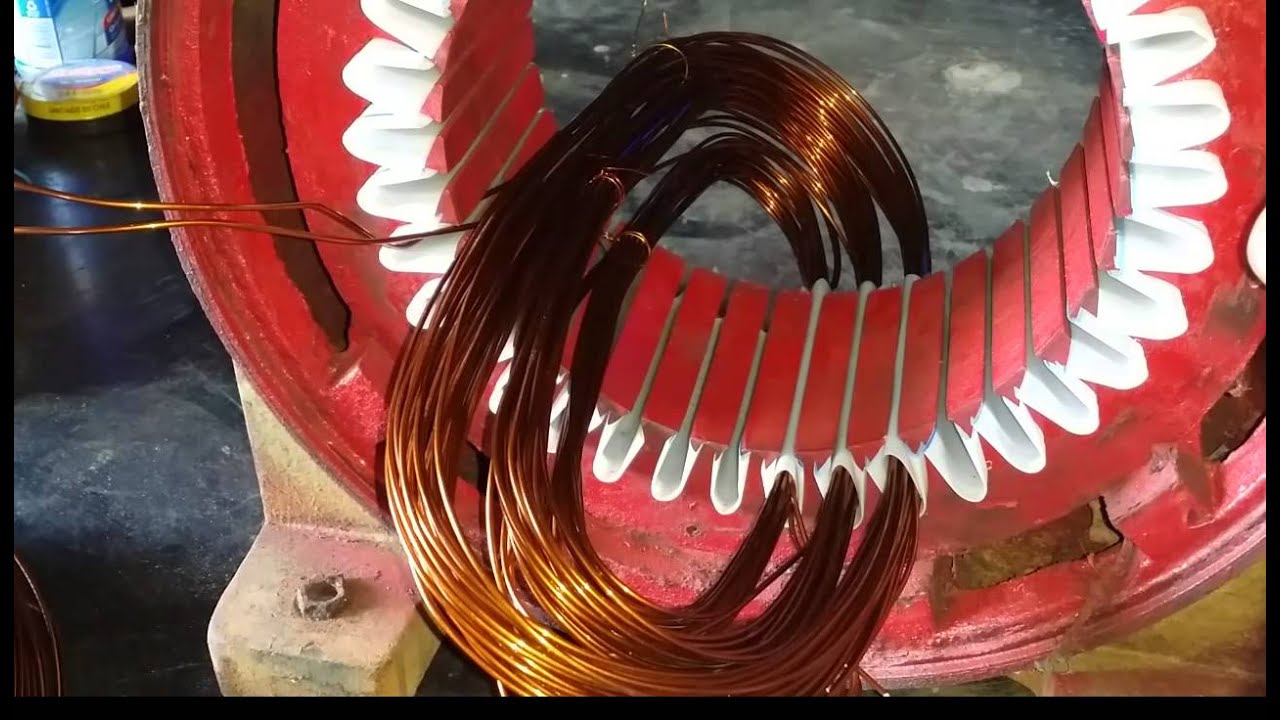
Materi Kuliah Transformer #1
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script discusses the function and principles of transformers in electrical power systems. It explains how transformers use electromagnetic induction to step up or step down voltage levels, essential for power distribution. The script covers different types of transformers, including power transformers and electronic transformers, their core components, and the concept of mutual induction. It also touches on wireless charging technology, efficiency, and isolation, providing a comprehensive overview of transformers' role in electrical systems.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Transformers are electrical devices that step up or step down voltage levels, essential for适配电力系统.
- ⚡ The primary function of a transformer is to convert AC voltage from one level to another, either increasing or decreasing it.
- 🏡 In residential settings, transformers are used to step down high voltages from the power grid, like 20kV, to standard household voltages like 220V.
- 🌐 Transformers operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, inducing voltage in the secondary coil from the primary coil.
- 🔧 There are different types of transformers, including those with an iron core and those with an air core, each designed for specific applications.
- 🔗 The transformer consists of a primary and a secondary side, with the turns ratio between the coils determining the voltage transformation ratio.
- 📊 The voltage transformation ratio is directly proportional to the turns ratio of the primary to the secondary coils.
- 🔵 The efficiency of transformers is typically high, with losses occurring mainly in the form of heat due to resistance in the coils and core.
- 🌐 Transformers provide electrical isolation between the primary and secondary circuits, which is crucial for safety and preventing electrical faults.
- 🔄 Autotransformers offer variable voltage outputs by having multiple taps on the secondary winding, allowing for adjustable voltage steps.
- 📚 The script discusses the theory and applications of transformers, including their role in power distribution and electronic devices.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a transformer?
-A transformer's primary function is to convert or step up and step down the voltage levels of alternating current (AC) electricity, typically used to increase voltage for long-distance transmission or decrease it for local distribution and use.
How does a transformer operate?
-A transformer operates on the principles of electromagnetic induction. When an AC voltage is applied to the primary coil, it creates a varying magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil.
What are the two main parts of a transformer?
-The two main parts of a transformer are the primary and secondary windings. The primary winding is connected to the input voltage, while the secondary winding is where the output voltage is taken.
Why is a transformer more efficient than other types of electrical devices?
-Transformers are more efficient because they transfer energy through electromagnetic induction rather than through a direct electrical connection, which reduces losses due to resistance.
What is the role of the core in a transformer?
-The core in a transformer is used to concentrate and guide the magnetic flux created by the primary coil through the secondary coil, thus improving the coupling between the coils and the efficiency of the transformer.
What is meant by the term 'turns ratio' in transformers?
-The turns ratio in transformers refers to the ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the number of turns in the secondary coil. It determines the relationship between the input and output voltages.
How does the efficiency of a transformer relate to its losses?
-The efficiency of a transformer is inversely related to its losses. Higher losses, such as those due to resistive heating in the coils or core losses, result in lower efficiency.
What is the purpose of isolation in a transformer?
-Isolation in a transformer serves to electrically separate the primary and secondary windings, preventing direct current flow between them and providing safety by isolating the user from high voltages.
What is an autotransformer and how does it differ from a standard transformer?
-An autotransformer has its primary and secondary windings electrically connected, sharing some turns. This type of transformer is often used for voltage adjustments within a smaller range and can be more compact and less expensive than standard transformers.
What are the applications of transformers in electrical systems?
-Transformers are used in electrical systems for voltage transformation, impedance matching, isolation, and galvanic separation. They are essential components in power distribution, electronic devices, and electrical machinery.
How can the turns ratio affect the voltage transformation in a transformer?
-The turns ratio directly affects the voltage transformation in a transformer. If the turns ratio is greater than 1, it results in a step-up transformer; if less than 1, it results in a step-down transformer. The output voltage is the input voltage multiplied by the turns ratio.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)