Pemerintahan Megawati - Masa Reformasi - Sejarah Indonesia
Summary
TLDRThis video covers the period of Indonesia's Reform Era under President Megawati Soekarnoputri. It explores her key policies, including constitutional amendments, economic recovery efforts, and the fight against corruption, through the establishment of institutions like the KPK. Despite early successes, challenges arose with economic struggles, such as inflation and controversial privatization decisions. The video also delves into the 2004 presidential election, where Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono triumphed in the second round, marking the end of Megawati's presidency. The video provides a detailed view of her administration’s impacts on Indonesia’s politics, economy, and governance.
Takeaways
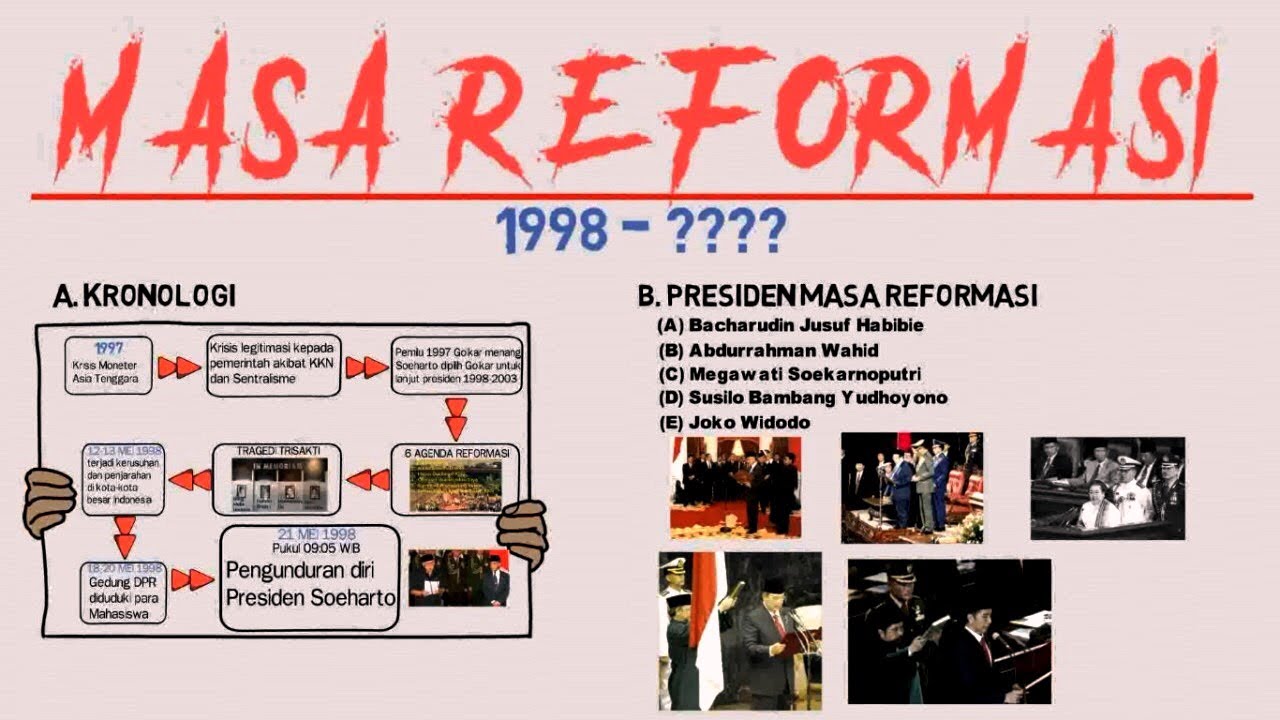
- 😀 Megawati Soekarnoputri became the 5th President of Indonesia on July 23, 2001, after Abdurrahman Wahid's resignation.
- 😀 She formed the 'Gotong-Royong Cabinet' with five main goals: eliminate corruption, manage the economic crisis, continue political development, uphold the rule of law, and create a favorable social and cultural environment.
- 😀 Megawati's administration implemented several constitutional reforms, including amendments to the 1945 Constitution, creating the Constitutional Court, and establishing the Corruption Eradication Commission (KPK).
- 😀 In the economic sector, Megawati's government focused on reducing inflation, stabilizing the Rupiah, and privatizing state-owned enterprises to manage the national debt, including selling shares in Indosat.
- 😀 Megawati's policies also aimed to resolve the regional disparities in Aceh and Papua by increasing local autonomy and sharing 70% of natural resource revenues with these regions.
- 😀 The government's diplomacy was tested with the loss of the Sipadan and Ligitan islands to Malaysia in 2001, signaling weaknesses in Indonesia's foreign relations.
- 😀 Despite initial successes, Megawati faced growing criticism due to economic downturns, particularly after fuel price hikes and increased taxes in 2002-2003.
- 😀 Megawati's privatization of state-owned companies, including the controversial sale of Indosat, remains a contentious issue in Indonesian politics.
- 😀 The 2004 elections were the first to allow direct public voting for legislative and presidential candidates. The presidential election went to two rounds, with Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono and Jusuf Kalla winning in the second round.
- 😀 Despite her efforts to stabilize the economy, Megawati’s popularity declined leading to her defeat in the 2004 presidential election, marking the end of her administration.
- 😀 The 2004 election results led to the rise of Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono as president, setting the stage for the next phase of Indonesia’s reform era.
Q & A
What was the main objective of Megawati Soekarnoputri's administration during her first year in office?
-The primary goal of Megawati's administration was to address the ongoing economic crisis, improve political stability, and promote social harmony through the Gotong Royong Cabinet, which focused on eliminating corruption, improving the economy, and ensuring a just legal system.
What were the five main agendas of Megawati's Gotong Royong Cabinet?
-The five main agendas of the Gotong Royong Cabinet were: (1) Eradicate corruption, collusion, and nepotism (KKN), (2) Take steps to rescue the people from the prolonged economic crisis, (3) Continue political development, (4) Maintain the supremacy of law, and (5) Create a conducive social and cultural environment.
What legal reforms did President Megawati introduce during her administration?
-Under President Megawati, key legal reforms included amending the 1945 Constitution, establishing the independent judiciary (including the Constitutional Court and the KPK), and enacting laws on elections, decentralization, and the press.
How did Megawati's government attempt to manage Indonesia's economic recovery after the 1998 crisis?
-Megawati's government focused on stabilizing the economy by controlling inflation, improving the value of the Rupiah, and implementing policies like debt restructuring with the Paris Club and the IMF, and privatizing state-owned enterprises to manage national debt.
What were the economic impacts of privatizing state-owned companies during Megawati's presidency?
-Privatizing state-owned enterprises, such as the sale of Indosat, helped raise funds to pay off national debt, which in turn supported a more stable economy. However, it also sparked controversy, especially regarding the sale of strategic companies to foreign entities.
How did Megawati's administration address the issue of regional autonomy, especially in Aceh and Papua?
-To address regional disparities, Megawati introduced policies such as increasing the revenue share from natural resources for regions like Aceh and Papua. These regions were allocated 70% of the revenue from their natural resources, aiming to reduce separatist sentiments.
What was the significance of the 2001 amendments to Indonesia's Constitution during Megawati's presidency?
-The 2001 constitutional amendments under Megawati's government marked a significant shift towards strengthening democratic processes and decentralization. The reforms included the establishment of an independent judiciary and key provisions to ensure greater accountability in governance.
What led to the loss of Indonesia's territorial claim over the Sipadan and Ligitan islands?
-Indonesia lost the Sipadan and Ligitan islands to Malaysia due to the ruling of the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in 2001, which determined that the islands belonged to Malaysia. This outcome highlighted weaknesses in Indonesia’s foreign diplomacy during Megawati’s presidency.
How did Megawati's decision to raise fuel prices and electricity tariffs impact her public approval?
-The decision to raise fuel prices, electricity tariffs, and taxes during her presidency led to a decline in public trust and approval. These controversial policies, aimed at addressing economic challenges, resulted in widespread discontent among the public.
What was the outcome of the 2004 presidential election in Indonesia?
-In the 2004 presidential election, Megawati lost to Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono in a two-round contest. In the first round, no candidate received more than 50% of the vote, but in the second round, Yudhoyono and his running mate Jusuf Kalla won with 60.62% of the vote.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Masa Orde Reformasi: Masa Pemerintahan Abdurrahman Whid dan Megawati Soekarnoputri | Part 2

REFORMASI 1998 HINGGA KINI

Bagaimana Sistem Ekonomi Internasional Mulai Dari Masa Kepemimpinan Presiden Pertama Sampai Saat ini

PEMBANGUNAN DI INDONESIA PADA MASA REFORMASI | IPS SMP Kelas 9

IPS kelas 9 BAB 3 tantangan pembangunan Indonesia masa Orde Baru dan Reformasi kurmer rangkuman sem2
MASA REFORMASI (1998-????)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
