Fundamental Principles of Flow
Summary
TLDRThis transcript delves into the complexities of fluid dynamics, exploring concepts such as streamlines, velocity vectors, vorticity, and rotational flow. It explains the principles of relative motion and how unsteady flows can be simplified into steady ones through mathematical modeling. The text further discusses how fluid motion is governed by forces like pressure, viscosity, and mass attraction, offering insight into phenomena like cavitation and separation. It also touches on the practical applications of these theories, such as in the design of jet propulsion and the operation of flow meters, providing a comprehensive understanding of fluid behavior in various contexts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Streamlines, path lines, and streak lines are key concepts in visualizing fluid flow, with steady flow resulting in identical patterns, and unsteady flow causing variations over time.
- 😀 The principle of relative motion can simplify unsteady flow to steady flow, making analysis easier by eliminating time-based variations in flow patterns.
- 😀 Vorticity, which refers to angular velocity at a point in the fluid, is visualized using vortex lines and relates directly to the circulation in vortex filaments.
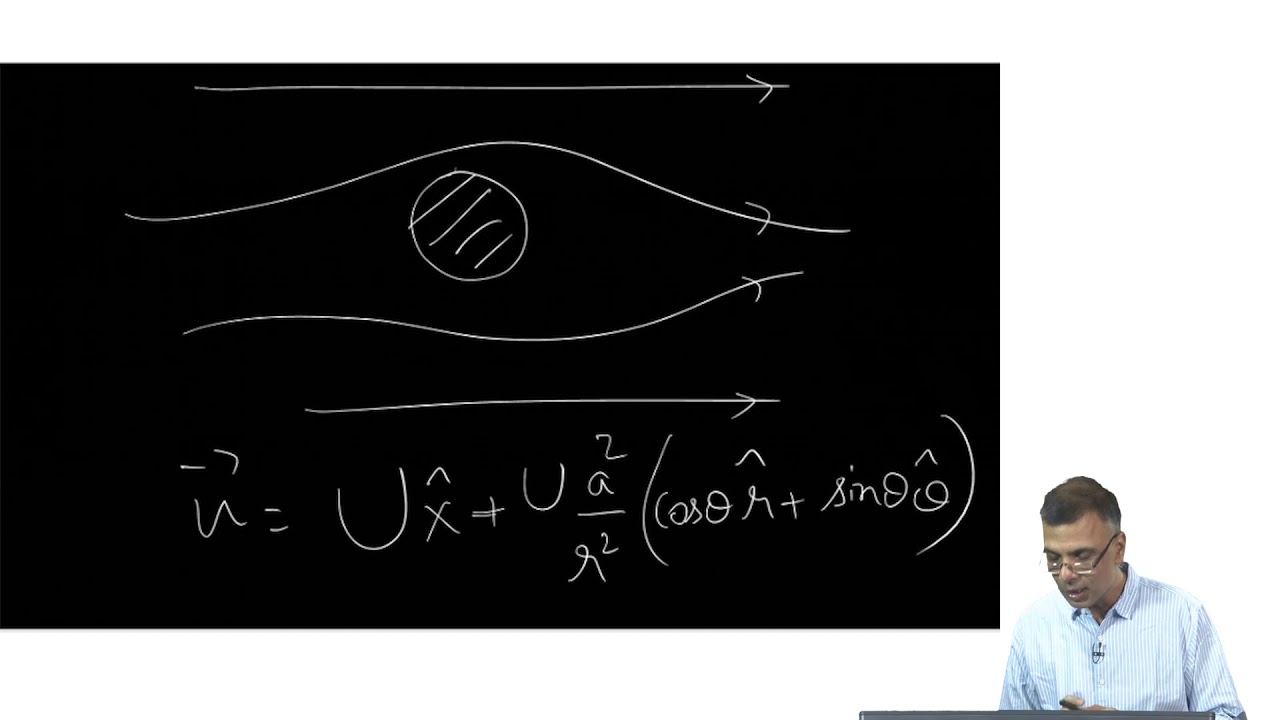
- 😀 The relationship between pressure and velocity in steady, irrotational flow is described by the sum of dynamic and static pressure, which is conserved along the flow.
- 😀 Continuity and energy equations help determine the rate of flow, velocity distribution, and pressure changes within a fluid system.
- 😀 Flow nets can be used to visualize and analyze flow through permeable materials, such as groundwater flow through soil or electrical flow in conductors.
- 😀 Pressure gradients and acceleration in the fluid are directly tied to the fluid's velocity changes, with higher velocity requiring a decrease in pressure.
- 😀 Cavitation occurs when the pressure drops below vapor pressure, leading to vapor formation within the fluid, which can disrupt flow dynamics.
- 😀 Separation occurs at boundary regions when rapid deceleration or angular boundaries disrupt the flow, leading to detachment and loss of flow consistency.
- 😀 In practical applications, the force required to modify a fluid's velocity or direction is related to its mass, velocity change, and momentum, as seen in jet propulsion systems.
- 😀 The continuity, momentum, and energy equations are essential for solving fluid dynamics problems, and can be applied together to understand jet propulsion, nozzle flow, and other fluid systems.
Q & A
What is the purpose of visualizing fluid flow using techniques like dye or aluminum powder?
-The purpose of visualizing fluid flow is to make the otherwise invisible movement of fluids like air or water visible, allowing for the analysis of the velocity vectors' magnitude and direction at various points through the field.
How do streamlines differ in steady and unsteady flow?
-In steady flow, streamlines remain constant and do not change with time. In unsteady flow, the pattern of streamlines changes with time due to relative motion between the observer and the fluid, causing different patterns such as path lines and streak lines.
What is the principle of relative motion, and how does it simplify fluid flow analysis?
-The principle of relative motion states that unsteady flow can be made steady by considering the relative motion between the fluid and the point of observation. This simplification leads to identical streamlines, path lines, and streak lines, making the mathematical expressions simpler.
What are the two types of acceleration in fluid flow?
-The two types of acceleration in fluid flow are local acceleration, which is the variation in velocity at each point with time, and convective acceleration, which is the variation in velocity from point to point along a streamline.
What is a stream tube, and what does it represent?
-A stream tube is a passage formed by a closed surface controlled by a group of streamlines, containing a flow of fluid. It represents a pathway in which there is no flow through the walls, and the flow rate remains constant along its length.
What is vorticity, and how is it related to fluid motion?
-Vorticity is the angular velocity of a fluid at a point, representing the rotation of the fluid. It is associated with vortex lines and can indicate whether the flow is rotational or irrotational.
How does pressure affect fluid flow in terms of acceleration?
-Pressure differences cause fluid to accelerate. If the pressure is higher at one point than at another, the fluid will accelerate in the direction of the pressure drop. This relationship is governed by the Newtonian force law.
What is cavitation, and why does it limit the use of the pressure-velocity relationship?
-Cavitation occurs when fluid pressure drops so low that the fluid begins to boil, creating vapor pockets. This phenomenon disrupts the continuity and pressure-velocity relationship, as the flow becomes discontinuous.
What are the three types of forces acting on a fluid body?
-The three types of forces acting on a fluid body are: normal forces (pressure), tangential forces (shear or viscosity), and body forces (such as gravity and inertia).
How are the continuity, momentum, and energy equations used in fluid flow analysis?
-These three equations are used together to describe fluid behavior: the continuity equation relates velocity and flow rate, the momentum equation links force and velocity change, and the energy equation connects pressure, velocity, and density for analyzing flow through systems like nozzles and jets.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Rotational and irrotational flow [Aerodynamics #7]
mod03lec11 - Recap - Potential flows, Bernoulli constant and its applications

9. Vorticity (1 of 2)

06 Analisa Secara Differensial dari Aliran Fluida Part1 MEKFLU

BE3002 Transport Phenomena in Biosystem Module 2_Segment 1

Prinsip Dinamika Fluida | Fluida | Part 4 | Fisika Dasar
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
